Natural Ways to Get Rid of Knee Pain When Straightening Leg after Sitting
- Hydration. It is important to drink plenty of water and fluids to flush out toxins from the body and keep yourself well hydrated.
- Diet. It is important to maintain a well-balanced, healthy diet. ...
- Exercise. This is important to maintain joint mobility. ...
- Limb Elevation. ...
- Ice Packs. ...
- Anti Inflammatory Foods. ...
- Magnesium. ...
What causes pain behind the knee on back of leg?
Feb 27, 2021 · This can include: Switching to low-impact exercise: Cycling and swimming can put less stress on the knee joints than running or tennis. Physical therapy: This can help to increase a person’s range of motion, flexibility, and strength in the legs. Pain medication: NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, and ...
Why does my knee hurt when I straighten it?
Back of knee pain when straightening leg is a common problem for runners. The most likely cause of this is iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS). ITBS occurs when the IT band becomes tight and rubs on bone or bursa in the area, causing inflammation and pain. This happens because, over time, repetitive movements like running can lead to the shortening of muscles and tendons which …
What can cause pain below knee cap without injury?
Apr 12, 2022 · Running injuries, such as back of knee soreness when straightening leg, are prevalent among athletes. The iliotibial band syndrome is the most likely cause of this problem (ITBS). Inflammation and discomfort are caused when the IT band becomes too tight and pushes on the bone or bursa in the area, causing it to become inflamed.
What is causing pain on the inside of my knee?
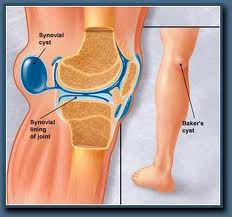
Feb 15, 2022 · Baker’s cyst – fluid build-up behind your kneecap that causes pain when straightening out your leg because there is extra pressure placed onto this area due to gravity pulling down on whatever weight-bearing structure you have underneath the patellar tendon such as cartilage or a meniscus tear.
How do you relieve pain behind the knee?
Rest, ice, compression, and elevation If you have sudden, intense pain in the back of your knee, the doctor may recommend that you rest and apply ice to your knee. In some cases, your doctor may also ask you to elevate (prop up) your leg while you're sitting down to help improve the blood flow in your leg.Jan 26, 2021
Why does the back of my knee hurt when I straighten?
A swelling at the back of the knee and calf causing pain, and a feeling of tightness when straightening the leg. This may be due to a Baker's Cyst, which is an accumulation of synovial fluid in the popliteal fossa. The synovial fluid is over-produced, due often to a trauma to the knee or in conditions such as arthritis ...Oct 16, 2018
How long does it take for the back of your knee to heal?
For knee sprains or strains, the healing time is typically 2 to 4 weeks. For major injuries as a result of trauma, it can take from 4 up to 12 months.Jan 31, 2020
Why does the back of my leg hurt behind the knee?
Damage to a muscle, tendon, ligament, or other connective tissue could cause posterior knee pain. Such injuries can be acute or caused by overuse. Hamstring injuries, meniscus tears, and injuries to the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) are three injuries that may cause pain in the back of the knee.Feb 9, 2022
Should I be worried about pain behind knee?
If you experience severe pain and swelling behind the knee, then you must see your doctor. Sometimes, large Baker's cysts can become painful. Other causes include DVT or popliteal aneurysms.
What is back of leg behind knee called?
Pain in the back of the knee, called the popliteal fossa, is common, but there is a wide range of causes, ranging from ligament injury to arthritis.
How do you know if you tore something behind your knee?
Swelling or stiffness. Pain, especially when twisting or rotating your knee. Difficulty straightening your knee fully. Feeling as though your knee is locked in place when you try to move it.Jan 6, 2022
How do I know if I tore a ligament in my knee?
What Does a Knee Ligament Injury Feel Like?Pain, often sudden and severe.A loud pop or snap during the injury.Swelling within the first 24 hours after the injury.A feeling of looseness in the joint.Inability to put weight on the joint without pain, or any weight at all.Nov 26, 2020
How long does a baker's cyst last?
