
Why choose carburizing heat treat?
Our superior quench and process controls enable the parts we heat treat (and not just the test pieces) to exceed the increasingly demanding property requirements of modern manufacturing. The carburizing heat treatment process for machined parts and stampings starts with austenitizing the heat-treat load in a controlled, carbon-rich atmosphere.
What type of Furnace is used for carburizing heat treatment?
All cycles for carburizing heat treatment of machined parts and stampings are run in one of our numerous batch-type furnaces. These furnaces allow for optimum process and lot control.
What is carburizing?
Carburizing also referred to as Case Hardening, is a heat treatment process that produces a surface that is resistant to wear, while maintaining the toughness and strength of the core. This treatment is applied to low carbon steel parts after machining, as well as high alloy steel bearings, gears, and other components.
What is the temperature of carburizing?
Gas carburizing is normally carried out at a temperature within the range of 900 to 950 °C. In oxy-acetylene welding, a carburizing flame is one with little oxygen, which produces a sooty, lower-temperature flame. It is often used to anneal metal, making it more malleable and flexible during the welding process.

What is carburizing and how it is done?
Carburization is a process which involves taking a low carbon steel and transforming it into a high carbon steel. This is done by exposing it to an atmosphere which is dense in carbon. Generally, items are carburized in furnaces, vats, and other enclosed entities.
Why is carburizing used?
Carburization can be used to increase the surface hardness of low carbon steel. Early carburization used a direct application of [(charcoal)] packed around the sample to be treated (initially referred to as case hardening), but modern techniques use carbon-bearing gases or plasmas (such as carbon dioxide or methane).
What is the difference between hardening and carburizing?
Case hardening is the process of hardening just the surface of the part. It is also known as carburizing. In the carburizing process, the low carbon component is placed in a furnace which contains a carefully controlled carbon atmosphere.
What is the carburizing temperature?
870 to 940 °CThe carburizing furnaces are either gas fired or electrically heated. The carburizing temperature varies from 870 to 940 °C the gas atmosphere for carburizing is pro- duced from liquid or gaseous hydrocarbons such as propane, butane or methane3.
What is the procedure for carburising?
The process of carburizing involves the use of heat, where steel or iron absorbs a liberal amount of carbon. This takes place as the metal undergoes heating with the presence of materials that contain carbon, like carbon monoxide and charcoal. The purpose of this process is to make the metal harder and manageable.
What are the three types of carburizing?
There are three types of carburising commonly used:gas carburising.liquid carburising (or cyaniding)solid (pack) carburising.
Why is carburizing better than nitriding?
Carburizing economically imparts a hard surface improving wear as well as increases the fatigue strength. An advantage of carburizing is the ability to impart deep cases, up to 0.300″ which is especially useful for very large gears, such as those used for steel rolling mill applications.
Which is better carburizing or nitriding?
Nitriding can be done at lower temperatures than carburizing. The diffusion of nitrogen gas normally occurs at low temperatures, and hardening occurs without quenching. Only the surface is hardened, the core remains the same. When a steel has undergone Nitriding process, it has excellent wear resistance.
What is Carburizing?
Carburizing is a case hardening process in which carbon diffuses into the surface layer of a steel part at a temperature high enough to change the steel grain structure. This change enables the steel to absorb carbon. The result is a wear-resistant layer that makes carburizing an ideal process in the production of strong, safe metals.
Method of Carburization
Carburization of steel involves heat treatment of the metallic surface using a source of carbon. Carburization can be used to increase the surface hardness of low carbon steel. Early carburization used a direct application of charcoal packed around the sample to be treated, but modern techniques use carbon-bearing gases or plasmas.
Types of Carburizing
In the past, depending on the carbon source, there were three types of carburizing methods: solid carburizing, liquid carburizing, and gas carburizing. Charcoal, molten salt, and carbon-containing gases such as natural gas and propane are used accordingly.
What is a carburizing furnace?
Carburising, carburizing (chiefly American English), or carburisation is a heat treatment process in which iron or steel absorbs carbon while the metal is heated in the presence of a carbon-bearing material, such as charcoal or carbon monoxide. The intent is to make the metal harder.
What is carburization used for?
Carburization can be used to increase the surface hardness of low carbon steel. Early carburization used a direct application of charcoal packed around the sample to be treated (initially referred to as case hardening ), but modern techniques use carbon-bearing gases or plasmas (such as carbon dioxide or methane ).
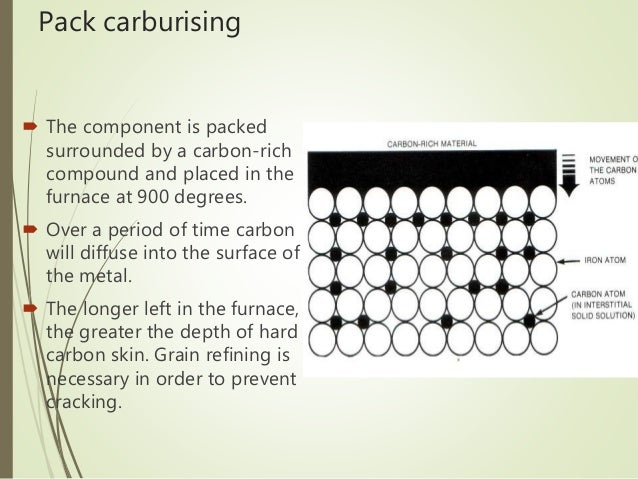
What is a pack carburizing container?
