
Medication
“There are a wide variety of potential treatments for TMJ, including self-management, physical therapy, medications, occlusal adjustments, intraoral appliances, and surgery. Evidence based clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of TMJs do not currently exist, despite the fact that treatment is common.
Procedures
Stabilization splints are the most widely used treatments for TMJ disorders. Studies of their effectiveness in providing pain relief, however, have been inconclusive. If a stabilization splint is recommended, it should be used only for a short time and …
Therapy
Jan 12, 2022 · Other Treatment Options Jaw Surgery. Surgery may be needed when structures of the jaw need to be significantly changed. Your orthodontists will... Medications. Some people are able to manage their symptoms using medications. Pain relief and anti-inflammatory drugs... Therapies. For some individuals, ...
Nutrition
since 1936 tmj has been primarily treated by dentists, however today, we know tmj to be a complex condition with many biological systems (circulatory, digestive, endocrine, exocrine, immune, muscular, nervous, reproductive, respiratory, and skeletal) playing a role, indicating the need to bring the medical and other allied health professionals in …
What is the best treatment for TMJ?
Mar 18, 2022 · When home treatment does not work, medical treatment for temporomandibular joint (TMJ) syndrome includes dental splints, Botox injections, physical therapy, prescription medications, and in severe cases, surgery. The prognosis for TMD is generally good as people usually can manage the disorder with self-care and home remedies.
How is TMJ diagnosed and treated?
Stabilization splints (biteplate, nightguard) are the most widely used treatments for TMJ disorders. Studies of their effectiveness in providing pain relief, however, have been inconclusive. Irreversible treatments have not been proven to work and may make the problem worse. Examples of irreversible treatments are:
Do TMJ disorders always require treatment?
Treatment may include: Resting the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) Medicine or pain relievers Relaxation techniques and stress management Behavior changes (to reduce or stop teeth clenching) Physical therapy An orthopedic appliance or mouthguard worn in the mouth (to reduce teeth grinding) Posture training Diet changes (to rest the jaw muscles)
What are the causes and cure of TMJ disorder?

What is the most common treatment for TMJ?
Bite guards are the most widely recommended treatment for moderate TMJ symptoms. Research has found that splints can reduce TMJ pain and the risk of long-term side effects is minimal. There are two main types of dental splint, a TMJ mouthguard, and a bruxism (tooth grinding) mouthguard.Jan 6, 2021
How is TMJ corrected?
If your jaw disorder is related to a misalignment, your pain specialist or dentist may recommend physical therapy for the jaw area, orthodontic treatment, such as a jaw splint, braces, or a TMJ retainer. These jaw treatments can realign your smile for a more comfortable bite which, in turn, can address your symptoms.Sep 30, 2021
What is treatment for temporomandibular disorder?
What are some examples of nonsurgical TMJ treatments?Apply moist heat or cold packs. Apply an ice pack to the side of your face and temple area for about 10 minutes for acute pain. ... Eat soft foods. ... Take medications. ... Wear a splint or night guard. ... Undergo corrective dental treatments. ... Avoid extreme jaw movements.Jun 21, 2021
Can TMJ issues be cured?
Unfortunately, there is no cure for arthritis. This means that for anyone suffering from TMJ due to arthritis, there's also no cure for the TMJ disorder. An eroded disk or a connective tissue disease may similarly have no cure. However, there are steps you can take to manage your TMJ pain.Mar 23, 2021
Is TMJ permanent?
TMJ disorders disappear by themselves without needing any professional help in many cases. However, if the pain is impacting your everyday activities, you will find it helpful to seek medical help.Jan 1, 2021
What is the main cause of TMJ?
Sometimes the main cause is excessive strain on the jaw joints and the muscle group that controls chewing, swallowing, and speech. This strain may be a result of bruxism. This is the habitual, involuntary clenching or grinding of the teeth. But trauma to the jaw, the head, or the neck may cause TMD.
Is TMJ a medical issue?
TMJ as a medical problem Patients who develop TMJ may wonder which provider to contact for treatment. The condition can be a medical problem due to certain diseases that cause pain in the facial area or inflammation in the jaw joint itself.
How long will TMJ pain last?
Flare-ups vary from person to person, depending on the underlying cause or trigger. Whether TMJ disorder is actively being managed by a doctor can also influence how long a flare-up lasts. Most flare-ups last anywhere from two days to a few weeks.May 18, 2021
Is TMJ an infection?
TMJ infection is required to be carefully examined since its initial symptoms start from pain and limitation of jaw movement similary to common temporomandibular joint disorders (TMD). Failure to initially diagnose TMJ infection may results in aggravation of symptoms and development of complications.
Can TMJ be caused by stress?
One of the contributing factors to TMJ disorders is a high-stress level. When you're feeling stressed, you might clench your jaw or grind your teeth both during the day and when you're asleep. Although this habit might seem harmless, it can lead to tooth wear, cracked teeth, and temporomandibular joint disorder.Jan 12, 2021
Is TMJ disorder temporary?
