
Medication
Typical follow-up schedules after ovarian cancer. Even if you have completed treatment, you will likely have follow-up visits with your doctor for many years. It is very important to go to all of your follow-up appointments. During these visits, your doctors will ask questions about any problems you may have and may do exams and lab tests or x ...
Procedures
Ovarian cancer is still the fourth cause of death by cancer among women and the most fatal among gynecological tumors. The purpose of this symposium is, year after year, to report and discuss the new developments in the treatment of patients with ovarian cancer, the majority of whom still present with advanced disease.
Self-care
be used to evaluate the response of ovarian cancer to therapy, such as chemotherapy. Lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract radiography (https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/lowergi) is an x-ray examination of the large intestine (colon). The lower gastrointestinal tract is filled with barium with the use of a flexible tube inserted in the
How to diagnose ovarian cancer?
Most women with ovarian cancer will have some type of surgery to remove the tumor. Depending on the type of ovarian cancer and how advanced it is, you might need other types of treatment as well, either before or after surgery, or sometimes both.
What are the treatments for ovarian cancer?
Aug 22, 2020 · All patients with ovarian cancer will have surgery as part of their overall evaluation and treatment for ovarian cancer. Initially this is to obtain a biopsy specimen to confirm the diagnosis, determine the stage of the cancer, and to provide local treatment of the cancer in the pelvis and abdomen.
How to follow up after ovarian cancer treatment?
Sep 23, 2021 · The first treatment for stage 1 ovarian cancer is surgery to remove the tumor. Usually, a surgeon will remove the uterus, both ovaries, and the fallopian tubes. The treatment after surgery depends ...
What is the Ovarian Cancer Symposium?
Sep 28, 2015 · The randomized, controlled Adjuvant Hormone Therapy trial was launched in 1990 to assess survival outcomes in women with epithelial ovarian cancer who received HRT with estrogen alone. The primary endpoint of the study was overall survival (as measured from the time of random assignment to death from any cause).

Which Treatments Are Used For Ovarian Cancer?
There are several ways to treat ovarian cancer, depending on its type and stage.Local treatments: Some treatments are local, meaning they treat the...
How Is Ovarian Cancer Typically Treated?
Most women with ovarian cancer will have some type of surgery to remove the tumor. Depending on the type of ovarian cancer and how advanced it is,...
Who Treats Ovarian Cancer?
Doctors on your cancer treatment team might include: 1. A gynecologic oncologist: a gynecology doctor who is specially trained to use surgery to tr...
Making Treatment Decisions
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decisi...
Help Getting Through Cancer Treatment
Your cancer care team will be your first source of information and support, but there are other resources for help when you need it. Hospital- or c...
What to do if you have ovarian cancer?
If you have (or have had) ovarian cancer, you probably want to know if there are things you can do that might lower your risk of the cancer growing or coming back, such as exercising, eating a certain type of diet, or taking nutritional supplements.
What is the follow up for ovarian cancer?
Follow-up for ovarian cancer usually includes blood tests for tumor markers or hormones that help recognize recurrence. The choice of which blood tests to do depends on the type of cancer a woman has.
What blood test is used to detect ovarian cancer?
Blood tests for tumor markers 1 For epithelial ovarian cancer, CA-125 is the tumor marker used most often to check for recurrence. But it is not clear if checking for CA-125 levels and treating you before you have symptoms will help you live longer. Treatment based only on CA-125 levels and not symptoms can increase side effects, so it is important to discuss the pros and cons of CA-125 monitoring and quality of life with your doctor. Tests for other tumor markers, such as CA 19-9, CEA, and HE-4, are used most often for women whose CA-125 levels never went up. 2 For germ cell tumors, blood is tested for alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and/or human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). 3 For stromal cancers, checking levels of hormones like estrogen, testosterone, and inhibin is sometimes helpful.
What is a survivorship plan?
This plan might include: A schedule for other tests you might need in the future, such as early detection (screening) tests for other types of cancer, or tests to look for long-term health effects from your cancer or its treatment.
How long do side effects of cancer last?
Some cancer treatment side effects may last a long time or might not even show up until years after you have finished treatment. Your doctor visits are a good time to ask questions and talk about any changes or problems you notice or concerns you have. To some extent, the frequency of follow up visits and tests will depend on the stage ...
What is the importance of follow up appointments?
During these visits, your doctors will ask questions about any problems you may have and may do exams and lab tests or x-rays and scans to look for signs of cancer or treatment side effects.
Is it important to keep health insurance after cancer treatment?
Even after treatment, it’s very important to keep health insurance. Tests and doctor visits cost a lot, and even though no one wants to think of their cancer coming back , this could happen.
What kind of doctor treats ovarian cancer?
Based on your treatment options, you might have different types of doctors on your treatment team. These doctors could include: 1 A gynecologic oncologist: a gynecology doctor who is specially trained to use surgery to treat ovarian cancer; many times they are also the ones to give chemotherapy and other medicines to treat ovarian cancer 2 A radiation oncologist: a doctor who uses radiation to treat cancer 3 A medical oncologist: a doctor who uses chemotherapy and other medicines to treat cancer
What is the number to call for cancer treatment?
Call our National Cancer Information Center at 1-800-227-2345 and speak with one of our trained specialists. Palliative Care. Find Support Programs and Services in Your Area.
What is a radiation oncologist?
A radiation oncologist: a doctor who uses radiation to treat cancer. A medical oncologist: a doctor who uses chemotherapy and other medicines to treat cancer. Many other specialists might be part of your treatment team as well, including physician assistants, nurse practitioners, nurses, psychologists, sex counselors, social workers, nutritionists, ...
