Chemical precipitation in water and wastewater treatment is the change in form of materials dissolved in water into solid particles. Chemical precipitation is used to remove ionic constituents from water by the addition of counter-ions to reduce their solubility.
What is chemical precipitation in wastewater treatment?
Chemical precipitation in water and wastewater treatment is the change in form of materials dissolved in water into solid particles. Chemical precipitation is used to remove ionic constituents from water by the addition of counter-ions to reduce their solubility.
How do metal precipitation water treatment systems work?
Metal precipitation water treatment systems utilize delicate processes that incorporates multiple removal mechanisms to extract metal sediment from water. This is a much-needed process because heavy metals like copper, lead, nickel, mercury, and cadmium are often present in industrial wastewaters.
What is the chemical process of precipitation?
The chemical process of precipitation involves the addition of suitable agents to the wastewater which can transform dissolved substances to ones that are not easily soluble. With this transformation, the material precipitates and lowers the concentration of the material.
How are chemicals used in wastewater treatment?
Chemicals are used during wastewater treatment in an array of processes to expedite disinfection. These chemical processes, which induce chemical reactions, are called chemical unit processes and are used alongside biological and physical cleaning processes to achieve various water standards.

What is chemical precipitation method?
Chemical precipitation is the process of conversion of a solution into solid by converting the substance into insoluble form or by making the solution a super saturated one. From: Journal of King Saud University - Science, 2019.
How does chemical precipitation happen?
Precipitation reactions occur when cations and anions in aqueous solution combine to form an insoluble ionic solid called a precipitate. Whether or not such a reaction occurs can be determined by using the solubility rules for common ionic solids.
What is an example of chemical precipitation?
One of the best examples of precipitation reactions is the chemical reaction between potassium chloride and silver nitrate, in which solid silver chloride is precipitated out. This is the insoluble salt formed as a product of the precipitation reaction.
What are the chemical reactions in water treatment?
There are several distinct chemical unit processes, including chemical coagulation, chemical precipitation, chemical oxidation, and advanced oxidation, ion exchange, and chemical neutralization and stabilization, which can be applied to wastewater during cleaning.
What is the difference between dissolution and precipitation?
Precipitation is the process of a compound coming out of solution. It is the opposite of dissolution or solvation. In dissolution, the solute particles separate from each other and are surrounded by solvent molecules. In precipitation, the solute particles find each other and form a solid together.
What does precipitation mean in the water cycle?
Precipitation is water released from clouds in the form of rain, freezing rain, sleet, snow, or hail. It is the primary connection in the water cycle that provides for the delivery of atmospheric water to the Earth. Most precipitation falls as rain.
What are 2 examples of precipitate?
Examples of Precipitation ReactionsReaction between potassium iodide and lead nitrate in water, forming lead iodide as a precipitate and aqueous potassium nitrate: ... Reaction between sodium fluoride and silver nitrate in water, forming solid silver fluoride and aqueous sodium nitrate:More items...•
What happens precipitation reaction?
A precipitation reaction is one in which dissolved substances react to form one (or more) solid products. Many reactions of this type involve the exchange of ions between ionic compounds in aqueous solution and are sometimes referred to as double displacement, double replacement, or metathesis reactions.
What do you mean by a precipitation reaction explain by giving examples?
Answer. A precipitate is an insoluble substance. A reaction in which any insoluble solid precipitate is formed is called Precipitation Reaction. For example, When Sodium Sulphate solution is mixed with Barium Chloride solution It forms Barium Sulphate and Sodium Chloride solution.
How are precipitation reactions used to purify water?
In precipitation reactions, as noted on the main page, substances that are dissolved in water react to form a solid. The main goal of the precipitation portion of the wastewater treatment process is to remove soluble metal ions and phosphates from water.
What is chemical treatment process?
Chemical treatment is used by most CB facilities. Treatment includes chlorination for disinfection purposes and oxidation of some impurities in the water. The water is then softened through the addition of lime to reduce alkalinity by removing magnesium and calcium bicarbonates.
