
Medication
Topical steroids are the mainstay treatment for mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis. They are safe and effective when used correctly. The strength of a topical steroid is determined by the structure of the molecule. The weakest steroid used for the shortest time to …
Therapy
Eczema/atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition with a remitting and relapsing course diagnosed clinically with onset, often in early childhood, of pruritic, erythematous skin lesions which are excoriated, sometimes exudative in the acute phase; turning lichenified in the long term. 1 Worldwide prevalence of eczema is up to 20% of children and 3 % of adults.
Nutrition
Apr 13, 2022 · If those eczema treatments don’t work, a dermatologist may prescribe a systemic treatment, such as: JAK inhibitors azathioprine cyclosporine …
How long does it take to cure atopic dermatitis?
Aug 11, 2021 · A healthcare provider can create a treatment plan to manage symptoms. Treatment options can include medications, skin care, and phototherapy, which uses ultraviolet light to treat symptoms. 1 A Word From Verywell Atopic dermatitis is the most common form of eczema. It can cause the skin to be itchy, red, and uncomfortable.
What are the best home remedies for atopic dermatitis?
Nine Essential Ways You Can Treat Atopic Dermatitis Pimecrolimus (Elidel) and tacrolimus (Protopic) are Non-Steroid Topical Ointments That Fight Inflammation Of Atopic... Crisaborole topical treatment for Children and Adults for Mild to Moderate Atopic Dermatitis. Crisaborole (Eucrisa) is a... ...
Can atopic dermatitis be controlled through diet?
The type of treatment depends on the type of dermatitis and its location. Step number one is to avoid whatever triggers the dermatitis. That may be stress, a chemical, tobacco smoke and/or a number of other irritants that cause or worsen your dermatitis. Step …
How to cure rash or dermatitis naturally?
Nov 10, 2021 · The most effective long-term treatment of feline atopic dermatitis involves determining what your cat is allergic to. Your vet may first want you to start with a food trial which involves putting your cat on a prescription, hydrolyzed diet , which helps to determine which protein your cat is allergic to (as cats are more likely to be allergic to proteins versus grains).
See more

What is the best treatment for patients with atopic dermatitis?
Topical corticosteroids are first-line treatment for atopic dermatitis flare-ups. Topical calcineurin inhibitors are second-line treatment for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Antibiotics are not useful in reducing flare-ups of atopic dermatitis unless there is clear evidence of a secondary infection.Jul 1, 2012
What kills atopic dermatitis?
What is the treatment for atopic dermatitis?Topical corticosteroid creams and ointments are the most frequently used treatment. ... Tacrolimus (Protopic) and pimecrolimus (Elidel) are non-steroid topical ointments that contain molecules that inhibit a substance called calcineurin which is important in inflammation.More items...
Can atopic dermatitis be cured?
No cure has been found for atopic dermatitis. But treatments and self-care measures can relieve itching and prevent new outbreaks. For example, it helps to avoid harsh soaps, moisturize your skin regularly, and apply medicated creams or ointments.Jun 12, 2020
What is the main cause of atopic dermatitis?
Known triggers for atopic dermatitis include exposure to allergens such as pollen, pet dander or peanuts, or by stress, dry skin and infection. Skin irritants such as some fabrics, soaps and household cleaners may also trigger an atopic dermatitis flare.Dec 21, 2016
What is the best cream to put on eczema?
The Best Treatments for Eczema, According to DermatologistsVanicream Moisturizing Cream. ... CeraVe Moisturizing Cream. ... CeraVe Healing Ointment. ... Aquaphor Healing Ointment. ... Aveeno Eczema Therapy Itch Relief Balm. ... Cetaphil Baby Eczema Soothing Lotion with Colloidal Oatmeal.More items...•May 13, 2021
How long does atopic dermatitis last?
With proper treatment, flare-ups may last one to three weeks, notes Harvard Health Publishing. Chronic eczema such as atopic dermatitis can go into remission with the help of a good preventative treatment plan. “Remission” means that the disease is not active and you remain free of symptoms.May 10, 2021
How do you get rid of atopic dermatitis fast?
Lifestyle and home remediesMoisturize your skin at least twice a day. ... Apply an anti-itch cream to the affected area. ... Take an oral allergy or anti-itch medication. ... Don't scratch. ... Apply bandages. ... Take a warm bath. ... Choose mild soaps without dyes or perfumes. ... Use a humidifier.More items...•Jun 12, 2020
What is the difference between eczema and atopic dermatitis?
Eczema is most common in babies but also affects children and adults. Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition. It is caused by an allergic reaction. It is the most common type of eczema.Apr 24, 2020
Is Vaseline good for eczema?
Petroleum jelly is well tolerated and works well for sensitive skin, which makes it an ideal treatment for eczema flare-ups. Unlike some products that can sting and cause discomfort, petroleum jelly has moisturizing and soothing properties that alleviate irritation, redness, and discomfort.
Can atopic dermatitis spread?
No. No type of dermatitis is contagious. It can't be spread to anyone else.Oct 28, 2020
Why am I getting dermatitis all of a sudden?
A common cause of dermatitis is contact with something that irritates your skin or triggers an allergic reaction — for example, poison ivy, perfume, lotion and jewelry containing nickel.Sep 22, 2021
Why does atopic dermatitis get worse at night?
The good news is you're not going crazy; the bad news is that eczema symptoms can get worse at night. Here's why: Your body's levels of cortisol peak in the middle of the night. This hormone helps control inflammation and itch, so that's why you feel naturally less itchy first thing in the morning.Dec 29, 2020
What triggers atopic dermatitis?
Skin irritants: Where possible avoid triggers that can directly inflame the skin. These may include fabrics, chemicals, humidity , and dryness. Food: The relationship between atopic dermatitis and food is complex. Food allergies may exacerbate atopic dermatitis, but avoidance diets do not cure the problem.
What is the purpose of emollients?
Emollients make the skin slippery so take care with emollients in the bath, shower, and when holding babies. Sodium lauryl sulphate (SLS) is a surfactant used to mix the oil and water in emollients. It irritates dermatitis when left on for prolonged periods. Emollients to be left on the skin should be SLS-free.
Can food allergies cause dermatitis?
Food allergies may exacerbate atopic dermatitis, but avoidance diets do not cure the problem. Avoidance may exacerbate atopic dermatitis. Food allergy testing is needed if there is concern of an immediate life-threatening reaction ( anaphylaxis ).
What is coal tar used for?
Coal tar is a distillate from coal used in a variety of topical preparations including shampoos, lotions, and creams, sometimes mixed with a topical steroid to treat scaly atopic dermatitis. The smell can be off-putting.
Do emollients help with dermatitis?
Emollients are an essential aspect of care for all types of dermatitis. They need to be continued long term in atopic dermatitis even if the skin looks and feels comfortable. They should be applied regularly and liberally.
What is crisaborole used for?
Crisaborole was approved by the FDA in 2016 as a topical treatment for mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis in patients 2 years of age and older . It works by inhibiting phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4). [see also Key clinical-trial evidence for crisaborole]
Can atopic dermatitis be treated with antibiotics?
Antiseptics. It is common for patients with atopic dermatitis to have bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus colonising the skin. Sometimes the skin can become infected by these organisms. Antiseptics can be used during an infection and to try to prevent infection, but with care as they can irritate the skin.
How to treat atopic dermatitis in children?
Keep the inside of your home at a cool, stable temperature and consistent humidity levels. Get restful sleep. If you or your child is unable to get restful sleep at night because of itching and scratching, talk to your doctor about options to better control the atopic dermatitis. Avoid exposure to the smallpox vaccine.
What kind of doctor treats atopic dermatitis?
