What is MLE and how does it work?
The MLE process takes advantage of the carbon found in the influent waste stream to avoid the use of other carbon sources like methanol or acetate that must be purchased. Many utilities are modifying their disinfection method to eliminate the storage, use and handling of 100 percent gaseous chlorine.
What is MLE process flow scheme?
The MLE process flow scheme is a popular treatment method for nitrogen removal and can be found as separate unit processes or as a part of the Carrousel/oxidation ditch process using pre-denitrification. Nitrification takes place in the aeration basins that follow the anoxic tanks, and nitrate-rich MLSS is pumped...
What is the difference between denitrification and Mle?
Denitrification of the nitrate takes place with the addition of influent wastewater containing carbon, the nitrate recycle stream and the return sludge from the clarifiers. The MLE process takes advantage of the carbon found in the influent waste stream to avoid the use of other carbon sources like methanol or acetate that must be purchased.
What is membrane bioreactor wastewater treatment?
Membrane bioreactors are a unique wastewater treatment process designed for municipal and industrial uses. They are a combination of a membrane process, like microfiltration or ultrafiltration, with a suspended-growth bioreactor.
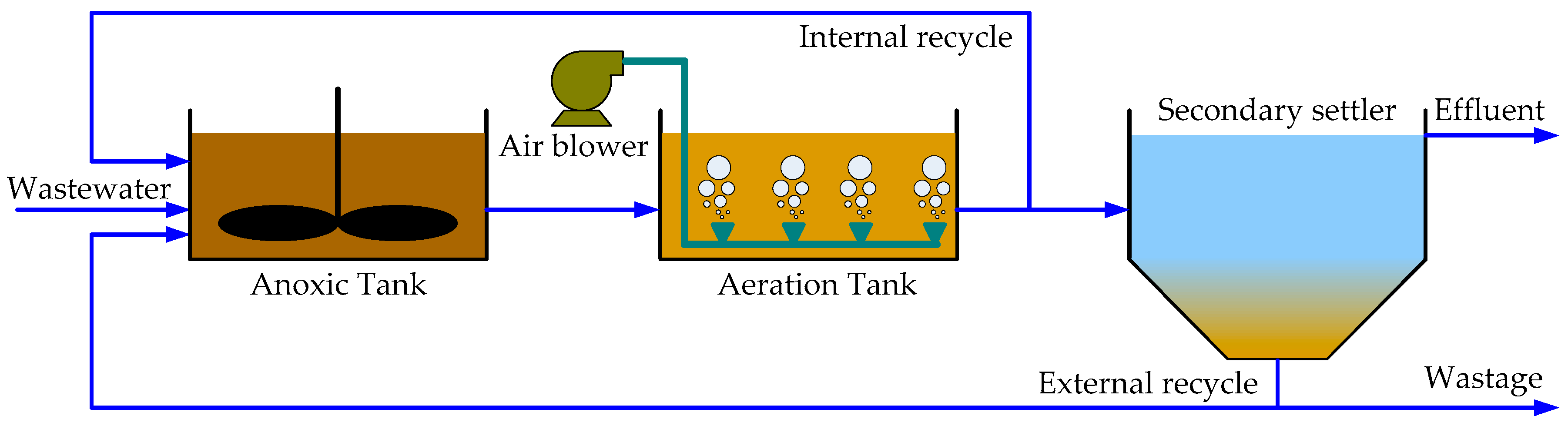
What is MLE wastewater treatment process?
The MLE process consists of modifying a conventional activated sludge process by creating or adding an anoxic zone upstream of the aerobic zone. An internal recycle pump system returns nitrate-rich mixed liquor created in the nitrifying aerobic zone to be mixed with the influent in the anoxic zone.
What is extended aeration activated sludge?
The extended aeration process is one modification of the activated sludge process which provides biological treatment for the removal of biodegradable organic wastes under aerobic conditions. Air may be supplied by mechanical or diffused aeration to provide the oxygen required to sustain the aerobic biological process.
What is high rate activated sludge?
Abstract. The high-rate activated sludge (HRAS) process is a technology suitable for the removal and redirection of organics from wastewater to energy generating processes in an efficient manner.