What is chemical treatment?
Chemical treatment (of hazardous waste) refers to the treatment methods that are used to effect the complete breakdown of hazardous waste into non-toxic gases or, more frequently, to modify the chemical properties of the waste, for example, through reduction of water solubility or neutralisation of acidity or ...
Is precipitation a chemical change?
A precipitation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two soluble salts in aqueous solution combine and one of the products is an insoluble salt called a precipitate.
How do you identify a precipitate in a chemical reaction?
An Example of Identifying a Precipitate We would expect them to undergo a double displacement reaction with each other. By examining the solubility rules we see that, while most sulfates are soluble, barium sulfate is not. Because it is insoluble in water we know that it is the precipitate.
What type of reaction is a precipitation reaction?
A precipitation reaction is one in which dissolved substances react to form one (or more) solid products. Many reactions of this type involve the exchange of ions between ionic compounds in aqueous solution and are sometimes referred to as double displacement, double replacement, or metathesis reactions.
What are two types of precipitation?
The different types of precipitation are:Rain. Most commonly observed, drops larger than drizzle (0.02 inch / 0.5 mm or more) are considered rain. ... Drizzle. Fairly uniform precipitation composed exclusively of fine drops very close together. ... Ice Pellets (Sleet) ... Hail. ... Small Hail (Snow Pellets) ... Snow. ... Snow Grains. ... Ice Crystals.
What is precipitation water treatment?
Precipitation water treatment systems are used to remove chemicals, heavy metals, and other metal pollutants from wastewater. Metal precipitation water treatment systems utilize delicate processes that incorporates multiple removal mechanisms to extract metal sediment from water. This is a much-needed process because heavy metals like copper, lead, nickel, mercury, and cadmium are often present in industrial wastewaters. These heavy metals can be reduced to insoluble forms through the introduction of sulfides, hydroxides, or carbonate ions to the wastewater. Now reduced into insoluble precipitates, they can be safely filtered out of the wastewater, which can then be safely discharged once it’s been shown to contain low metal concentrations.
What are the heavy metals in wastewater?
This is a much-needed process because heavy metals like copper, lead, nickel, mercury, and cadmium are often present in industrial wastewaters. These heavy metals can be reduced to insoluble forms through the introduction of sulfides, hydroxides, or carbonate ions to the wastewater.
Can you filter out heavy metals from wastewater?
Now reduced into insoluble precipitates, they can be safely filtered out of the wastewater, which can then be safely discharged once it’s been shown to contain low metal concentrations. Chemical precipitation wastewater treatment is used for more than just heavy metal removal from wastewater.
What is the process of precipitation?
The chemical process of precipitation involves the addition of suitable agents to the wastewater which can transform dissolved substances to ones that are not easily soluble. With this transformation, the material precipitates and lowers the concentration of the material.
What is wastewater treatment?
The initial stage of wastewater treatment involves mechanical processes, which remove some 20-30% of solids in the water. First, the wastewater is directed to a screen or a sieve drum that filters out impurities that are relatively coarse, such as leaves, textiles, paper, or other large materials. A series of screens are used with various degrees ...