The following health care providers may diagnose and treat atopic dermatitis: Dermatologists, who specialize in conditions of the skin, hair, and nails. You may want to find a dermatologist that specializes in treating atopic dermatitis. Allergists, who specialize in treating allergies.
What is it called when your skin is itchy?
Atopic dermatitis, often called eczema, is a chronic (long-lasting) disease that causes the skin to become inflamed and irritated, making it extremely itchy. Atopic dermatitis is a common condition that usually begins in childhood; however, anyone can get the disease. Living with atopic dermatitis can be hard, but treatment can help control ...
What are the symptoms of atopic dermatitis?
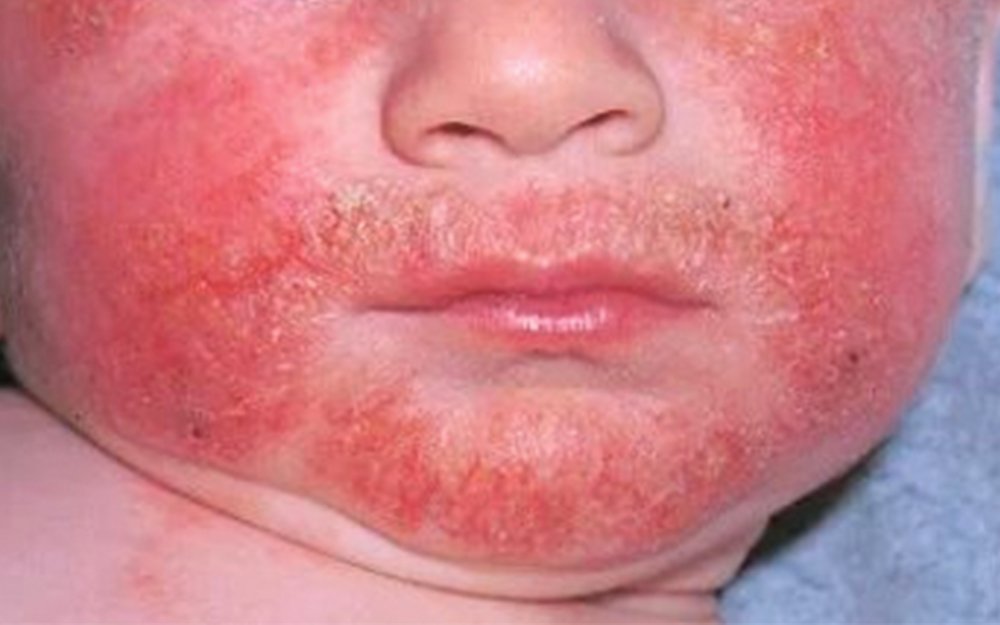
The most common symptom of atopic dermatitis is itching, which can be severe. Other common symptoms include: Red to dark brown, dry patches of skin. Rashes that that may ooze, weep clear fluid, or bleed when scratched. Thickening and hardening of the skin. The rash can appear anywhere on the body.
What causes redness and itching on the face?
Atopic dermatitis, often called eczema, is a chronic (long-lasting) disease that causes the skin to become inflamed and irritated, making it extremely itchy. Scratching leads to: Redness. Swelling.
Definition
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a form of eczema. It is a chronic skin disorder that can cause the skin to be irritated, inflamed, and itchy. 1
The Types of Eczema
Although atopic dermatitis is sometimes referred to simply as "eczema," AD is actually one kind of many possible forms of eczema.
Atopic Dermatitis Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is unknown, but researchers suspect a number of risk factors could play a role, including the following:
Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
The most common form of atopic dermatitis is itchy skin. Other symptoms include: 8
When to Seek Treatment
You should discuss any symptoms that worry you with a medical professional.
A Word From Verywell
Atopic dermatitis is the most common form of eczema. It can cause the skin to be itchy, red, and uncomfortable. The exact cause is unknown, but genetics and the immune system are believed to play a role.