What is step feed aeration?
A modification of the conventional activated sludge process. In step-feed aeration, primary effluent enters the aeration tank at several points along the length of the tank, rather than at the beginning or head of the tank and flowing through the entire tank in a plug flow mode.
What is FM ratio wastewater?
The F/M ratio is a process control number that helps you to determine the proper number of microorganisms for your system. To do this calculation, you will need the following information: Influent Flow into your activated sludge system (Flow MGD) Influent CBOD (mg/l) concentration into your aeration tank.
What is MLSS concentration?
MLSS are the concentration of suspended solids in mixed liquor, usually expressed in grams per litre (Wateronline, 2011).
What is the difference between Step feed and step aeration?
Step Feed Activated Sludge - The Step feed process (sometimes called Step Aeration) is a modification of the activated sludge process in which sewage is introduced at two or more points in the aeration tank while return sludge is introduced only at the head end of the aeration tank.
What is contact stabilization?
A modification of the conventional activated sludge process that uses two aeration tanks. One tank is for separate reaeration of the return sludge for at least four hours before it is permitted to flow into the other aeration tank to be mixed with the primary effluent requiring treatment.
What is complete mix activated sludge?
Complete mixing activated sludge systems are those activated sludge systems where the incoming wastes are uniformly mixed with the activated sludge to maintain all suspended solids in suspension with a uniform oxygen uptake rate throughout the entire aeration tank and a mini- mum dissolved oxygen concentration of 0.5 ...
How does MLE work?
The MLE process consists of modifying a conventional activated sludge process by creating or adding an anoxic zone upstream of the aerobic zone. An internal recycle pump system returns nitrate-rich mixed liquor created in the nitrifying aerobic zone to be mixed with the influent in the anoxic zone. The amount of nitrates potentially removed in the anoxic zone depends on the recycle flow and availability of influent BOD.
What is MBR treatment?
MBR treatment plants can produce a consistent, high-quality effluent that is excellent for public access reuse, urban irrigation and other reclaimed water uses. It is also suitable for discharge to coastal, surface or brackish waterways. 4. Sequencing Batch Reactors (SBR)
What is IFAS in wastewater treatment?
IFAS technology is the first process specifically designed for ideal operation in municipal wastewater treatment/activated sludge processes . Typically, IFAS is a retrofit solution for conventional activated sludge systems that are at or beyond capacity, providing minimal plant downtime, zero facility construction and optimization of existing equipment.
What is MBBR process?
The MBBR process uses thousands of polyethylene biofilm carriers operating in mixed motion within an aerated wastewater treatment basin. Each biocarrier provides a protected surface area to support the growth of bacteria; the high-density bacteria population, in turn, helps achieve high-rate biodegradation within the system, thus supporting BOD reduction, nitrification and total nitrogen removal.
What is a membrane bioreactor?
Membrane bioreactors are a unique wastewater treatment process designed for municipal and industrial uses. They are a combination of a membrane process, like microfiltration or ultrafiltration, with a suspended-growth bioreactor.
Is aerated wastewater mixed with RAS?
In the anaerobic zone , only RAS from the clarifiers and influent wastewater are mixed, not aerated. Bacteria called phosphate-accumulating organisms (PAOs) compete for the available carbon, but must release their molecules of polyphosphate from their own cells to allow for the food to be taken into the cell.
Oxidation Reduction Potential (ORP)
Measuring the oxidation reduction potential (ORP) is such an easy, insightful test to perform, it’s a shame this poorly understood parameter is so underutilized. Of course, it’s that very lack of understanding that leaves ORP testing hidden away in the shadows.
ORP Measurements In the Field
When I measure the oxidation-reduction potential at a wastewater plant I like to present the data as shown in the graphic below. This simple bar graph communicates a lot, easily and quickly, letting you know at a glance if there are any potential problems.
Rotary Disk Aerator
The charts and table on this page may be a little difficult to read. If you click here (or on any of the graphics above) you can open up a PDF for easier viewing/printing.
Recommended ORP Document Downloads
1. " Black magic can work wonders for wastewater treatment " from Hach wastewater specialist Mr. Bob Dabkowski.