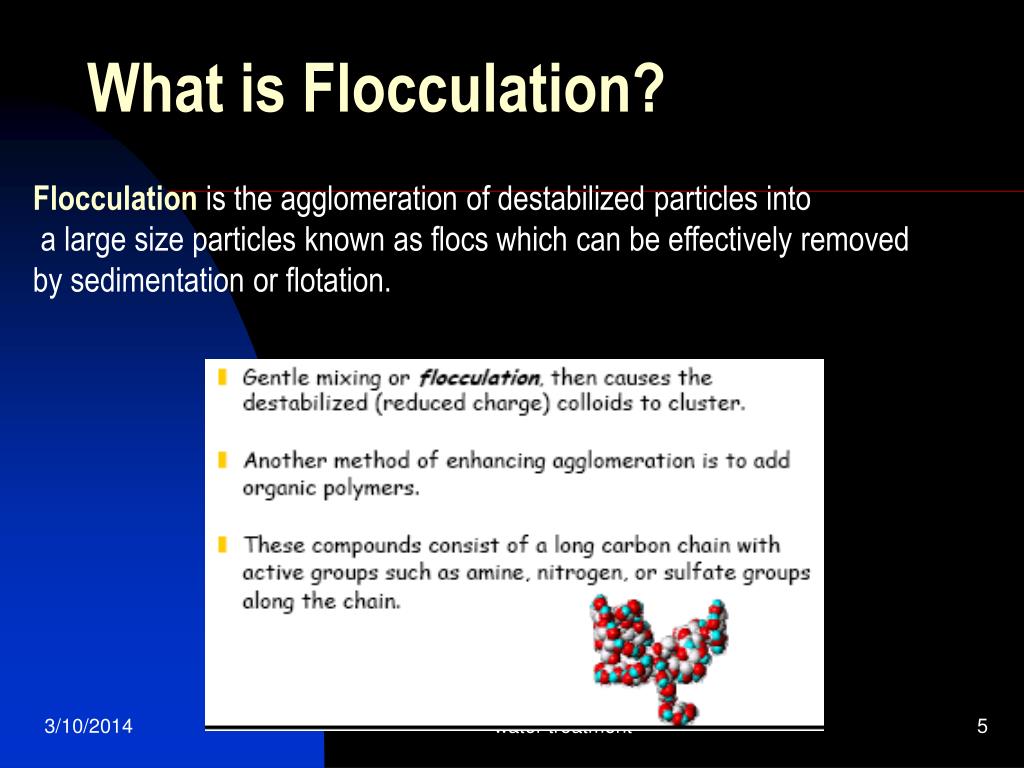
What is flocculant in wastewater?
Flocculation uses flocculants to help remove very fine particles from wastewater that would not normally accumulate as larger agglomerates as a result of their electrical repulsion from having an identical charge. By adding specialty chemicals, larger formulations of particles will occur which will then settle out in a sedimentation process.
How does chemical stabilization work?
Chemical Stabilization. This chemical wastewater treatment process works in a similar fashion as chemical oxidation. Sludge is treated with a large amount of a given oxidant, such as chlorine. The introduction of the oxidant slows down the rate of biological growth within the sludge and also helps deodorize the mixture.
How to remove metals from wastewater?
Chemical precipitation is the most common method for removing dissolved metals from wastewater solution containing toxic metals. To convert the dissolved metals into solid particle form, a precipitation reagent is added to the mixture. A chemical reaction, triggered by the reagent, causes the dissolved metals to form solid particles. Filtration can then be used to remove the particles from the mixture. How well the process works is dependent upon the kind of metal present, the concentration of the metal, and the kind of reagent used. In hydroxide precipitation, a commonly used chemical precipitation process, calcium or sodium hydroxide is used as the reagent to create solid metal hydroxides. However, it can be difficult to create hydroxides from dissolved metal particles in wastewater because many wastewater solutions contain mixed metals.
How does alkaline chlorination work?
The pollutants then undergo structural modification, becoming less destructive compounds. Alkaline chlorination uses chlorine as an oxidant against cyanide. However, alkaline chlorination as a chemical oxidation process can lead to the creation of toxic chlorinated compounds, and additional steps may be required. Advanced oxidation can help remove any organic compounds that are produced as a byproduct of chemical oxidation, through processes such as steam stripping, air stripping, or activated carbon adsorption.
What chemicals are used to disinfect wastewater?
Specialized chemicals such as chlorine, hydrogen peroxide, sodium chlorite, and sodium hypochlorite (bleach) act as agents that disinfect, sanitize, and assist in the purification of wastewater at treatment facilities. There are several distinct chemical unit processes, including chemical coagulation, chemical precipitation, chemical oxidation, ...
What is the purpose of precipitation?