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
Can older women get ovarian cancer?
Age alone isn’t a determining factor since several studies have shown that older women tolerate ovarian cancer treatments well. It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decision that best fits your needs.
Can alternative treatments help with cancer?
Alternative treatments are used instead of a doctor’s medical treatment. Although some of these methods might be helpful in relieving symptoms or helping you feel better, many have not been proven to work. Some might even be harmful. Be sure to talk to your cancer care team about any method you are thinking about using.
Can you continue cancer treatment?
Whether or not you continue treatment, there are still things you can do to help maintain or improve your quality of life.
What is the treatment for ovarian cancer?
The successful treatment of ovarian cancer requires the involvement and coordination of several different treatment approaches, including surgery, systemic therapy, and, in rare cases, radiation therapy. Nearly all women with ovarian cancer will undergo surgery and systemic treatment.
What is the role of surgery in ovarian cancer?
The role of surgery in the initial management of ovarian cancer is to obtain a biopsy specimen of the cancer to confirm the diagnosis, determine the stage of cancer and to provide local treatment of the cancer in the pelvis and abdomen.
What are the procedures for laparotomy?
Typical debulking during the laparotomy includes: 1 A total hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) 2 Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes) 3 Omentectomy (removal of a flap of fatty tissue covering the bowel in the abdomen). 4 Removal of any visible cancer within the abdomen. 5 If the cancer appears to be limited to the ovaries or the pelvis, the surgeon will also cut small pieces of tissue (biopsy) from the upper abdomen. 6 Peritoneal washings -collection of abdominal fluid samples and removal of lymph nodes so that they can be examined under a microscope to determine whether they contain cancer.
What kind of doctor treats ovarian cancer?
Specific treatment can depend on both the stage and the genomic profile of the cancer. Individuals should seek care from a gynecologic oncologist, these are the doctors specifically trained to diagnose and treat patients with ovarian cancer.
How does radiation kill cancer cells?
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy uses high-energy rays to damage or kill cancer cells by preventing them from growing and dividing . Similar to surgery, radiation therapy is a local treatment and is not useful in eradicating cancer cells that have already spread to other parts of the body. Radiation therapy may be externally or internally delivered. External radiation delivers high-energy rays directly to the tumor site from a machine outside the body. Internal radiation, or brachytherapy, involves the implantation of a small amount of radioactive material in or near the cancer.
What is systemic therapy?
Systemic Therapy: Precision Cancer Medicine, Chemotherapy, and Immunotherapy. Systemic therapy is any treatment directed at destroying cancer cells throughout the body. Many patients with ovarian cancer already have small amounts of cancer that were not removed with surgery.
How does chemotherapy work?
Cancer chemotherapy may consist of single drugs or combinations of drugs, and can be administered through a vein, injected into a body cavity, or delivered orally in the form of a pill. Chemotherapy is different from surgery or radiation therapy in that the cancer-fighting drugs circulate in the blood to parts of the body where the cancer may have spread and can kill or eliminate cancers cells at sites great distances from the original cancer. The drugs are usually given in cycles so that a recovery period follows every treatment period.
How long does ovarian cancer last?
The majority of deaths were due to ovarian cancer. The mean overall survival at 20 years after diagnosis was 8.5 years for patients in the hormone therapy groups and 5.7 years for women in the control group. The study authors observed a similar effect for relapse-free survival.
When was the randomized controlled adjuvant hormone therapy trial?
The randomized, controlled Adjuvant Hormone Therapy trial was launched in 1990 to assess survival outcomes in women with epithelial ovarian cancer who received HRT with estrogen alone. The primary endpoint of the study was overall survival (as measured from the time of random assignment to death from any cause). The main secondary endpoint was relapse-free survival (as measured from the time of random assignment to disease relapse or death from any cause).
Does hormone replacement therapy cause hot flashes?
This can cause some women to experience adverse health effects, including hot flashes as well as an increased risk of bone fractures and coronary heart disease. Hormone replacement therapy has been shown to reduce menopausal symptoms, which affect many women with ovarian cancer. Although some women with ovarian cancer experience severe menopausal ...
Can you take hormone replacement after ovarian cancer?
"These results show that women who have severe menopausal symptoms after ovarian cancer treatment can safely take hormone replacement therapy, and this may, in fact, infer benefits in terms of overall survival in addition to known advantages in terms of quality of life," the study authors wrote.
What is the low accrual for the study?
The study authors also noted that when the trial began in 1990, the data were collected based on the known prognostic and therapeutic options at the time. As a result, there are "several potentially relevant factors that cannot be assessed in these analyses, such as the use of post-relapse treatment," the authors wrote.
Can ovarian cancer be treated with surgery?
Background. Surgery is one of the standard treatment options for women with ovarian cancer. Premenopausal women who undergo surgical treatment for the disease will experience premature menopause as a result of the loss of ovarian estrogen.
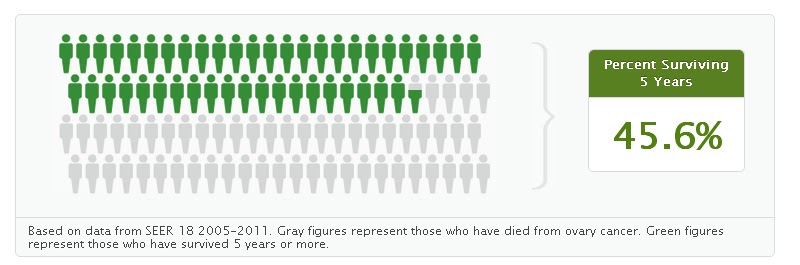
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment