Why do researchers try to replicate results?
Write the treatment combinations for the basic 2 2 design. Add a column next to it and type c to add the factor C with it. Now use the treatment combinations for the three variables A, B, and C to develop the treatment combinations for four variables A, B, C, and D. And so on. Table 5. Flowless system for writing the treatment combinations.
What are the advantages of using multiple replicates?
You can replicate combinations of factor levels, groups of factor level combinations, or entire designs. For example, if you have three factors with two levels each and you test all combinations of factor levels (full factorial design), one replicate of the entire design would have 8 runs (2 3). You can choose to do the design one time or have ...
What is a replicate?
The importance of replication. Not just definitions but individual acts of experimentation must be checked for reliability. Research must be repeated before a finding can be accepted as well-established. Findings obtained at one time might not hold true at another time with different researchers or different experimental subjects.
Should I use multiple replicates in my screening design?
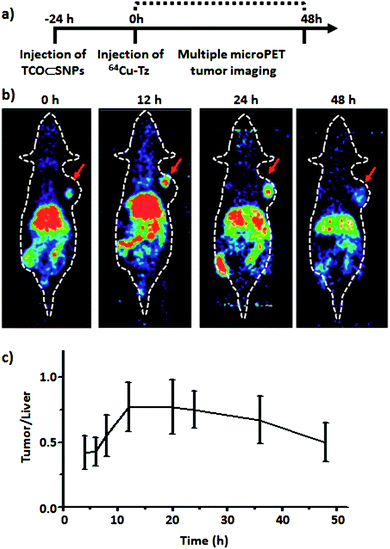
Combination therapy is the suggested way to increase treatment efficacy, to prevent the development of drug resistance, and to reduce the duration of treatment. ... Combination medical therapy may be necessary in patients with moderate-to-severe hypercortisolism, in which case using a combination of medications at lower effective doses may be ...
What is the purpose of replication of treatments?
What is the purpose of repeating an experiment?
Why is it important to replicate results?
Why is it necessary to replicate and randomize treatment in experiment?
What is a primary reason for replicating the findings of a study?
Why is replication so important in psychological research?
Why is it necessary to assign subjects to treatments at random?
What are two main purposes for using repetition when conducting experiments quizlet?
Why we use completely randomized design?
Why is replication important in science?
Replication is vital to science. It helps make science a self-correcting system. Any time a result is surprising, researchers will try to replicate it, to see if the phenomenon is dependable or just a fluke (a one-time occurrence). Operational definitions are critically important in aiding replication.
What is a type 1 error?
Replication failures may also expose what statisticians call a Type 1 error, a finding of statistical significance that is due to random error or luck of the draw. If an effect cannot be repeated reliably, scientists need to find out about it. That is why replications are performed.
What is operational definition?
An operational definition spells out exactly how to measure something. To replicate an experiment, one must know how the original researcher performed measurements. Hence operational definitions must be known precisely, to replicate research.
Can glaucoma be reversible?
When they do occur, side effects are often easily reversible by stopping the medication. Only rarely are vision- or life-threatening side effects seen. Medical therapy is less costly over the short term, and because many glaucoma patients are elderly, the cost of medical treatment may never exceed that of surgery.
How much does ezetimibe reduce LDL cholesterol?
A 15% to 20% decrease in LDL cholesterol is approximately equivalent to tripling the dose of the statin.
Does endometriosis affect fertility?
Medical therapy directed against treatment of endometriosis alone does not improve fertility in women with endometriosis-associated infertility 18 and has actually been associated with a reduction of fertility in these women. This may be due either to some direct negative effect of the medications or to the fact that the natural age-related decline in fertility is manifest following 6 months or more of treatment and eventual resumption of ovarian function. Medical therapy is therefore contraindicated for the symptom of infertility associated with endometriosis. However, medical therapy as an adjunct to assisted reproductive techniques appears to be helpful. In women with infertility associated with advanced stages of endometriosis, an extended course of a GnRH agonist given before ovulation induction and intrauterine insemination was found to improve fecundity over a shorter course of GnRH agonist. 19
Does statin reduce LDL?
For every doubling the dose of the statin, there is a further decrease in LDL cholesterol of approximately 6%. Therefore, the use of combination therapy with the aforementioned nonstatin drugs results in LDL cholesterol reductions equivalent to or greater than the highest dose of the statin.
Oona McPolin Follow
Do you prepare your samples/standards in duplicate without really thinking about it? If challenged on why, would your answer be something like, "it's good practice, isn't it?" The use of replicates in analytical procedures is commonplace but it is important to understand why you are doing it and also what the results are telling you.#N#There are different types of replicates in analytical methods, which are used for different purposes.
DHILIP ANAND.K.C
Kindly let me know if any literature reference available for the same or if any guidance available
Oona McPolin
Hi DHILIP, I would advise that any evaluation of solution stability should use prepared solutions that are as close as possible to a real method test solution. In the case you have mentioned, where the impurities are originally prepared in highly organic solvents, it would depend on how much the spiking changes the composition of the diluent.
What are the main drugs used to treat HIV?