The aim of precipitation is to precipitate the chemical from dissolved substances in the wastewater by adding a reagent, which forms an insoluble compound with the to-be-separated matter. Positive ions such as (heavy) metals, but also negative ions like phosphates and sulphates, can be removed via precipitation.
What is the ratio of precipitation to reagent?
In general, precipitation occurs in a 1 on 1 mole ratio; in other words, one molecule of dissolved matter (for example SO 42- present in the form of well soluble natrium sulphate) with 1 molecule of reagent (for example, barium derived from soluble barium chloride) forms an insoluble precipitate (barium sulphate in this case).
What is precipitation in graphics?
Precipitation is a suitable technique for the recuperation of silver from concentrated solutions (fixing baths) in the graphics sector. Precipitation is a contemporary technique for wastewater purification when processing mineral products, including for the removal of metals and fluoride.
Why is precipitation important?
Precipitation is a proven, relatively simple and effective technique. Precipitation can be used to obtain good results with a number of substances that are difficult to remove with other techniques. Another advantage of this technique is that very specific components can be removed, while not removing other substances;
What is the most commonly used technique for the removal of metals and some anions from wastewater?
Precipitation is the most well known and most commonly used technique for the removal of metals and some anions from wastewater. Precipitation applications can be found in every sector where metals are found in the wastewater. However, it is noticeable that alternative solutions are currently being selected.
How can heavy metals be precipitated?
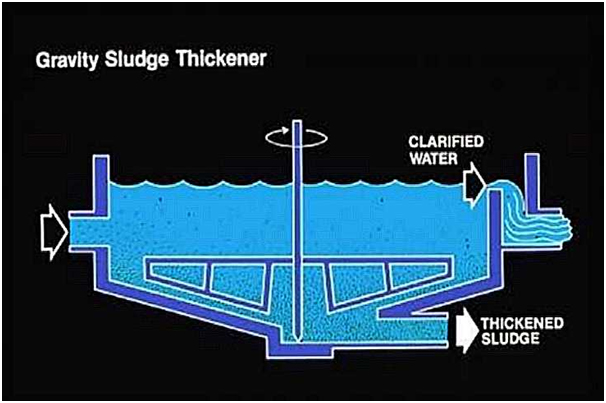
Other heavy metals can be precipitated as hydroxide by increasing the pH. Once a substance has been precipitated, it can be separated from the main stream using filtration, flotation or sedimentation. A polymer is often added to improve silt separation.
Does precipitation work poorly?
If a particular substance is selected, possibly co-precipitation, one should examine the optimum pH value, which substances will also be precipitate and which substances may influence precipitation. Precipitation does not work, or works poorly, when disruptive ions are present, like complex formers. Complex formers are substances that form ...
What is precipitation in chemistry?
Generally speaking, precipitation is a method of causing contaminants that are either dissolved or suspended in solution to settle out of solution as a solid precipitate, which can then be filtered, centrifuged, or otherwise separated from the liquid portion.
What is the process of removing dissolved compounds from water?
The removal of these dissolved compounds, called water softening, often proceeds by chemical precipitation . Lime (calcium oxide), when added to hard water, reacts to form calcium carbonate, which itself can act as a coagulant, sweeping ions out of solution in formation and settling.
What is a phosphate remover?
It is an effective tool for wastewater polishing and removal of particulate matter.
What is the chemical reaction of calcium hydroxide?
The calcium hydroxide reacts in the wastewater solution to form calcium carbonate, which itself acts as a coagulant, sweeping particles out of solution. Additional Considerations The chemical agents most frequently used for chemical precipitation are shown in Table 1.
What factors affect the amount of chemicals needed for treatment?
The amount of chemicals required for treatment depends on the pH and alkalinity of the wastewater, the phosphate level, and the point of injection and mixing modes , among other factors. Competing reactions often make it difficult to calculate the quantities of additives necessary for chemical precipitation.
What is the process of removing metals from water?
The removal of these dissolved compounds, called water softening , often proceeds by chemical precipitation.
Can metal salt be calculated on the basis of phosphate concentration?