A Baker's cyst usually goes away on its own, but it can take months or even years.Oct 28, 2009
Underlying Problems With Back Of Knee Pain When
There are many underlying problems that can cause knee pain. This is especially true with the back of the knee pain which can be caused by many different things. It’s important to go to a doctor and find the root of the problem so you can begin treating it right away. The longer you wait, the worse things might get!
Treatment Options For Back Of Knee Pain
There are some at-home treatment plans that you can try which may help to reduce your back knee pain.
Steps Doctors Usually Take To Treat Back Of Knee Pain
If you want to know in advance the treatment plan most doctors will take if you are experiencing then knee pain, then keep reading. A doctor will first find out if the knee pain is part of a larger existing health condition, such as arthritis.
Final Thoughts
When it comes to knee pain, the cause is often not as simple as one thinks.
Change of Swelling in the Knee
One of the most common causes of pain and stiffness with knee extension that we see is due to swelling after an acute injury.
Meniscus Tear
Another common cause of pain with straightening the knee is a meniscus tear. There are two crescent-shaped discs called Menisci in between the Femur and Tibia (thigh bone and lower leg) on each leg.
Knee Osteoarthritis
Pain from Osteoarthritis is common with knee extension. Osteoarthritis is the wear and tear of the joint over time. Once you have arthritis it can limit your ability to straighten and bend the knee.
Chondromalacia
Chondromalacia is wear and tear underneath the kneecap that results in a loss of articular cartilage. There may be pain with knee extension as the kneecap moves up and down within the groove on the Femur and with activities such as stairs or squatting.
Patella Bursitis
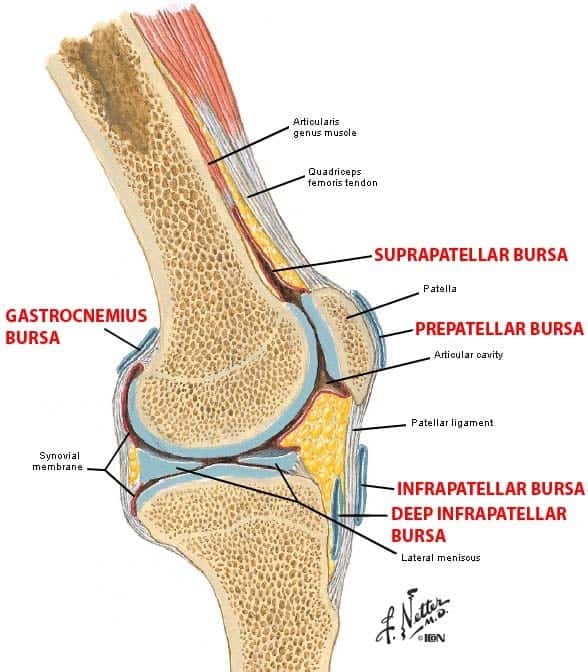
Bursitis is an inflammation of the bursa sacs in and around the knee. Many different pain patterns can occur with this problem including pain behind or under the kneecap but often the pain will get worse as you try to straighten your leg out. This can also be aggravated by kneeling on the knee or with forceful muscle use such as squats or lunges.
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
Patellofemoral pain syndrome is pain over the front of the knee cap. It can be aggravated by activities such as stairs or squatting and usually produces pain that’s worse with activity, especially when going upstairs. It’s the result of too much force over a certain period of time on the patella.
Patella Tendonitis
Patella Tendonitis presents as pain at the Patellar Tendon where it attaches to the Tibia. It’s often aggravated by activities such as stairs, squatting, and jumping. It may feel like a sharp pain below your knee cap.
What to do if your knee hurts after a knee replacement?
But, in any case, it’s best to go to a physical therapist or a doctor so you can get back to your daily activities as soon as possible. Book an appointment with your doctor if the pain started after a knee injury or if you have previous health conditions like diabetes, knee OA, or gout.
How to treat knee instability?
