
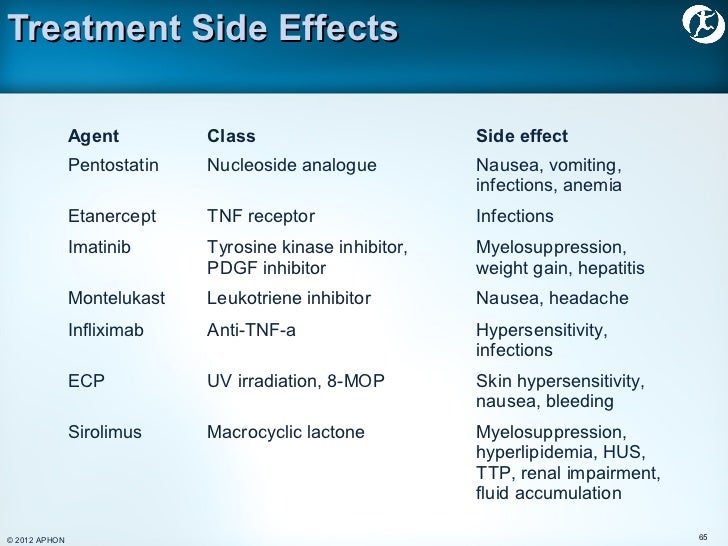
Long-term side effects can include:
- Breast changes: The breasts may shrink or become more dense after radiation. Some women have reported problems breastfeeding.
- Brachial plexopathy: Radiation to the breast or chest wall can sometimes damage the nerves that run through the arm, wrist, and hand. ...
- Lymphedema: Lymphedema is swelling of the arm, hand, or chest. ...
How soon might you get side effects from radiation therapy?
The side effects of radiation therapy depend on the area of the body that receives radiation. Early side effects happen shortly after you receive radiation therapy. Late side effects can happen months to years after you receive radiation therapy. Late side effects of radiation therapy may be permanent.
How long does it take to recover from radiation treatment?
The general effects of radiation therapy like fatigue, nausea, and headaches resolve fairly quickly after treatment. Your body just needs time to process the radiation but can recover within a few weeks. Delayed side effects of radiation therapy, on the other hand, may require further treatment to alleviate.
What are the negative effects of radiation therapy?
- Diarrhea
- Hair loss in the treatment area
- Mouth changes such as soreness, dryness and difficulty swallowing (if radiation to head and neck area)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sexual impact (tenderness and soreness of genital organs if radiation to this area)
- Blood count changes
How long does radiation stay in your body after treatment?
How Long Does Radiation Stay in the Body? Radiation does not stay in the body after the treatments have ended and will not be able to stay in the body unless there is a radioactive device implanted into the cancerous parts of the body. After receiving radiation, a person will not be radioactive. Radiation has been used in the medical field as a ...
What is a potential long-term side effect of radiation therapy?
you might have permanent hair loss within the treated area. you might develop red spidery marks on your skin (telangiectasia) caused by small broken blood vessels. drainage channels to the arms or legs can become partly blocked resulting in swelling called lymphoedema.
Can you fully recover from radiation?
Radiation not only kills or slows the growth of cancer cells, it can also affect nearby healthy cells. The healthy cells almost always recover after treatment is over. But sometimes people may have side effects that are severe or do not get better.
How long does radiation stay in your body after treatment?
For most people, the cancer experience doesn't end on the last day of radiation therapy. Radiation therapy usually does not have an immediate effect, and it could take days, weeks or months to see any change in the cancer. The cancer cells may keep dying for weeks or months after the end of treatment.
What are some long-term effects of radiation?
Exposure to very high levels of radiation, such as being close to an atomic blast, can cause acute health effects such as skin burns and acute radiation syndrome (“radiation sickness"). It can also result in long-term health effects such as cancer and cardiovascular disease.
What are the worst side effects of radiotherapy?
Treatment areas and possible side effectsPart of the body being treatedPossible side effectsHead and NeckFatigue Hair loss Mouth problems Skin changes Taste changes Throat problems, such as trouble swallowing Less active thyroid gland6 more rows•Jan 11, 2022
Do tumors grow back after radiation?