Moreover, many competing chemical reactions can take place alongside these, meaning that the amount of metal salt to add to the solution cannot simply be calculated on the basis of the phosphate concentration, but must be determined in the laboratory for each case (Tchobanoglous and Burton, 1991).
What is the hard water level?
In the United States, hard water is mostly found in the mid western and western states. It ranges between 120-250 mg/L as CaCO3or beyond 250 mg/L as CaCO3 for very hard waters.
How much of the Earth's water is ground water?
More than 60 percent of the Earth’s water is ground water and hard water is found in more than 85% of the country. The water travels through rocks and soil picking up minerals including calcium and magnesium, ions which produce hard water. (Water Review, Consumer report, 1990).
What is the purpose of precipitation reaction?
The main goal of the precipitation portion of the wastewater treatment process is to remove soluble metal ions and phosphates from water. Before delving into the reactions, it is useful to re-examine the solubility rules ...
What is wastewater treatment?
In the process of being used, whether it be for irrigation, drinking, bathing, or industrial applications, it needs to be cleaned before being the wastewater is used again. This process is called wastewater treatment and consists of the following major steps: Below is a photograph of a wastewater treatment facility.
What chemicals are used to remove ions from water?
In order to remove these ions from the water supply, 2 chemicals are commonly used, lime (Ca (OH) 2) and soda ash (Na 2 CO 3 ). This occurs in the following chemical pathway:
Why is water treatment important?
Water treatment is performed in order to improve water quality. The processes employed for water treatment depend on the quality of the water supply. In all cases, water has to be disinfected in order to deactivate any existing microorganisms present in water. So far, this technique was proved to be the most important for the protection ...
What is biological waste water treatment?
Biological waste water treatment is the primary method of preparing food-processing waste water flows for return to the environment. Increasing waste water loads on existing plants and more stringent government discharge requirements have put considerable pressure on the food-processing industry to refine and understand better the design and management of biological waste water treatment processes. Though activated sludge and other biological treatment processes are still frequently operated by general guidelines and ‘rules of thumb,’ facility design and operation must be guided by consideration of both the physical and biological aspects of waste water treatment. Various modifications and combinations of aerobic and anaerobic biological treatment processes are commonly used in the food-processing industry.
What are the most important problems in water?
If the water originates from a surface water supply such as a river, lake, or dam, then the suspended particles are the most important problem. Different techniques to remove suspended particles include the addition of coagulants and the use of membranes.
What is the most effective method of removing bacteria and viruses from raw water prior to conventional treatment?
zooplankton) and macro-invertebrate filter feeders also reduce pathogen numbers. Apart from pre-chlorination, storage is the most effective method of removing bacteria and viruses from raw water prior to conventional treatment.
What is MF water treatment?
MF is used to remove turbidity and larger microorganisms. Water treatment in existing installations uses immersed membrane modules that are simply placed in water tanks where a vacuum at the permeate side drives the collection of purified water.
How to improve the taste of water?
1. Understand the treatment need: For many consumers, simply improving the taste of the water is their primary treatment need. For some, there may be health contaminants that must be treated. And others may have very hard water, causing issues with lime scale around fixtures and possibly damaging appliances. 2.
What will the future of brewing water systems be like?
Brewery water treatment systems of the future will be very flexible, allowing breweries to tailor-make their water for different products. At the same time, these future water treatment systems will aim to achieve optimum efficiency in terms of operating cost and especially wastewater produced. The advances in analysis techniques will inevitably lead to further challenges, as it will be possible to detect certain components that are not an issue today but will then need to be removed. It will also continue to be vital for brewers to pay attention to their water supply to avoid surprising and unexpected quality defects in the finished product.