Frequently Asked Questions
To diagnose atopic dermatitis, a medical provider will examine the skin, take a medical history, and ask about any symptoms. In some cases, consultation with an allergist-immunologist (a doctor trained to diagnose and treat allergies) or a dermatologist (a specialist in skin, hair, and nails) may be necessary.
What is the FDA approved treatment for atopic dermatitis?
The FDA recently approved Dupilumab (Dupixent) for treatment of mild to severe atopic dermatitis in grownups. It is an anti-IL-4 antibody that is done through injection two times every month and shows great promise in the managing of severe atopic dermatitis.
What are the effects of corticosteroids?
Typically, these medicines are used only in resistant instances, and the patient only uses them for short periods. The impacts of systemic corticosteroids can include cataracts, thinned or weakened bones, infections, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and skin damage. It can be harmful if you stop taking corticosteroids suddenly, so it is essential that the doctor and patient function together in changing the corticosteroid dosage.
What is crisaborole used for?
Crisaborole (Eucrisa) is a recently approved topical treatment for children and adults with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis (AD) which seems to function by inhibiting a different portion of the inflammatory cascade in the skin.
What is cyclosporine used for?
Among grownups, immunosuppressive medicines, like cyclosporine, are also used to treat severe instances of atopic dermatitis that don’t respond to other types of therapy. Immunosuppressive medications restrict the overactive immune system by blocking the production of some immune cells and curbing the activities of others. The side effects of cyclosporine can include tingling or numbness, high blood pressure, nausea, headaches, vomiting, kidney problems, and a possible increased risk of infections and cancer. There is also a relapse possibility after the drug after the patient stops taking medicine. Due to their harmful side effects, systemic corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs are used only in severe instances and then for as short a period as possible. Patients that want systemic immunosuppressive or corticosteroids drugs should visit a dermatologist or an allergist specializing in the care of atopic dermatitis to assist in identifying trigger factors and alternative therapies.
What causes dermatitis?
Dermatitis is caused by a combination of immune system activation, genetics and environmental triggers. Immune system. Sometimes your immune system overreacts. If you have atopic dermatitis, your immune system reacts to seemingly small irritants or allergens. This causes inflammation.
How common is dermatitis?
Some types of dermatitis are very common while others are less common. Atopic dermatitis affects two percent to three percent of adults and 25% of children. Contact dermatitis happens at some point to 15% to 20% of people.
Why does my skin get red and itchy?
Atopic dermatitis happens when there is damage to the skin barrier. This causes the skin to become inflamed, red, dry, bumpy and itchy. Contact dermatitis. Contact dermatitis is an allergic or irritant reaction that causes a painful or itchy skin rash.
What is the term for a condition that causes redness and dryness on the skin?
Dermatitis. Dermatitis is a general term for conditions that cause inflammation of the skin. Examples include atopic dermatitis (eczema), contact dermatitis and seborrheic dermatitis (dandruff). These conditions cause red rashes, dry skin and itchiness among other symptoms.
What does it mean when you have a rash on your face?
Common symptoms include dry skin, redness and itchiness. In the word “dermatitis,” “derm” means “skin” and “itis” means “inflammation.”. The word as a whole means “inflammation of the skin.”. The rashes range from mild to severe and can cause a variety of problems, depending on their cause. Dermatitis causes no serious harm to your body.
What does psoriasis look like?
Both look like patches of red skin with flakes of skin on top of and around the redness. However, in psoriasis, the scales are often thicker and the edges of those scales are well-defined. Seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis do overlap in a condition called “sebopsoriasis.”. That is when you have the symptoms of both.
What causes redness on the forehead?
Rosacea can cause red skin that looks like dermatitis. However, rosacea can also cause pimples, and the redness is typically found on your forehead, nose, chin and cheeks. Have your healthcare provider take a look at your skin to determine if your condition is dermatitis, rosacea , or something else.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle
Over-The-Counter (OTC) Therapies
Prescriptions
Summary
Specialist to consult
A Word from Verywell
Frequently Asked Questions