Normal cells close to the cancer can also become damaged by radiation, but most recover and go back to working normally. If radiotherapy doesn't kill all of the cancer cells, they will regrow at some point in the future.
What is the most common acute side effect of radiation treatment?
Fatigue is the most common acute side effect of radiation therapy. It is believed to be caused by the large amount of energy that is used by the body to heal itself in response to radiation therapy. Most people begin to feel fatigued about 2 weeks after radiation treatments begin.
Is radiation worse than chemo?
The radiation beams change the DNA makeup of the tumor, causing it to shrink or die. This type of cancer treatment has fewer side effects than chemotherapy since it only targets one area of the body.
What should I avoid after radiation?
Avoid raw vegetables and fruits, and other hard, dry foods such as chips or pretzels. It's also best to avoid salty, spicy or acidic foods if you are experiencing these symptoms. Your care team can recommend nutrient-based oral care solutions if you are experiencing mucositis or mouth sores caused by cancer treatment.
Does radiation stay in your body forever?
The radiation stays in the body for anywhere from a few minutes to a few days. Most people receive internal radiation therapy for just a few minutes. Sometimes, internal radiation therapy can be given for more time. If so, they stay in a private room to limit other people's exposure to radiation.
When do radiation side effects peak?
The side effects of radiotherapy usually peak up to two weeks after treatment has finished. The effects of radiotherapy continue developing, and it may take a further couple of weeks to several months for you to feel normal, depending on the area of the body that has been treated.
What are 5 effects of radiation?
Radiation Effects on HumansDose (rem)Effects5-20Possible late effects; possible chromosomal damage.20-100Temporary reduction in white blood cells.100-200Mild radiation sickness within a few hours: vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue; reduction in resistance to infection.4 more rows
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Brain
People with brain tumors often get stereotactic radiosurgery (radiation given in one large dose) if the cancer is in only one or a few sites in the...
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Head Or Neck
People who get radiation to the head and neck might have side effects such as: 1. Soreness (or even open sores) in the mouth or throat 2. Dry mouth...
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Breast
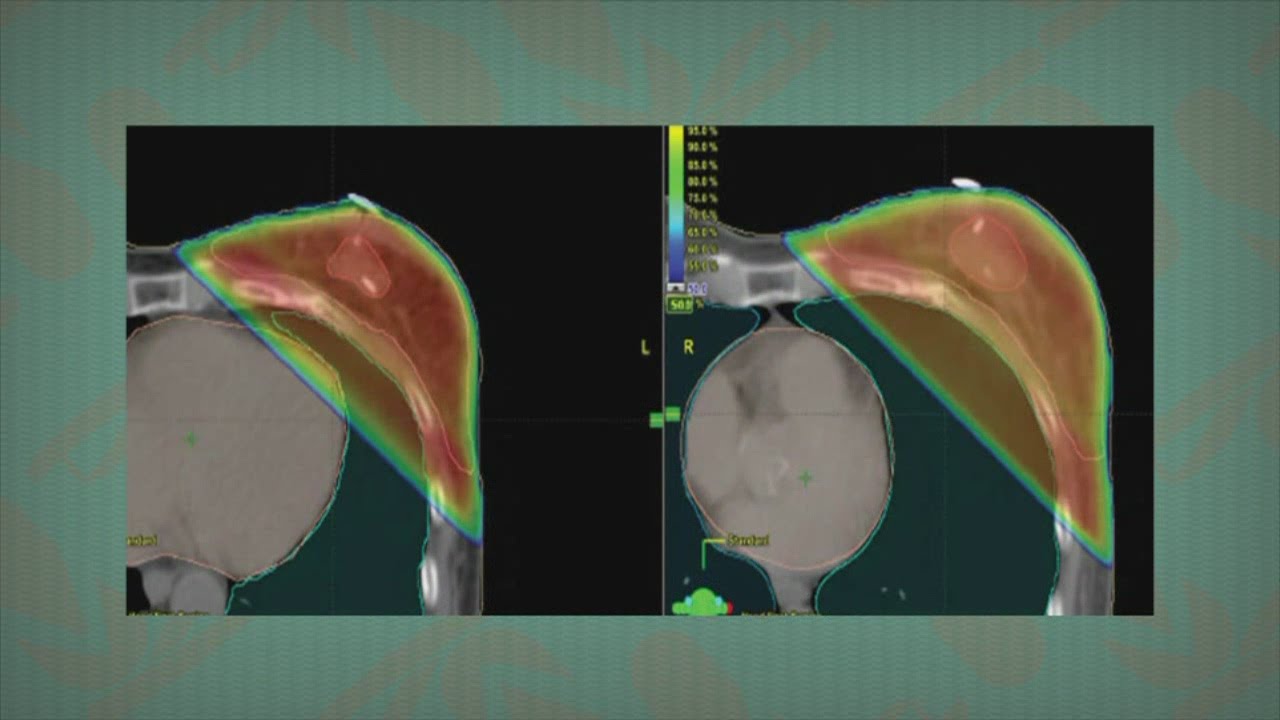
If you have radiation to the breast, it can affect your heart or lungs as well causing other side effects.