The four protease inhibitors currently approved for the treatment of HIV infection are saquinavir (Fortovase, Invirase), ritonavir (Novir), indinavir (Crixivan) and nelfinavir (Viracept). The standard dosages and common side effects of these agents are summarized in Table 1. These agents all share a common mechanism of action: they prevent maturation of virus protein by competitively inhibiting HIV protease, an enzyme essential for viral protein cleavage. When this protein cleavage is blocked, immature noninfectious virus particles are produced. 31 The HIV protease inhibitors all share a number of other properties: they are difficult to synthesize, they have little effect on mammalian proteases, they are metabolized by hepatic and intestinal cytochrome P 450 enzymes, they have multiple important pharmacokinetic interactions with other medications and they have limited central nervous system penetration. 31
When did zidovudine become available?
The first of these agents, zidovudine (AZT, ZDV; Retrovir), became available in 1987.
What was the first drug to be used for HIV?
Nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitors were the first group of agents shown to be effective in the treatment of HIV infection. The first of these agents, zidovudine (AZT, ZDV; Retrovir), became available in 1987.
What is flipped classroom?
Flipped classrooms have become an interesting alternative to traditional lecture-based courses throughout the undergraduate curriculum. In this article, we compare a flipped classroom approach to the traditional lecture-based approach to teaching introductory biostatistics to first-year graduate students in public health. The traditional course was...
What is an experimental unit?
An experimental unit is one particular element from the subject population under study. Each experimental unit will receive a certain treatment (specific combination of levels of each factor), and its response will be measured.
Who is Norman Breslow?
Since the early 1970’s, Norman Breslow has made enormous contributions to statistical theory and its applications in epidemiology, and he was a founding member and principal statistician of the Wilms Tumor Study Group, which is credited with great improvements in the treatment and understanding of this disease. Applications of the biostatistical me...
What is combination chemotherapy?
Combination chemotherapy is the use of more than one medication at a time to treat cancer. Since chemotherapy drugs affect cancer cells at different points in the cell cycle, using a combination of drugs increases the chance that all of the cancer cells will be eliminated. At the same time, however, multiple drugs may increase the risk ...
When was combination chemotherapy first used?
The use of combination chemotherapy to treat cancer was inspired in the 1960s when scientists wondered whether the approach to treating tuberculosis—using a combination of antibiotics to reduce the risk of resistance—would work for treating cancer as well.
Is combination chemotherapy good for cancer?
Benefits. Disadvantages and Risks. Combination chemotherapy is the use of more than one medication at a time to treat cancer. Since chemotherapy drugs affect cancer cells at different points in the cell cycle, using a combination of drugs increases the chance that all of the cancer cells will be eliminated. At the same time, however, multiple drugs ...
Can chemotherapy drugs cause cancer?
Since chemotherapy drugs affect cancer cells at different points in the cell cycle, using a combination of drugs increases the chance that all of the cancer cells will be eliminated. At the same time, however, multiple drugs may increase the risk of drug interactions.
Is combination chemotherapy more effective than single chemotherapy?
In the 1970s, combination chemotherapy was found to be more effective than single drugs for people with lung cancer, as well as more effective than "sequential chemotherapy"—i.e., using chemotherapy drugs one after the other. 3. In the last decade, chemotherapy has been added to a type of immunotherapy called checkpoint inhibition.
Does immunotherapy work with chemotherapy?
When chemotherapy is used along with immunotherapy, benefits may go beyond using the combination of drugs. Immunotherapy drugs work by helping the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. 7
Does chemotherapy work?
A Word From Verywell. Combination chemotherapy can sometimes work to extend life, reduce the risk of cancer recurrence, and/or improve the results from immunotherapy. That said, adding more medications can increase the side effects and rigor of treatment.
What is simultaneous treatment?
The same is true for simultaneous-treatment designs; a design that is appropriate for situations where one wishes to evaluate the concurrent or simultaneous application of two or more treatments in a single case. Rapid or random alteration of treatment is not required with simultaneous-treatment design.
What is a carryover effect?
A carry-over effect occurs when the presentation of one condition somehow affects the impact of the subsequent condition, regardless of the presentation order of the conditions. Potentially this can occur in two ways. The effects of two conditions can change in opposite directions, or in the same direction.
What is an ATD?
The alternating treatment design (ATD) consists of rapid and random or semirandom alteration of two or more conditions such that each has an approximately equal probability of being present during each measurement opportunity. As an example, it was observed during a clinical training case that a student therapist, during many sessions, would alternate between two conditions: leaning away from the client and becoming cold and predictable when he was uncomfortable, and leaning towards the client and becoming warm and open when feeling comfortable. The client would disclose less when the therapist leaned away, and more when he leaned forward. If it were assumed that the therapist had preplanned the within-session alternations, an ATD as shown in Figure 6 would be obtained. The condition present in the example at any given time of measurement is rapidly alternating. No phase exists; however, if the data in each respective treatment condition are examined separately, the relative level and trend of each condition can be compared between the two data series (hence the name between-series designs).
What is single case design?
Although usually labeled a quasi-experimental time-series design, single-case research designs are described in this article as a separate form of research design (formerly termed single-subject or N = 1 research) that have a long and influential history in psychology and education (e.g., Kratochwill, 1978; Levin et al., 2003) and can serve as an alternative to using large, aggregate group designs ( Shadish and Rindskopf, 2007 ). Single-case research designs bear similarly to time-series design and have often been regarded as quasi-experimental because they usually do not (but could) include randomization in the experiment. In the single-case design, replication is scheduled to help rule out various threats to validity. Single-case designs can involve a single participant or group as the unit but differ from repeated measures and hierarchical linear modeling (HLM) designs because multiple observations are taken over a long period of time within a design structure of replication and/or randomization of the conditions of the experiment.
