
Medication
To assign a stage to your melanoma, your doctor will:
- Determine the thickness. The thickness of a melanoma is determined by carefully examining the melanoma under a microscope and measuring it with a special tool. ...
- See if the melanoma has spread to the lymph nodes. ...
- Look for signs of cancer beyond the skin. ...
Procedures
Your doctor or nurse will show you how to check your skin for melanoma. If you have any symptoms that you are worried about, you can contact your hospital doctor or specialist nurse between follow up appointments. Your doctor might discharge you 5 years after you complete your treatment. Or you might continue with yearly follow up appointments.
Therapy
This means 92 of every 100 people diagnosed with melanoma will be alive in 5 years. In the very early stages the 5-year survival rate is 99%. Once melanoma has spread to the lymph nodes the 5-year survival rate is 63%.
Nutrition
almost all people (almost 100%) will survive their melanoma for 1 year or more after they are diagnosed; around 90 out of every 100 people (around 90%) will survive their melanoma for 5 years or more after diagnosis; more than 85 out of every 100 people (more than 85%) will survive their melanoma for 10 years or more after they are diagnosed
What is the first step in treating melanoma?
How often should you see your doctor after melanoma treatment?
How long do you have to live with melanoma?
What is the life expectancy of melanoma?
How do you get rid of melanoma on face?
It is usually treated by surgery (wide excision) to remove the melanoma and a small margin of normal skin around it. The removed sample is then sent to a lab to be looked at with a microscope. If cancer cells are seen at the edges of the sample, a second, wider excision of the area may be done.
How serious is melanoma on the face?
Melanoma can grow very quickly. It can become life-threatening in as little as 6 weeks and, if untreated, it can spread to other parts of the body. Melanoma can appear on skin not normally exposed to the sun. Nodular melanoma is a highly dangerous form of melanoma that looks different from common melanomas.
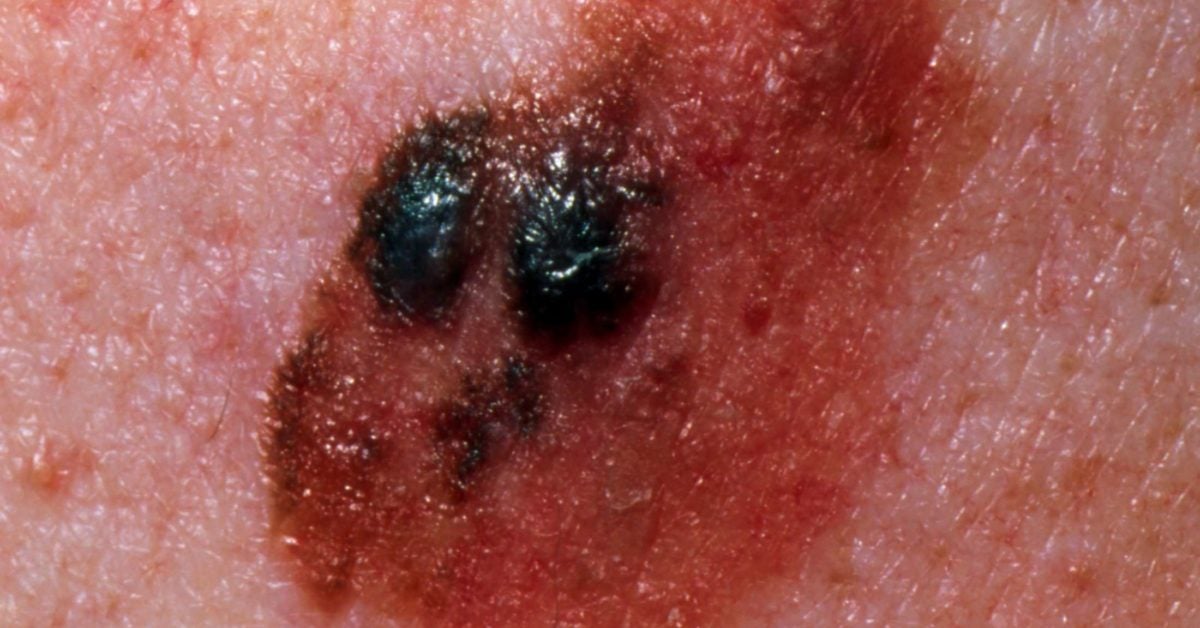
What does melanoma look like on the face?
Border that is irregular: The edges are often ragged, notched, or blurred in outline. The pigment may spread into the surrounding skin. Color that is uneven: Shades of black, brown, and tan may be present. Areas of white, gray, red, pink, or blue may also be seen.
Where does melanoma on the face spread to?
Melanoma often spreads to: Tissue under the skin. Lymph nodes. Lungs.
How quickly should melanoma be removed?
Hypothesis-based, informal guidelines recommend treatment within 4–6 weeks. In this study, median surgical intervals varied significantly between clinics and departments, but nearly all were within a 6-week frame. Key words: melanoma, surgical interval, treatment time, melanoma survival, time factors.
Do Dermatologists remove melanoma?
A dermatologist can often perform this surgery during an office visit while you remain awake. During excision surgery in a dermatologist's office, your dermatologist removes any remaining melanoma tumor and some normal-looking skin along the edges. In the earliest stages, this surgery often cures melanoma.
What does Stage 1 melanoma look like?
Stage IA Melanoma: The melanoma tumor is less than 1.0 millimeter thick (less than the size of a sharpened pencil point) with or without ulceration (broken skin) when viewed under the microscope. Stage IB Melanoma: The melanoma tumor is more than 1.0 millimeter and less than 2.0 millimeters thick without ulceration.
What does early stage melanoma look like?
What to look for: Usually, the most obvious warning signs of early stage melanoma are changes to your moles or spots: in size, shape, colour or in how they look or how they feel. Melanoma can also appear as a new mole (more commonly in people aged 50 years or more)2.
How long can you live with melanoma untreated?
5-year relative survival rates for melanoma skin cancerSEER stage5-year relative survival rateLocalized99%Regional68%Distant30%All SEER stages combined93%Mar 1, 2022
Is melanoma a death sentence?
Metastatic melanoma was once almost a death sentence, with a median survival of less than a year. Now, some patients are living for years, with a few out at more than 10 years.
What is the life expectancy of someone with melanoma?
Survival for all stages of melanoma around 90 out of every 100 people (around 90%) will survive their melanoma for 5 years or more after diagnosis. more than 85 out of every 100 people (more than 85%) will survive their melanoma for 10 years or more after they are diagnosed.
Is Stage 1 melanoma serious?
Stage 1 is considered a 'thin melanoma'. If your melanoma is caught before it is too thick the prognosis is very good. Nearly 19 in 20 people who have a stage 1 melanoma are alive at least five years after being diagnosed. Stage 1 is the least serious type of melanoma.
How to cope with melanoma?
Here are some ideas to help you cope: Learn enough about melanoma to make decisions about your care. Ask your doctor about your cancer, including your treatment options and, if you like, your prognosis. As you learn more about cancer, you may become more confident in making treatment decisions. Keep friends and family close.
How to treat melanoma that has spread beyond the skin?
Treating melanomas that have spread beyond the skin. If melanoma has spread beyond the skin, treatment options may include: Surgery to remove affected lymph nodes. If melanoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes, your surgeon may remove the affected nodes.
What is the procedure to remove melanoma from lymph nodes?
If there's a risk that the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, your doctor may recommend a procedure known as a sentinel node biopsy. During a sentinel node biopsy, a dye is injected in the area where your melanoma was removed. The dye flows to the nearby lymph nodes.
How to treat early stage melanoma?
Treatment for early-stage melanomas usually includes surgery to remove the melanoma. A very thin melanoma may be removed entirely during the biopsy and require no further treatment. Otherwise, your surgeon will remove the cancer as well as a border of normal skin and a layer of tissue beneath the skin.
What is the stage of melanoma?
Melanoma is staged using the Roman numerals 0 through IV. At stage 0 and stage I, a melanoma is small and has a very successful treatment rate. But the higher the numeral, the lower the chances of a full recovery. By stage IV, the cancer has spread beyond your skin to other organs, such as your lungs or liver.
How does thickness affect melanoma?
The thickness of a melanoma helps doctors decide on a treatment plan. In general, the thicker the tumor, the more serious the disease. Thinner melanomas may only require surgery to remove the cancer and some normal tissue around it.
How to assign stage to melanoma?
To assign a stage to your melanoma, your doctor will: Determine the thickness. The thickness of a melanoma is determined by carefully examining the melanoma under a microscope and measuring it with a special tool. The thickness of a melanoma helps doctors decide on a treatment plan.
How is melanoma treated?
Immunotherapy for Melanoma Skin Cancer. Targeted Therapy Drugs for Melanoma Skin Cancer. Chemotherapy for Melanoma Skin Cancer. Radiation Therapy for Melanoma Skin Cancer.
What is the difference between a dermatologist and a radiation oncologist?
A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy. A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy.
What kind of doctor treats cancer?
Depending on your options, you may have different types of doctors on your treatment team. These doctors may include: 1 A dermatologist: a doctor who treats diseases of the skin 2 A surgical oncologist (or oncologic surgeon ): a doctor who uses surgery to treat cancer 3 A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy 4 A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
What is a radiation oncologist?
A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy. Many other specialists may be involved in your care as well, including physician assistants (PAs), nurse practitioners (NPs), nurses, psychologists, social workers, rehabilitation specialists, and other health professionals. Health Professionals Associated with Cancer Care.
What are the things to consider when making a decision about cancer treatment?
Some important things to consider include: Your age and overall health. The stage (extent) of your cancer.
What are the services offered by the American Cancer Society?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. The American Cancer Society also has programs and services – including rides to treatment, lodging, and more – to help you get through treatment.
What are the treatment options for melanoma?
Options include: Surgical removal of the melanoma. Immunotherapy. Targeted therapy. Chemotherapy. Radiation.
How to treat melanoma early?
Tumors discovered at an early stage are confined to the upper layers of the skin and have no evidence of spread. These melanomas are treated by excisional surgery. Usually, this is the only treatment required.
What is advanced melanomas?
Advanced melanomas are those that have spread beyond the original tumor, most often reaching the lymph nodes and/or distant organs and becoming more difficult to treat. In recent years, new immunotherapies and targeted therapies have achieved positive results in many patients with stage III and stage IV melanoma.
What to do if you have melanoma in your lymph node?
If melanoma is found in the sentinel node, your physician may examine the rest of the nodes in this lymphatic basin and remove any that contain cancer cells. After surgery, additional treatment may be recommended, including immunotherapy or radiation to decrease the chance that the melanoma will come back.
What is the use of immunotherapy to destroy cancer cells?
Pioneering breakthroughs in immunotherapy — the use of medicines to stimulate a patient’s immune system to destroy cancer cells — have led to significant progress in treating patients with advanced melanoma.
How long does it take for Mohs surgery to remove melanoma?
Surgeons may, under certain circumstances, recommend removal of melanoma by Mohs surgery. The procedure is done in stages over a few days to remove all of the cancer cells in layers while sparing healthy tissue and leaving the smallest possible scar.
Where is melanoma in situ?
Melanoma in situ (stage 0) is localized to the outermost layer of skin (the epidermis). Stage I melanoma has invaded the second layer of skin (the dermis). In both stage 0 and stage I melanoma cases, the physician uses a scalpel to remove any remaining tumor plus a “safety margin” of surrounding normal tissue.
How to treat skin cancer on nose?
Some of the best treatments for skin cancer on the nose and face include: Mohs Surgery: “Often considered the most effective way to treat skin cancer on the face or nose, Mohs Surgery allows doctors to perform small incisions only at the affected area to remove the cancerous cells, rather than having to cut away large sections ...
What is the second most common form of skin cancer?
Squamous Cells Carcinoma: The second most common form of skin cancer, squamous cells are a type of epithelial cell, found in the skin as well as tissues lining the body’s cavities, organs, and blood vessels.
How many people get skin cancer each year?
In the U.S., over three million people receive a non-melanoma skin cancer diagnosis each year, with rates of malignant melanoma, ...
Where does skin cancer manifest?
One of the more common areas where skin cancer manifests is the face, including the lips, cheeks, forehead, scalp, eyelids, and nose. These areas also prove challenging to treat. Three common types of skin cancer include:
Can you test skin during a face surgery?
Doctors can also test the remaining skin during the surgery to ensure no cancerous cells remain. Excision: This procedure requires the doctor to surgically cut out the cancer cells and may prove challenging to perform on areas of the face, where surgical margins can extend into cosmetic and functionally important anatomic areas.
Does skin cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Basel Cell Carcinoma: “The most common form of skin cancer, these growths do not usually spread to other parts of the body like malignant melanomas, but they can prove quite serious” says Dr. Mamelak. They may resemble open sores or pink bumps that just do not seem to go away.
Can melanoma spread to other organs?
Malignant Melanoma: Often the most aggressive form of skin cancer, malignant melanoma can spread quickly to other organs and should receive treatment immediately. “Each of these types of skin cancer can occur on the face, presenting unique challenges for treating the disease,” states Dr. Mamelak.
What does a doctor look for in a melanoma report?
The doctor is looking for cancer cells. What this doctor sees while looking at your tissue will be explained in the pathology report, including whether cancer cells were seen. If melanoma cells are seen, the report will include many important details, including: How deeply the melanoma tumor has grown into the skin.
What is the stage of melanoma?
Stages of melanoma. Stage 0. Also called melanoma in situ, this means the cancer occurs in the top layer of skin. Stage 1. The cancer is found only in the skin, but the tumor has grown thicker. In stage 1A, the skin covering the melanoma remains intact.
How do you know if you have skin cancer?
Having a skin biopsy is the only way to know for sure whether you have skin cancer. The tissue that your dermatologist removes will be sent to a lab, where a doctor, such as a dermatopathologist, will examine it under a high-powered microscope. The doctor is looking for cancer cells.
How thick is melanoma?
The melanoma has grown thick, with the thickness ranging from 1.01 millimeters to greater than 4.0 millimeters. While thick, the cancer has not grown deeper than the skin or spread to nearby skin. Stage 3. The melanoma has spread to either: • One or more nearby lymph node (often called a lymph gland) • Nearby skin.
What is the survival rate of melanoma?
Survival rate is “the percentage of people who will be alive within a certain time period, such as 5 years, after being diagnosed with a certain stage of melanoma. Each stage of melanoma has its own survival rate. Before you search for the melanoma survival rates, it’s important to keep the following facts in mind:
What is the procedure to remove cancer cells?
Removing some normal-looking skin helps to remove stray cancer cells. What your dermatologist removes will be looked at under a microscope. This time the doctor is looking for cancer cells in the normal-looking skin.
What is it called when you have a spot on your skin?
This can be done during an office visit and is called a skin biopsy. This is a simple procedure, which a dermatologist can quickly, safely, and easily perform.
Treatment by Stage
For patients with stage I and stage IA (≤1 mm thick, no ulceration, mitotic rate < 1/mm 2 with no adverse features) melanoma, treatment recommendations include wide-excision surgery
Treatment for Disease Progression Following Ipilimumab and BRAF Inhibitor Treatment
Treatment options for unresectable or metastatic melanoma and disease progression following ipilimumab treatment are as follows:
Oncolytic Immunotherapy
Talimogene laherparepvec (Imlygic) is a genetically modified oncolytic viral therapy indicated for the local treatment of unresectable cutaneous, subcutaneous, and nodal lesions in patients with melanoma recurrence after initial surgery {ref17}
What is the most common type of melanoma?
The most common type of melanoma is superficial spreading melanoma. It tends to spread across the surface of the skin, has uneven borders, and varies in color from brown to black, pink, or red. Nodular melanoma is another type that grows down into deeper layers of the skin and may appear as a raised bump or growth.
Why is my neck melanoma?
neck. face. This may be because these areas have more exposure to the sun than other parts of the body. Melanoma can form in areas that don’t receive much sun, such as the soles of your feet, palms of your hands, and fingernail beds. Sometimes, the skin will appear normal even though melanoma has begun to develop.
What is the name of the cancer that starts in skin cells?
Prevention. Outlook. Melanoma is a specific kind of skin cancer. It begins in skin cells called melanocytes. Melanocytes produce melanin, the substance that gives your skin color. Only about 1 percent of skin cancers are melanomas. Melanoma is also called malignant melanoma or cutaneous melanoma.
What is stage 3 melanoma?
Stage 3 melanoma has spread away from the primary tumor or into nearby lymph nodes. Wide-excision surgery is used to remove the tumor and affected lymph nodes. In stage 4 melanoma, cancer has spread to distant sites. The skin tumors and some enlarged lymph nodes can be surgically removed.
How do you know if you have melanoma?
Early signs and symptoms of melanoma are: changes to an existing mole. the development of a new, unusual growth on your skin. If melanoma cells are still making melanin, the tumors tend to be brown or black. Some melanomas don’t make melanin, so those tumors can be tan, pink, or white.
Where does metastatic melanoma occur?
Metastatic melanoma occurs when the cancer spreads, or metastasizes, to other parts of the body, possibly including the lymph nodes, organs, or bones. Other rare types of melanoma also exist, and while it most commonly affects the skin, some affect internal tissues, as well as the eyes.
How does radiation help with cancer?
Radiation can also help relieve symptoms of cancer that has metastasized. Isolated limb perfusion. This involves infusing only the affected arm or leg with a heated solution of chemotherapy.
How to prevent skin cancer on face?
Prevention. Your face is the most sun-kissed part of your body. Avoiding the sun (and other sources of UV light) is the best way to reduce your risk for skin cancers on the face (or anywhere!) It's best to avoid indoor tanning beds and extended sun sessions outside.
How to reduce skin cancer risk?
Sunscreen isn't the only way to lower your skin cancer risk. Try these tips: Wear medium-dark sunglasses. Look for glasses with large lenses in a wraparound style that curves in close to the face—the more coverage, the better. 50 Any lens that has 99 to 100% UV blocking is acceptable.
Where does sebaceous gland carcinoma occur?
SGCs can occur anywhere, but most occur on the upper and lower eyelids because they have the most sebaceous glands. They're often referred to as eyelid cancers .
What type of cancer is most common on the face?
Skin cancers that tend to occur more often on the face include actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. The face is also a common site of melanoma and there are several other lesser-common skin cancers that can affect the face. The risk of getting skin cancers on the face increases with high amounts ...
What is the most common type of skin cancer?
Basal cell carcinoma ( BCC) is the most common type of skin cancer. It is diagnosed in approximately 4 million people per year in the U.S. and makes up about 80% of non-melanoma skin cancers. 13 They're common on the head and neck but can happen anywhere. Most cases can be treated and cured.
Why is my face cancer?
Because it is exposed to the sun more than other parts of the body, the skin on your face is especially vulnerable to skin cancer. And skin cancer on the face can be mistaken for other conditions—such as age spots, pimples, scarring, acne, styes, and cysts. Skin cancers that tend to occur more often on the face include actinic keratosis, ...
What are the risk factors for melanoma?
Risk factors for melanoma include: 22. Fair skin, freckles, light hair, and eyes; a tendency to burn instead of tan (melanoma is 20 times more common in Whites) 20.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
Treatment
- The best treatment for your melanoma depends on the size and stage of cancer, your overall health, and your personal preferences.
Terminology
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Prevention
- A cancer diagnosis can change your life forever. Each person finds his or her own way of coping with the emotional and physical changes cancer brings. But when you're first diagnosed with cancer, sometimes it's difficult to know what to do next. Here are some ideas to help you cope: 1. Learn enough about melanoma to make decisions about your care.Ask your doctor about your c…
Medical uses
- Start by seeing your family doctor if you notice any skin changes that concern you. Depending on your situation and the outcome of any tests, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in skin diseases (dermatologist) or to a doctor who specializes in cancer treatment (oncologist). Because appointments can be brief, and because there's often a lot to discuss, it's a good idea t…
Prognosis
- The first step in treatment is removal of the primary melanoma tumor, and the standard method of doing this is by surgical excision (cutting it out). Surgery has made great advances in the past decade, and much less tissue is removed than was customary in the past. Patients do just as well after the lesser surgery, which is easier to tolerate and p...
Benefits
- Surgical excision is also called resection, and the borders of the entire area excised are known as the margins.
Research
- Discolorations and areas that are depressed or raised following the surgery can be concealed with cosmetics specially formulated to provide camouflage. If the melanoma is larger and requires more extensive surgery, a better cosmetic appearance can be obtained with flaps made from skin near the tumor, or with grafts of skin taken from another part of the body. For grafting, the skin i…
Advantages
- Surgical excision is also called resection, and the borders of the entire area excised are known as the margins. Surgical excision is used to treat all types of skin cancer. At its best given an experienced surgeon and a small, well-placed tumor it offers results that are both medically and cosmetically excellent.
Clinical significance
- Wounds heal rapidly, usually in a week or two. Scarring depends on many factors, including how the tumor is situated and the patient's care of the wound after the procedure.
Example
- In the new approach to surgery, much less of the normal skin around the tumor is removed. The margins are therefore much narrower than they were in the past. This spares significant amounts of tissue and reduces the need for postoperative cosmetic reconstructive surgery. Mohs surgery differs from other techniques since the microscopic examination of all excised tissues during th…