Knee joint instability. Treatment includes physical therapy, weight management, and a strength training regime. The goal of these methods is to delay the progression of arthritis. On the other hand, severe cases may require knee replacement surgery.
What causes knee pain?
1) Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS) This is the most common cause of knee pain with studies suggesting 25-40% of active people suffering from it. ( 2, 3) PFPS is also known as “runner’s knee”, but it can affect anyone – not just runners.
What is the most common knee injury?
Chondromalacia patellae is another common knee injury that’s present in approximately 20% of people with PFPS. It’s also more common in women than men. ( 3) It happens when the cartilage behind the kneecap gets damaged due to wear and tear.
How to treat patellofemoral pain?
Generally, the best treatment for patellofemoral pain syndrome includes rest, physical therapy, and wearing appropriate knee braces. These are usually effective at reducing time spent away from sports.
What is the term for a sac filled with fluid that reduces friction between tendons and bones, helping them move
4) Knee bursitis. A bursa is a sac filled with fluid that reduces friction between tendons and bones, helping them move better. Bursitis happens when this sac gets swollen or inflamed. And, since there are multiple bursae in your knee, there are also several types of bursitis.
How to prevent knee injury?
You’ll be more susceptible to knee injuries if your leg muscles are weak because they won’t be able to: Stabilize your knee when you’re walking, exercising, or doing your daily activities. Control the kneecap and keep it in its place. Protect your ligaments, tendons, and other tissues.
Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) injury
The posterior cruciate ligament, located in the back of the knee, is responsible for holding the knee in place and providing stability to the joint. It helps keep the shinbone from moving too far backward.
Treatment
Treatment can include rest, ice, compression, and elevation, using knee braces to stop the knee from moving, and physical therapy.
Treatment
Rest, anti-inflammatory painkillers, flexibility training, and physical therapy can be successful treatments for tendinopathy.
Biceps femoris tendinopathy
Biceps femoris tendinopathy affects the biceps femoris tendon in the hamstrings.
Treatment
Physical therapy, cold packs, and resting the affected knee can all help to treat biceps femoris tendinopathy.
Chondromalacia
Chondromalacia patella is when the cartilage underneath the kneecap breaks down. This means that when a person uses the knee joint, there is no cushioning between the kneecap and the thigh bone, which causes friction.
Arthritis
According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS), the most common types of arthritis are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
What is the best treatment for knee pain?
The best first-line treatment for posterior knee pain is a combination of rest, physical therapy, and over-the-counter NSAID medications like ibuprofen. If pain persists, stronger medications like prescription NSAID topicals may be useful. For the most extreme cases, injections or surgery may be a consideration.
Why does my knee hurt?
The knee will appear swollen and bruised ( 30 ). In rare cases, posterior knee pain may indicate a cancerous bone tumor, such as a tumor caused by osteosarcoma. This kind of cancer can affect anyone, including younger people, and is characterized by a tender knee and the presence of a protruding mass.
What age is a risk factor for knee pain?
Older age is a risk factor ( 16, 17 ). Signs of this condition include swelling in the knees or thighs, knee pain that extends up to the thigh and hip, and trouble with bending the knee. Pain increases with movement ( 17 ). .
How to relieve knee pain from overuse?
You should limit your physical activity if this is the case. Apply ice to your knee in 15 to 20-minute increments, several times a day, and use an elastic band to compress the area.
What causes knee pain?
The two forms of arthritis most likely to cause knee pain are osteoarthritis (OA), which gradually wears down the joint cartilage, and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), an autoimmune disease in which the body mistakenly attacks the joints, are most likely to cause posterior knee pain ( 4, 5, 6 ).
What is the tear on the outside of the knee?
Torn Meniscus. Meniscal tears account for a majority of knee injuries. Each knee has two menisci: the U-shaped medial meniscus, located on the inside of the knee, and the S-shaped lateral meniscus, on the outside of the knee. Tears form when the knee forcefully twists or turns.
What joint is the knee joint?
For some context, the knee is a joint consisting of the tibia (shinbone), femur (thighbone), and the patella (kneecap).