In most cases, the pain and discomfort associated with TMJ disorders is temporary and can be relieved with self-managed care or nonsurgical treatments. Surgery is typically a last resort after conservative measures have failed, but some people with TMJ disorders may benefit from surgical treatments.Dec 28, 2018
Can you get better with TMJ?
The treating community remains in chaos and controversy about TMJ treatments. The advice we must still offer patients is – you may get better on treatments; you may be unaffected by treatments; you may even get better in spite of treatment, or you may get worse.
Is TMJ surgery reversible?
Conservative treatments do not invade the tissues of the face, jaw, or joint, or involve surgery.
Can reversible treatment cause permanent changes in jaw?
Reversible treatments do not cause permanent changes in the structure or position of the jaw or teeth. If TMJ issues become persistent and severe, moving toward aggressive treatments does not necessarily ensure improvement of the symptoms.
What are the causes of TMJ?
Factors that may increase the risk of developing TMJ disorders include: Various types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Jaw injury. Long-term (chronic) grinding or clenching of teeth. Certain connective tissue diseases that cause problems that may affect the temporomandibular joint.
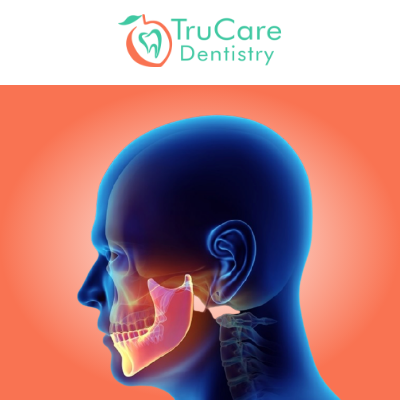
Where is the TMJ located?
TMJ disorders affect the temporomandibular joint, located on each side of your head in front of your ears. A soft cartilage disk acts as a cushion between the bones of the joint, so the joint can move smoothly.
Why does my jaw feel like it's clicking?
Aching facial pain. Locking of the joint, making it difficult to open or close your mouth. TMJ disorders can also cause a clicking sound or grating sensation when you open your mouth or chew. But if there's no pain or limitation of movement associated with your jaw clicking, you probably don't need treatment for a TMJ disorder.
Why does my TMJ hurt?
Painful TMJ disorders can occur if: The disk erodes or moves out of its proper alignment. The joint's cartilage is damaged by arthritis. The joint is damaged by a blow or other impact. In many cases, however, the cause of TMJ disorders isn't clear.
Can TMJ be treated?
In most cases, the pain and discomfort associated with TMJ disorders is temporary and can be relieved with self-managed care or nonsurgical treatments. Surgery is typically a last resort after conservative measures have failed, but some people with TMJ disorders may benefit from surgical treatments.
Benefits of Treating TMJ
You may be wondering if your TMJ disorder requires treatment. Even under ideal conditions, the TMJs are placed under great pressure every day. TMJ disorders put extra stress on those joints.
What Is the Best Treatment for TMJ?
Dental misalignment can throw off your jaw alignment. Your dental occlusion allows the jaws to rest together at night in a manner that does not stress the TMJs.
Other Treatment Options
Orthodontic treatments are considered the best TMJ disorder treatment for the vast majority of people who suffer from TMD. In rare cases, patients may require jaw surgery to address severe TMJ disorder symptoms.
Which Option Is Right for Me?
If you are experiencing the symptoms of TMJ disorder, your first step should be to schedule an exam with your orthodontist. During your exam, your orthodontist will inquire into your symptoms.
Learn More About TMJ Disorder Treatments
TMJ disorder can disrupt your quality of life and make it difficult to speak and eat with ease. The sooner you can have your symptoms diagnosed and treated, the sooner you can return to enjoying life fully.
What is the best treatment for TMJ?
TMJ disorders often responds to home remedies, including ice packs to the joint, over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs ), avoiding chewing gum, massage or gentle stretches of the jaw and neck, and stress reduction.
What is TMJ syndrome?
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) syndrome is a disorder of the jaw muscles and nerves caused by injury or inflammation to the temporomandibular joint. The temporomandibular joint is the connection between the jawbone and the skull. The injured or inflamed temporomandibular joint leads to pain with chewing, clicking, crackling, ...
What is TMJ in medical terms?
Facts you should know about temporomandibular joint (TMJ) syndrome. The temporomandibular joint is the joint that connects your jaw to your skull. When this joint is injured or damaged, it can lead to a localized pain disorder called temporomandibular joint ( TMJ) syndrome or temporomandibular disorder (TMD).
What are the symptoms of TMJ?
Signs and symptoms of temporomandibular joint (TMJ) syndrome include. jaw pain, jaw clicking and popping, ear pain / earache, popping sounds in ears, headaches, stiff or sore jaw muscles, pain in the temple area, or. locking of the jaw joint.
What causes pain in the temporomandibular joint?