In pack carburizing, the workpiece and carbon are enclosed in a container to ensure that contact is maintained over as much surface area as possible. Pack carburizing containers are usually made of carbon steel coated with aluminum or heat-resisting nickel-chromium alloy and sealed at all openings with fire clay.
What are the advantages of carburizing over carbonitriding?
Also the advantages of carburizing over carbonitriding are greater case depth (case depths of greater than 0.3 inch are possible), less distortion, and better impact strength. This makes it perfect for high strength and wear applications (e.g. scissors or swords).
What is gas carburizing?
In general, gas carburizing is used for parts that are large. Liquid carburizing is used for small and medium parts and pack carburizing can be used for large parts and individual processing of small parts in bulk. Vacuum carburizing (low pressure carburizing or LPC) can be applied across a large spectrum of parts when used in conjunction with either oil or high pressure gas quenching (HPGQ), depending on the alloying elements within the base material.
What is the process of absorbing carbon?
Carburizing. Not to be confused with carbonization, carburation, or carbonation. Carburising, carburizing (chiefly American English), or carburisation is a heat treatment process in which iron or steel absorbs carbon while the metal is heated in the presence of a carbon-bearing material, such as charcoal or carbon monoxide.
How does carbon harden steel?
If the carbon remains in solid solution, the steel is then heat treated to harden it. Both of these mechanisms strengthen the surface of the metal, the former by forming pearlite or martensite, and the latter via the formation of carbides. Both of these materials are hard and resist abrasion.
Why is heat treatment of carburized steel so complicated?
Thus, the heat treatment of a carburised steel is complicated because, in the same piece, the carbon content varies. Still, heat treatment can be given to obtain desired results based on metallurgical principles learnt so far.
What temperature is carburized steel heated to?
Slowly cooled carburised steel is heated to above Ac 3 /A cm (whichever is higher) temperature (grain size of core is refined and cementite network is dissolved and shall be eliminated), and then quenched.
What temperature is carburising gas?
Gas carburising temperature of 900-940°C, is used to obtain required case depth with a surface carbon of 0.7-0.8%. Then temperature of furnace (or parts) is decreased to 830°C to then quench in suitable quenching medium.
What is sub zero treatment?
Sub-zero treatment is often applied to hardened carburised components, specially of those alloy steels which retain large amount of austenite. This not only improves hardness and wear resistance but also gives dimensional stability to parts. Sub-zero treatment is done immediately after quenching before stabilisation of austenite occurs.
What is the cheapest method of heat treatment?
Three heat treatments can be given. The cheapest and the simplest method are to quench directly from the carburising temperature. The hardened case shall have less hardness because; of large amount of retained austenite obtained and the absence of proeutectoid cementite (cementite is slightly more hard than martensite.
Why are carburetor parts heat treated?
Carburised parts are generally heat treated for following reasons: 1. To develop hard and wear resistant surfaces. 2. The long lime and high temperatures during carburising may cause grain coarsening in core and or case. These may be refined to improve their properties like impact strength, etc. 3.
Does carburising cause cracks?
If carburising has resulted in cementite network at the surface, it induces brittleness to cause cracks even during grinding. It has to be broken, if possible. To improve the wear resistance and hardness, the carburised components are quenched from the austenitic range. The component may cither be quenched from the carburising temperature, ...
What is carburizing steel?
Carburization is a process which involves taking a low carbon steel and transforming it into a high carbon steel. This is done by exposing it to an atmosphere which is dense in carbon. Generally, items are carburized in furnaces, vats, and other enclosed entities. By heating a steel item in a carbon-dense atmosphere, ...
What is liquid carburization?
Liquid carburization is a form of carburization which takes place in a sort of liquid vat. This vat is filled with a mixture of substances, typically including cyanide and salt.
Why is high temperature important for carburizing steel?
High temperatures allow carbon molecules to diffuse into the steel items which are being hard cased. One of the most popular carburization processes in the world, it consistently produces a uniformly-carburized steel. This makes it very useful for mass carburization purposes.
Why is carburized steel good?
Another major benefit of carburized steel is that it possesses a soft interior. Because it possesses a soft interior, it's easy to manipulate into different shapes. This makes it especially useful for when you're trying to manufacture intricate metal items with hard surfaces (ie. internal machine components).
How many different types of carburization are there?
There is not just one carburization process available. In fact, generally, there are four different types of carburization used. Each different process offers its own advantages and disadvantages. The four processes are as follows:
What is case hardening?