Mechanical Wastewater Treatment Processes
- The initial stage of wastewater treatment involves mechanical processes, which remove some 20-30% of solids in the water. First, the wastewater is directed to a screen or a sieve drum that filters out impurities that are relatively coarse, such as leaves, textiles, paper, or other large materials. A series of screens are used with various degrees of fineness from several centimeters down to a …
Biological Wastewater Treatment Processes
- Following the mechanical treatment stage, effluent is passed to a biological-based process for further purification. Aeration tanks are utilized to add oxygen to the water and to put the water into circulation through the use of propellers. The oxygen stimulates the growth of bacteria and microorganisms which feed off of any organic contaminants in the water and convert those into …
Chemical Wastewater Treatment Processes
- Chemicals are used during wastewater treatment in an array of processes to expedite disinfection. These chemical processes, which induce chemical reactions, are called chemical unit processes and are used alongside biological and physical cleaning processes to achieve various water standards. Specialized chemicals such as chlorine, hydrogen peroxid...
Summary
- Processing of wastewater for use, or recycling and reuse, represents a unification of several distinct technologies, including specialized chemicals, mechanical filtration products, purification systems, specially designed equipment, and wastewater treatment servicesto obtain satisfactory solutions to the challenges of water purification and remediation. This article provided a review …
Method and Installation Description
Specific Advantages and Disadvantages
- Precipitation is a proven, relatively simple and effective technique. Precipitation can be used to obtain good results with a number of substances that are difficult to remove with other techniques. Another advantage of this technique is that very specific components can be removed, while not removing other substances; thus there is a high degree of selectivity. In som…
Application
- Precipitation is the most well known and most commonly used technique for the removal of metals and some anions from wastewater. Precipitation applications can be found in every sector where metals are found in the wastewater. However, it is noticeable that alternative solutions are currently being selected. The reasons for this include the relatively high effluent concentrations, …
Boundary Conditions
- A major boundary condition is the chemical composition of the water. If a particular substance is selected, possibly co-precipitation, one should examine the optimum pH value, which substances will also be precipitate and which substances may influence precipitation. Precipitation does not work, or works poorly, when disruptive ions are present, like complex formers. Complex formers …
Effectiveness
- Precipitation has a high yield. The attainable end concentration is determined by the compound’s solubility product. It is difficult to determine an end concentration for combinations of pollutants, due to the interaction of substances with each other. Attainable end concentrations for single metals with Ca(OH)2 as reagent are 1-10 mg/l and approximately 0.1-1 mg/l for copper, lead, silv…
Support Aids
- Chemicals as reagents; examples include iron chloride, polyaluminium chloride, milk of lime, iron hydroxide and natrium sulphide. Acid and/or base often need to be added for pH correction.
Environmental Issues
- Chemical silt is formed as a by-product, whereby the dry-matter content is very important for a potential follow-up step. Silt from heavy metal precipitation is regarded as dangerous waste.
Costs
- The costs for this technique are greatly determined by the choice of reagent. The level of dosage is determined by the quantity of material to be precipitated. Case 1: Study of a company active in the metal sector (2008). Precipitation of the metals Cr and Mo with Fe(SO4) and polymer from a wastewater flow of 3 m³/hour. Investment costs will be € 545.000 including reactor, building, sil…
Comments
- Disruptive substances can negatively influence the process. Be careful for the forming of harmful complexes or harmful by-products (like, for example, hydrogen sulphide).
References
- AEA Technology, Manual of Effluent Process Technology, Environmental & Process Engineering Department, Harwell (GB), 1991
- Baeyens J., Hosten L. and Van Vaerenbergh E., Wastewater purification, Environment Foundation - Kluwer Editorial, 1995
- EIPPCB, Reference Document on BAT in Common Waste Water and Waste Gas Treatment / …
- AEA Technology, Manual of Effluent Process Technology, Environmental & Process Engineering Department, Harwell (GB), 1991
- Baeyens J., Hosten L. and Van Vaerenbergh E., Wastewater purification, Environment Foundation - Kluwer Editorial, 1995
- EIPPCB, Reference Document on BAT in Common Waste Water and Waste Gas Treatment / Management Systems in the Chemical Sector, draft February 2009 (revision upon release)
- Metcalf & Eddy, Wastewater Engineering: treatment, disposal, reuse, McGraw-Hill, 1991