What is dialysis water used for?
Hemodialysis, a medical procedure in which dialysis water is transferred into the bodies of patients who have temporarily or permanently lost kidney function, uses dialysis water. It keeps body fluids in check by controlling the pH of the patient’s body.
What are the dialysis water treatment standards?
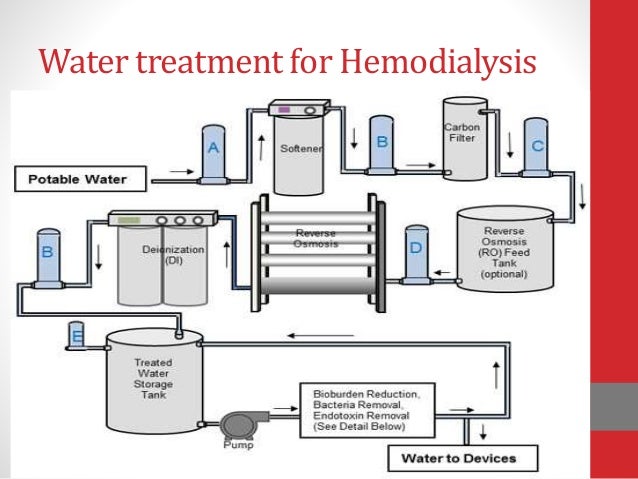
International standards have been established to encourage the construction of appropriate water treatment facilities for hemodialysis and to ensure the production of dialysis water suitable for use in hemodialysis on a regular basis. The water first passes through a multimedia filter, then two carbon tank filters.
What substances are removed from municipal water during dialysis?
Bacteria and endotoxin – the substances added to municipal water to suppress bacterial proliferation are removed in the water purification process for dialysis treatment. Passage of endotoxin, endotoxin fragments and other bacterial products across the dialyzer membrane and into the bloodstream can lead to pyrogenic reactions.
How often should the water be disinfected during dialysis?
Monthly disinfection is recommended. Whenever practical, design and engineer water systems in dialysis settings to avoid incorporating joints, dead-end pipes, and unused branches and taps that can harbor bacteria.

Why do dialysis patients need water treatment?
Tap water contains contaminants that may not be harmful through ingestion but cause harm to the hemodialysis patient if not inactivated or removed. Thus, tap water must be appropriately and adequately purified prior to its use for dialysate preparation. This can be achieved in the dialysis center or the patient's home.
What is water treatment system?
A process in which water passes through a water system that may include one or more filters for the purpose of removing turbidity, taste, color, iron or odor and certain chemicals such as chlorine.
What are the steps involved in the treatment of water used in dialysis?
Flocculation where particles that remain suspended are removed by adding a coagulant (e.g. aluminium or iron sulphates) to form larger complexes called flocs, which are then removed, through a process of filtration and adsorption. Softening : where calcium and magnesium salts are removed.
What is product water in dialysis?
The product water is the ultra pure water which enters the hemodialysis machine and is used to mix the dialysate for your dialysis treatment. The reject water contains the bacteria that was cleaned out of the water and is sent down the drain and discarded.
What are the 4 steps of water treatment?
4 Steps of Community Water TreatmentCoagulation and Flocculation. ... Sedimentation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection.
What are the 3 stages of water treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.
Can you drink water during dialysis treatment?
Most dialysis patients need to limit their fluid intake to 32 ounces per day. Manage your thirst. Your dietitian can help you find ways to manage your thirst such as sugar-free hard candies, ice chips, or frozen grapes. This will help you avoid drinking too much fluid between dialysis treatments.
What are 2 reasons for water treatment?
In this article, we explain five reasons why you might want to purify your drinking water.1 Add an extra layer of security. ... 2 Remove unwanted contaminants. ... 3 Protect your health. ... 4 Cut back on plastic to protect the environment. ... 5 Improve the taste and odor of your tap water.
What is the pH of dialysis?
Hemodialysis Preparation The RO water used in hemodialysis should be an isotonic solution with an optimal pH range of 6.8 – 7.8.
What percentage of dialysate is water?
90%More than 90% of the dialysate delivered to the dialyzer is water (Layman-Amato, 2013).
How much water is used for hemodialysis?
During an average week of hemodialysis, a patient can be exposed to 300-600 liters of water, providing multiple opportunities for potential patient exposure to waterborne pathogens. Adverse patient outcomes including outbreaks associated with water exposure in dialysis settings have resulted from patient exposure to water via a variety of pathways; including improper formulation of dialysate with water containing high levels of chemical or biological contaminants, contamination of injectable medications with tap water, and reprocessing of dialyzers with contaminated water. For the health and safety of hemodialysis patients, it is vital to ensure the water used to perform dialysis is safe and clean.
What is AAMI water?
AAMI Water Standards. The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) external icon. in conjunction with the International Standards Organization (ISO) have established chemical and microbiological standards for the water used to prepare dialysate, substitution fluid, or to reprocess hemodialyzers for renal replacement therapy.
Does a deionizer remove bacteria?
Deionization (DI) unit does not remove or destroy bacteria, so if DI is being used as the main water treatment (rather than RO), you will need a submicron or endotoxin/ultrafilter downstream of the DI unit. If an ultraviolet (UV) irradiator is used, the filter should be located after the UV irradiator.
What is the purpose of purified water for hemodialysis?
Purified water for hemodialysis is then distributed to individual dialysis machines to produce dialysate solution that remains free of contaminants. Inert material such as plastics are used to avoid chemical contaminants.
What is the purpose of endotoxin in water?