Case hardening is a process which involves adding a hard, protective shell to the outside of an otherwise soft steel. This process allows for intricately shaped metals to possess a strength and toughness that they otherwise wouldn't be able to possess. One of the most sophisticated and common forms of case hardening is carburizing.
Do carburized steels have soft interiors?
However, they don't provide the internal softness needed to be intricately shaped and formed. In essence, they don't provide the coveted combination of soft interior and hard exterior which is provided by carburized steel.
How does carburizing steel work?
Carburizing is the process of hardening steel by exposing it to carbon while the metal is being heated. The addition of carbon to the surface of the steel changes the chemistry and makes it more responsive to heat treatment while maintaining a softer and more ductile core hardness. The carbon is only absorbed at exposed surfaces, and the depth of penetration is proportional to the time in the furnace – hence the term case hardened. Case Hardening does create the potential for a harder steel than other hardening methods, but deep cases can take more time and be very expensive.
How does heat treatment work?
Heat treatment is used to alter the physical properties of a material – typically to increase the strength and wear characteristics of a chain while maintaining adequate toughness and ductility for the application. Heat treatment involves the use of heating, rapid cooling (quenching), and sometimes even chilling components to extreme temperatures to achieve a desired result.#N#All metals consist of a certain microstructure. The molecules shift positions when heated. When the metals are quenched, the molecules stay in a new microstructure with increased hardness levels and the desired increase in the strength and wear resistance of the components. The components of the chain are heat treated separately prior to assembly, which facilitates setting the target properties for each component to their ideal state. There are many different heat treatments methods that are used to tailor the hardness level and depth. The three most common methods of heat treatment for chain components are:
What is induction hardening?
Induction Hardening is used to harden specific sections of a part instead of the entire unit. While heat treating is an effective, and critical, way to increase the quality of your chain there are many other manufacturing processes such as stamping, bending and interference fits that are required to make a high quality and long-lasting chain.
What is chain heat treatment?
The 3 Most Common Chain Heat Treatment Practices. Heat treatment is used to alter the physical properties of a material – typically to increase the strength and wear characteristics of a chain while maintaining adequate toughness and ductility for the application.
What is hardening steel?
Through Hardening is a process of heating, quenching, and tempering the part. This process hardens and strengthens the materialevenly throughout the entire section of the part, unlike some methods which just harden the outer layer. The outcome is tempered steel that is harder and stronger, but still has adequate ductility and toughness.
Overview
Carburising, carburizing (chiefly American English), or carburisation is a heat treatment process in which iron or steel absorbs carbon while the metal is heated in the presence of a carbon-bearing material, such as charcoal or carbon monoxide. The intent is to make the metal harder. Depending on the amount of time and temperature, the affected area can vary in carbon content. Longer ca…
Method
Carburization of steel involves a heat treatment of the metallic surface using a source of carbon. Carburization can be used to increase the surface hardness of low carbon steel.
Early carburization used a direct application of [(charcoal)] packed around the sample to be treated (initially referred to as case hardening), but modern techniques use carbon-bearing gases or plasmas (such as carbon dioxide or methane). The process depends primarily upon ambient g…
Hardening agents
There are different types of elements or materials that can be used to perform this process, but these mainly consist of high carbon content material. A few typical hardening agents include carbon monoxide gas (CO), sodium cyanide and barium carbonate, or hardwood charcoal. In gas carburizing, carbon is given off by propane or natural gas. In liquid carburizing, the carbon is derived from a molten salt composed mainly of sodium cyanide (NaCN) and barium chloride (Ba…
Geometrical possibilities
There are all sorts of workpieces that can be carburized, which means almost limitless possibilities for the shape of materials that can be carburized. However careful consideration should be given to materials that contain nonuniform or non-symmetric sections. Different cross sections may have different cooling rates which can cause excessive stresses in the material and result in breakage.
Workpiece material
Typically the materials that are carbonized are low-carbon and alloy steels with initial carbon content ranging from 0.2 to 0.3%. The workpiece surface must be free from contaminants, such as oil, oxides, or alkaline solutions, which prevent or impede the diffusion of carbon into the workpiece surface.
Comparing different methods
In general, pack carburizing equipment can accommodate larger workpieces than liquid or gas carburizing equipment, but liquid or gas carburizing methods are faster and lend themselves to mechanized material handling. Also the advantages of carburizing over carbonitriding are greater case depth (case depths of greater than 0.3 inch are possible), less distortion, and better impact strength. This makes it perfect for high strength and wear applications (e.g. scissors or swords)…
Choice of equipment
In general, gas carburizing is used for parts that are large. Liquid carburizing is used for small and medium parts and pack carburizing can be used for large parts and individual processing of small parts in bulk. Vacuum carburizing (low pressure carburizing or LPC) can be applied across a large spectrum of parts when used in conjunction with either oil or high pressure gas quenching (HPGQ), depending on the alloying elements within the base material.
See also
• Carbonitriding
• Case hardening
• Cementation process
• Crucible steel
• Harvey armor (also known as Harveyized steel), an early application of carburizing