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Chest
Radiation treatment to the chest may cause side effects such as: 1. Sore throat 2. Swallowing problems 3. Loss of appetite 4. Cough 5. Shortness of...
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Abdomen (Belly)
If you are getting radiation to your stomach or some part of the abdomen (belly), you may have side effects such as: 1. Nausea 2. Vomiting 3. Belly...
If You’Re Having Radiation Therapy to The Pelvis
Radiation therapy to the pelvis (for example, as treatment for bladder, ovarian, or prostate cancer) can cause side effects such as: 1. Bladder pro...
What are the side effects of radiation?
Several variables can increase or decrease your risk of developing long-term side effects of radiotherapy. Some of these are: 2 1 Your age at the time of radiation 2 The dose of radiation you receive 3 The number of treatment sessions 4 The type of cancer treated 5 The area of the body that receives radiation 6 Other cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy 7 Other health conditions, such as heart disease or diabetes
What happens if you get radiation on your head?
Radiation to the head and neck region can damage to the salivary glands and tear ducts. This damage may result in permanent dry mouth or dry eyes. 16 Cataracts and dental decay may also be problems.
How does radiation therapy work?
Radiation therapy works by damaging DNA in cells. This damage isn't isolated to cancer cells, though; normal cells can be damaged as well. While radiation therapy has improved significantly such that less damage occurs to healthy cells than in the past, some healthy tissues are inevitably exposed. 2
What is radiation fibrosis?
Radiation Fibrosis Syndrome. Radiation fibrosis can be thought of simplistically as the loss of elasticity in tissues after radiation, due to permanent scarring. Many of the side effects below are caused by this fibrosis, which can occur in nearly any region of the body. 7 .
What cancers are associated with radiation?
Blood-related cancers such as acute myelogenous leukemia (AML), chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), and acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) are a rare side effect of radiation therapy, most commonly in the past from radiation for Hodgkin's disease or breast cancer.
When was radiation therapy first used?
Despite possible long-term side effects of radiation treatment, it's essential to point out that radiation therapy has come a long since it was introduced in 1903 , especially in recent years. With more precise dosing and newer methods of delivery, older studies may overestimate the risks.
Can radiation therapy cause heart problems?
Concern over long-term side effects of radiation therapy is becoming more common, as survival rates improve. Just as there can be long-term side effects of chemotherapy, radiation therapy may result in side effects that may begin and linger far after treatment has been completed. These can include heart problems, lung problems, thyroid problems, ...
How long does radiation side effects last?
Remember that the type of radiation side effects you might have depends on the prescribed dose and schedule. Most side effects go away within a few months of ending treatment. Some side effects may continue after treatment ends because it takes time for the healthy cells to recover from radiation. Side effects might limit your ability ...
How long does it take for radiation to cause side effects?
Late side effects can take months or even years to develop. They can occur in any normal tissue in the body that has received radiation. The risk of late side effects depends on the area treated as well as the radiation dose that was used. Careful treatment planning can help avoid serious long-term side effects.
How long does it take for radiation to show up in the brain?
Radiation to the brain can also have side effects that show up later – usually from 6 months to many years after treatment ends. These delayed effects can include serious problems such as memory loss, stroke-like symptoms, and poor brain function.