Bacteria and endotoxin – the substances added to municipal water to suppress bacterial proliferation are removed in the water purification process for dialysis treatment. Passage of endotoxin, endotoxin fragments and other bacterial products across the dialyzer membrane and into the bloodstream can lead to pyrogenic reactions.
Why is chloramine added to water?
Chloramine – added to water to prevent bacterial proliferation. It can cause hemolytic anemia (see Table 1 for other causes of hemolysis in patients on dialysis). Fluoride – added to water to reduce tooth decay. Large amounts of fluoride can elute from an exhausted deionizer and cause pruritis, nausea, and arrhythmia s.
Why inject hydrochloric acid?
Injection of hydrochloric acid to correct the pH in the case of excess alkalinity is sometimes required as this can disturb the carbon adsorption beds and the reverse osmosis (RO) membrane. Water softeners exchange calcium and magnesium for sodium that has been affixed to a resin bed.
Can hemodialysis water be contaminated?
Unsurprisingly then, patients on hemodialysis are particularly vulnerable to small molecular weight contaminants in the water used to prepare concentrates and dial ysis fluid. These small molecular weight contaminants can enter the blood unimpeded and accumulate in the body in the absence of kidney excretion.
Is chloramine toxic to dialysis patients?
It is toxic to dialysis patients, becoming sequestered in bone for long period of time, resulting in adynamic bone disease and osteomalacia. It can also cause the well-described dialysis encephalopathy syndrome. Chloramine – added to water to prevent bacterial proliferation.
How much water does hemodialysis take?
When you do hemodialysis (HD), your blood is exposed to 25 to 50 times or more water than you could drink in a week. Drinking water can have small amounts of bacteria, metals, and chemicals that don't harm most people—but could build up in your body and make you sick. Water treatment helps keep you safe.
What to do if water fails a water test?
Your center may ask you to bring in a sample of your water for testing. If it fails the tests, you may need to use bagged dialysate (i.e., NxStage®) instead of treating your water. Once your water is known to meet the EPA standards, you'll need a way to remove bacteria, chemicals, and metals.
What happens if you flush your water lines?
If they are flushing the lines, more metal may come through. If the water is murky, they may use more alum. Your dialysis home training staff will talk with your water treatment plant and tell them that you are doing home HD. They will alert you if your town does something to affect water quality.
How does reverse osmosis work?
Removing Chemicals and Metals. Reverse osmosis (RO) uses a membrane and pressure to remove dissolved chemicals and metals (solutes) from water. A pump is used to force water through the membrane. Pure water passes through, while chemicals and metals are sent to the drain. RO is also used to take salt out of seawater.
What happens when you drink soft water?
In the body, they can cause nausea and vomiting, liver damage, death of red blood cells, and other problems.
When was the water standard written?
U.S. Water Safety Standards. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) wrote standards for drinking water in 1974, with the Clean Water Act. Safe levels were set for a wide array of contaminants, from certain bacteria to asbestos, metals, pesticides, and even cyanide. 2.
Do you need to test water before using PureFlow?
Before every treatment (or with every batch with the PureFlow SL™) you will test the water with a simple test strip to make sure you do not have any chlorine or chloramines in the water. You will also need to take a sample of your water and send it to your lab on a schedule.
How much water is needed for dialysis?
To safely perform a dialysis operation, a large quantity of high purity dialysis water is needed. Single 4-hour dialysis treatment can use up to 150L of “ultra-pure” dialysis water.
Why is it important to get dialysis water tested?
As a result, it’s important to get the dialysis water testing done for quality assurance in accordance with the health department’s standards and guidelines. Purification devices and processes for the preparation of concentrates and dialysate, as well as the reprocessing of dialyzers for various uses.
What are the standards for dialysis?
AAMI standards are mostly considered for dialysis water testing that helps in addressing: 1 Purification devices and processes for the preparation of concentrates and dialysate, as well as the reprocessing of dialyzers for various uses. 2 The apparatus for storing and distributing this water. 3 Water pollutants, bacterial cell counts, and endotoxins have permissible and action threshold amounts.
What is superior quality water used for?
In the preparation of dialysis fluid, superior-quality water is used. It is a requirement for hemodialysis and associated treatments. International standards have been established to encourage the construction of appropriate water treatment facilities for hemodialysis and to ensure the production of dialysis water suitable for use in hemodialysis ...
What are the electrolytes in dialysis fluid?
Dialysis fluids are electrolyte solutions with concentrations that are close to extracellular fluid or plasma. They contain, or may contain: Sodium. Chloride. bicarbonate or lactate. Calcium. Magnesium. Potassium.
What is municipal water?
Municipal water contains a broad range of chemical and microbial pollutants. Hemodialysis, a medical procedure in which dialysis water is transferred into the bodies of patients who have temporarily or permanently lost kidney function, uses dialysis water.
What is a purification device?
Purification devices and processes for the preparation of concentrates and dialysate, as well as the reprocessing of dialyzers for various uses . The apparatus for storing and distributing this water. Water pollutants, bacterial cell counts, and endotoxins have permissible and action threshold amounts.
What is HD in nephrology?
Nephrology nurses with responsibility for hemodialysis (HD) need to know and understand the clinical ramifications of water treatment and dialysate preparation. Although some HD programs may have full-time technical staff who operate and test the water treatment and dialysate preparation systems, many programs rely on nursing staff members for ...
Is dialysate safe for HD?
This article details the reasons safe water and dialysate are critical for patients on HD; and reviews components of water treatment systems, dialysate concentrate preparation, and the monitoring and testing necessary to assure that both water and dialysate are safe for patient use.