The injured or inflamed temporomandibular joint leads to pain with chewing, clicking, crackling, and popping of the jaw; swelling on the sides of the face; nerve inflammation; headaches, including migraines; tooth grinding ( bru xism ); Eustachian tube dysfunction; and sometimes dislocation of the temporomandibular joint.
Why do people have jaw trauma?
People with jaw trauma or poorly positioned teeth have increased risk. People who have a genetic predisposition to pain sensitivity and increased stress responses may be more susceptible. Causes may include misalignment (malocclusion) of or trauma to the teeth or jaw. Source: iStock.
Where is TMD pain located?
The main TMD symptom is pain in the jaw joint. This joint is located just in front of the ear, and pain associated with TMD may involve the face, eye, forehead, ear, or neck. Signs and symptoms of temporomandibular joint dysfunction include the following: Pain or tenderness in the jaw, especially at the area of the joint.
What is the best treatment for TMJ?
Gentle jaw stretch ing and relaxation exercises. Stabilization splints (biteplate, nightguard) are the most widely used treatments for TMJ disorders. Studies of their effectiveness in providing pain relief, however, have been inconclusive.
What are the symptoms of TMJ?
TMJ pain is often described as a dull ache in the jaw joint and nearby areas, including the ear. Some people report no pain but have jaw dysfunction. Other symptoms can include: pain in the neck and shoulders. migraine and/or chronic headache. jaw muscle stiffness.
What is the joint that hinges the lower jaw to the skull?
The TMJ is the joint that hinges the lower jaw to the skull, enabling you to open and close your mouth. TMJ disorders are a group of conditions that cause pain in and around the TMJ and nearby muscles. Clenching your jaw and grinding your teeth puts an additional strain on the muscles of the jaw causing inflammation.
How to tell if you have TMJ?
Pain is one of the most common symptoms of TMJ Disorders. TMJ pain is often described as a dull ache in the jaw joint and nearby areas, including the ear. Some people report no pain but have jaw dysfunction. Other symptoms can include: 1 pain in the neck and shoulders 2 migraine and/or chronic headache 3 jaw muscle stiffness 4 limited movement or locking of the jaw 5 painful clicking, popping or grating in the jaw joint when opening or closing the mouth 6 a bite that feels "off" 7 ear pain, pressure and/or ringing in the ears 8 diminished hearing 9 dizziness and vision problems 10 tooth sensitivity
How long does it take for TMJ to go away?
Many people with TMJ problems get better without treatment. Often the problem goes away on its own in several weeks to months.
How long does TMJ last?
How to treat TMJ disorder. Since most common jaw joint and muscle problems are temporary, lasting only weeks or months, simple care, such as hot or cold compresses and over-the-counter medications, is all that is usually needed to relieve the discomfort.
How to tell if you have a swollen jaw?
migraine and/or chronic headache. jaw muscle stiffness. limited movement or locking of the jaw. painful clicking, popping or grating in the jaw joint when opening or closing the mouth. a bite that feels "off".
What is TMD in dentistry?
Temporomandibular disorders (TMD) are disorders of the jaw muscles, temporomandibular joints, and the nerves associated with chronic facial pain. Any problem that prevents the complex system of muscles, bones, and joints from working together in harmony may result in temporomandibular disorder. The National Institute of Dental ...
What causes TMD pain?
But trauma to the jaw, the head, or the neck may cause TMD. Arthritis and displacement of the jaw joint disks can also cause TMD pain. In other cases, another painful medical condition such as fibromyalgia or irritable bowel syndrome may overlap with or worsen the pain of TMD.
What are the symptoms of TMD?
The National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research classifies TMD by the following: 1 Myofascial pain. This is the most common form of TMD. It results in discomfort or pain in the fascia (connective tissue covering the muscles) and muscles that control jaw, neck and shoulder function. 2 Internal derangement of the joint. This means a dislocated jaw or displaced disk, (cushion of cartilage between the head of the jaw bone and the skull), or injury to the condyle (the rounded end of the jaw bone that articulates with the temporal skull bone). 3 Degenerative joint disease. This includes osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis in the jaw joint.
What is the most common form of TMD?
The National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research classifies TMD by the following: Myofascial pain. This is the most common form of TMD. It results in discomfort or pain in the fascia (connective tissue covering the muscles) and muscles that control jaw, neck and shoulder function.
What does TMD feel like?
Sensitivity of the teeth without the presence of an oral health disease. Numbness or tingling sensation in the fingers. A change in the way the upper and lower teeth fit together. The symptoms of TMD may look like other conditions or medical problems. See a dentist or your doctor for a diagnosis.
How do you know if you have TMD?
The following are the most common signs and symptoms of TMD: Jaw discomfort or soreness ( often most prevalent in the morning or late afternoon) Headaches. Pain spreading behind the eyes, in the face, shoulder, neck, and/or back. Earaches or ringing in the ears (not caused by an infection of the inner ear canal)
What are the factors that contribute to TMD?
A recent study by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research identified clinical, psychological, sensory, genetic, and nervous system factors that may put a person at higher risk of developing chronic TMD.
Treatment
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
Preparing For Your Appointment