What is the most common drug used for radiation therapy?
The one most commonly used today is amifostine. This drug may be used in people with head and neck cancer to reduce the mouth problems caused by radiation therapy. Not all doctors agree on how these drugs should be used in radiation therapy. These drugs have their own side effects, too, so be sure you understand what to look for.
What is the best treatment for radiation?
One way to reduce side effects is by using radioprotective drugs, but these are only used for certain types of radiation given to certain parts of the body. These drugs are given before radiation treatment to protect certain normal tissues in the treatment area. The one most commonly used today is amifostine. This drug may be used in people with head and neck cancer to reduce the mouth problems caused by radiation therapy.
What are the side effects of brachytherapy?
If your treatment includes brachytherapy (internal radiation implants), you might notice breast tenderness, tightness, redness, and bruising. You may also have some of the same side effects that happen with external radiation treatment.
How to take care of your mouth during radiation?
Here are some tips that may help you manage mouth problems: Avoid spicy and rough foods, such as raw vegetables, dry crackers, and nuts.
How long does it take for a person to recover from radiation?
Skin changes. Urinary and bladder changes. Healthy cells that are damaged during radiation treatment usually recover within a few months after treatment is over. But sometimes people may have side effects that do not improve. Other side effects may show up months or years after radiation therapy is over.
Does radiation make you tired?
People feel fatigue in different ways and you may feel more or less fatigue than someone else who is getting the same amount of radiation therapy to the same part of the body. Other radiation therapy side effects you may have depend on the part of the body that is treated.
Does radiation therapy cause cancer?
Radiation Therapy Side Effects. Radiation not only kills or slows the growth of cancer cells, it can also affect nearby healthy cells. Damage to healthy cells can cause side effects. Many people who get radiation therapy have fatigue. Fatigue is feeling exhausted and worn out.
What are the side effects of radiation?
Radiation to the head and neck has the potential to create the following long-term side effects (this is an incomplete list; speak to your doctor about other risks): 1 Cataracts 2 Cavities 3 Tooth decay 4 Cognitive and memory problems 5 Hypothyroidism 6 Secondary cancers (in other words, the radiation can cause new cancers down the road)
What are the long term effects of radiation on the abdomen?
Radiation to the abdomen has the potential to create the following long-term side effects (this is an incomplete list; speak to your doctor about other risks): Intestinal problems. Infertility in both men and women. Bladder problems. Secondary cancers. Osteoporosis. Advances in radiation therapy are making some of these long-term potential side ...
Does radiation therapy cause osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis. Advances in radiation therapy are making some of these long-term potential side effects less and less likely because the field of radiation is getting more and more precise, exposing less and less healthy tissue to the damaging effects of radiotherapy.
Does radiation affect the head and neck?
Radiation to the Head and Neck. Radiation to the head and neck has the potential to create the following long-term side effects (this is an incomplete list; speak to your doctor about other risks): Secondary cancers (in other words, the radiation can cause new cancers down the road)
Does radiation damage cells?
Radiation and Cell Damage. Radiation does tremendous damage to our cells. That's good news if referring to tumors, but if radiation is directed at a tumor in the chest, it is also exposing the patient's internal organs in that region to radiation – and doing potential damage to the organs.
Is radiation therapy safe for cancer patients?
Radiation therapy was and remains a major breakthrough in cancer treatment in general, but doctors and researchers are quick to caution that there are side effects from this therapy which should not be taken lightly.
Is radiation to the chest uncommon?
Radiation to the Chest. Radiation to the chest area is not uncommon for breast cancer, and is occasionally used in Hodgkin's lymphoma and some B-cell lymphomas where there is a bulky mass in the chest region.
How long do side effects of radiation last?
Other people experience more severe side effects. Reactions to the radiation therapy often start during the second or third week of treatment. Or, they may last for several weeks after the final treatment. Some side effects may be long term.
What are the side effects of radiation therapy?
Head and neck. Radiation therapy aimed at a person’s head or neck may cause these side effects: Dry mouth. Mouth and gum sores.
Why do people use radiation therapy?
High doses of radiation therapy are used to destroy cancer cells. Side effects come from damage to healthy cells and tissues near the treatment area. There have been major research advances in radiation therapy in recent years that have made it more precise.
How long does it take for a radiation reaction to show up?
Typically, these side effects start within days or weeks of radiation therapy. But they can also appear months or years later. Doctors treat radiation recall with medications called corticosteroids.
What is radiation recall?
Radiation recall is a rash that looks like a severe sunburn. It is rare and happens when certain types of chemotherapy are given during or soon after external-beam radiation therapy. The rash appears on the part of the body that received radiation.
What is the best way to treat cancer side effects?
Preventing and treating side effects is an important part of your overall cancer treatment. This is called palliative care or supportive care. Before treatment begins, ask what side effects are likely from the specific type of treatment you are receiving and when they may happen.
Does radiation cause hair loss?
Radiation therapy is called a local treatment. This means that it only affects the area of the body that is targeted. For example, radiation therapy to the scalp may cause hair loss. But people who have radiation therapy to other parts of their body do not usually lose the hair on their head.
What are the long term side effects of radiotherapy?
Depending on the area of the body you have treated, you might have any of these long term side effects after radiotherapy: you might develop red spidery marks on your skin ( telangiectasia) caused by small broken blood vessels. drainage channels to the arms or legs can become partly blocked resulting in ...
Can breast radiotherapy make your vagina narrower?
your breast might be a slightly different shape, feel firmer or harder after breast radiotherapy. your vagina could become narrower and less stretchy after treatment to your pelvic area. your arm may swell after treatment to your shoulder. your leg may swell after treatment to your groin.
Is radiotherapy more accurate than it has ever been?
Newer ways of giving radiotherapy. Radiotherapy is more accurate than it has ever been. Current radiotherapy techniques, such as conformal radiotherapy and intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT), accurately shape the radiotherapy beams to fit the cancer. This means less healthy tissue receives radiation, and so there are fewer side effects.
Does radiotherapy affect the body?
It is important to remember that radiotherapy only affects the area of the body being treated. Changes to a part of the body outside the treatment area won't have been caused by the radiotherapy.
How many cancer survivors are attributable to radiation?
According to a long-term study of more than 600,000 cancer survivors by U.S. National Cancer Institute researchers, an estimated eight percent of second cancers were attributable to radiation treatment for original cancer.
Why do women have chest pain after radiotherapy?
These symptoms may occur because the radiotherapy can damage the cells lining the lungs, causing inflammation or a hardening and thickening (fibrosis).
When did radiation therapy start?
We’ve come a long way since 1903 when Marie and Pierre Curie first introduced radiation therapy as a means of treating cancer and lupus. The field of radiation oncology is continually being improved to provide patients with better long-term disease outcomes, and fewer long-term side effects. This is still a relatively new treatment modality when it comes to following patients over their lifespan. Earlier detection and more effective treatments mean patients are living longer — in many cases, living well into old age. Until recently, long term side effects were not easily recognized simply because there had not been a significant population to observe.
Can you get cancer from radiation on the left side of your heart?
This is a potential problem if you have had cancer in your left breast since the heart is on the left side of the chest. Ideally, the heart is either not within the radiation area or only a small amount of the heart will receive any radiation, which helps to lower the risk of significant damage.
Can you move underarms after radiotherapy?
It’s fairly common for women who have radiotherapy to the area under the arm to experience some restriction in movement, especially if they’ve had surgery to their underarm area as well. This may make it difficult to carry heavy objects, perform other tasks that require lifting or do certain types of exercise.
Can radiation cause bone loss?
A rare late side effect of radiotherapy to the breast is damage to the bones, especially the ribs. The bones can become thinner and more brittle if you had certain chemotherapy drugs while undergoing radiation. If this happens, it can cause pain and make it hard for you to lift heavy objects or to exercise.
Mechanism of action
Risks
Prognosis
Pathophysiology
Overview
Prevention
Adverse effects
- Radiation therapy, especially radiation to the brain, to the base of the skull, and to the neck may result in cognitive problems such as memory loss and difficulty concentrating. Radiation oncologists now frequently treat people with a medication (one ordinarily used for Alzeimers) during radiation therapy and this has been found to reduce cognitiv...
Effects
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms
Safety