
Treatments are sometimes given for a long time to prevent symptoms from returning. Sometimes abscesses or wound infections need to be surgically drained. Because some Nocardia species are resistant to certain antibiotics, laboratory testing is needed to find out which species is causing the infection.
Is Nocardia life threatening?
Since a Nocardia infection is usually slow to respond to treatment, it can be life-threatening for those with weakened immune systems, especially if diagnosis and treatment are delayed. It’s important to seek treatment as soon as symptoms develop.
How long does nocardiosis last?
Nocardiosis may last from several months to years. It is essential that the infection be diagnosed and differentiated from tuberculosis and pneumonia. Nocardiosis is caused by Nocardia asteroides, a bacterium that is carried up into the air from the ground and may be inhaled.
What are the treatments for Nocardia infections?
Treatments are sometimes given for a long time to prevent symptoms from returning. Sometimes abscesses or wound infections need to be surgically drained. Because some Nocardia species are resistant to certain antibiotics, laboratory testing is needed to find out which species is causing the infection.
Why are Nocardia infections on the rise?
In the last 2 decades, Nocardia infections have increased significantly, likely as a result of improved detection and identification methods and an expanding immunocompromised population.
How long do you treat Nocardia?
Duration of treatment is generally prolonged to minimize risk of disease relapse. Immunocompetent patients with pulmonary or multifocal (non-CNS) nocardiosis may be successfully treated with 6 to 12 months of antimicrobial therapy.
What is the treatment of Nocardia?
Nocardia organisms are usually resistant to penicillin. Sulfonamide drugs may be prescribed. However, since most cases respond slowly, treatment with sulfonamide drugs must be continued for several months. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is often prescribed for immunosuppressed patients.
Can Nocardia be cured?
Nocardiosis usually can be cured with antibiotics, but not all of them will work against the bacteria. Your doctor might need to run some lab tests to see which ones will work best for you. Then you might need to take them for 6 weeks up to a year, depending on how serious your infection is.
How long does Nocardia take to grow?
Current diagnostic tests include: Gram staining and modified acid-fast staining from smears of draining areas or skin biopsy specimens. Nocardia may take up to 2-3 weeks to grow in the laboratory; specimens from multiple clinical sites should be submitted.
What antibiotics cover Nocardia?
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is the first-line treatment for Nocardia infections. In patients with a sulfa allergy, imipenem, ceftriaxone, or linezolid are options for first-line therapy.
Can Nocardia cause brain abscess?
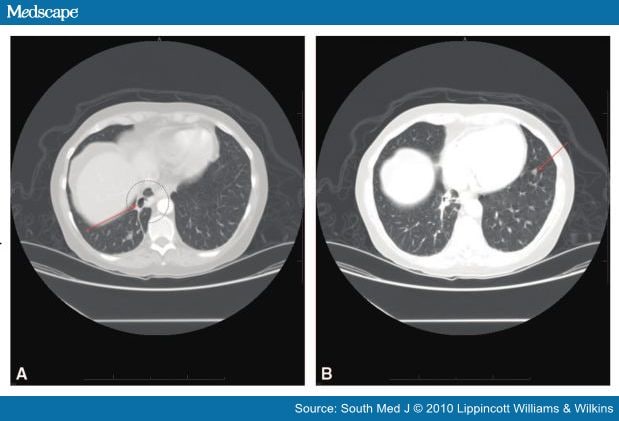
Nocardia species are a rare cause of cerebral abscess [3]. Nocardia brain abscess appears in a gradually progressive mass lesion, with specific neurologic findings. Seizures and focal neurological deficits are the most common clinical manifestations observed in patients with a Nocardia brain abscess [8].
Can a brain infection be cured?
If your abscess is deep inside your brain or it's 2.5 centimeters or less, it will probably be treated with antibiotics. Antibiotic medications will also be used to treat any underlying infections that may have been the cause of the brain abscess.
How serious is Nocardia?
Up to 44% of all people with infection in the brain or spinal cord die. The risk for death is much higher for patients with very weak immune systems—more than 85% of them die after developing nocardiosis of the brain or spinal cord.
How common is Nocardia?
Nocardiosis is a rare infectious disorder, that affects the brain, skin, and/or lungs. It occurs mainly in people with a weakened immune system but can affect anyone, and about one-third of infected people do not have any immune problems.. This condition usually starts in the lungs and can spread to other body organs.
How long does it take for a lung abscess to form?
This results in aspiration pneumonitis and progression to tissue necrosis 7-14 days later, resulting in formation of lung abscess. Other mechanisms for lung abscess formation include bacteremia or tricuspid valve endocarditis causing septic emboli (usually multiple) to the lung.
What is the reason why Nocardia is partially acid-fast?
Some species are partially acid-fast (meaning a less concentrated solution of sulfuric or hydrochloric acid should be used during the staining procedure) due to the presence of intermediate-length mycolic acids in their cell wall.
Does Nocardia cause pneumonia?
Nocardia infection develops when you breathe in (inhale) the bacteria. The infection causes pneumonia-like symptoms. The infection can spread to any part of the body.
Is nocardiosis a gram positive infection?
Nocardiosis is an uncommon gram-positive bacterial infection caused by aerobic actinomycetes in the genus Nocardia.Nocardiaspp have the ability to cause localize. It seems to us that you have your JavaScript disabled on your browser. JavaScript is required in order for our site to behave correctly. Please enable JavaScript to use our site.
Is nocardia a suppurative disease?
Nocardia spp have the ability to cause localized or systemic suppurative disease in humans and animals [1-5]. Nocardiosis is typically regarded as an opportunistic infection, but approximately one-third of infected patients are immunocompetent [5]. Two characteristics of nocardiosis are its ability to disseminate to virtually any organ, ...
Why is nocardiosis life threatening?
cases of nocardiosis occur each year. In about 60 percent of these cases, the infection is related to a weak immune system. Since a Nocardia infection is usually slow to respond to treatment, it can be life-threatening for those with weakened immune systems, especially if diagnosis and treatment are delayed. It’s important to seek treatment as soon ...
What is the cause of nocardiosis?
What Is Nocardiosis? Nocardiosis is a rare infection caused by the Nocardia asteroides bacterium. This type of bacteria can be found in the soil and water of regions around the world. People may become infected with this bacteria when they inhale it or when the bacteria enter an open wound.
What are the systems that are affected by nocardiosis?
digestive system. brain. kidneys . heart. eyes. bones. Though nocardiosis can develop in anyone, the condition is much more likely to affect people with very weak immune systems. An immune system may become compromised as a result of: cancer.
Can you take antibiotics for nocardiosis?
In most cases, nocardiosis can be treated successfully with antibiotics, especially when treatment is received early. However, the infection can become life-threatening when multiple areas of the body become infected at the same time. It’s especially dangerous for people with weakened immune systems.
Should clinicians be aware of nocardiosis?
Clinicians should be aware of nocardiosis in patients with different forms of immunosuppression. The identification of organisms, their patterns of antibiotic susceptibility and the adverse effects related to these drugs must be considered. Treatments can vary from traditional schemes with trimethop …. Clinicians should be aware of nocardiosis in ...
Is nocardiosis an infectious disease?
Introduction: Nocardiosis is an infectious actinomycetic disease with a variable clinical spectrum that makes it difficult to diagnose. It mainly affects immunosuppressed individuals. Advances in molecular genomic technology have helped in identifying new pathogenic Nocardia species. This has made identification of their specific antimicrobial sensitivity possible.
What are the different types of cutaneous nocardiosis?
Three types of primary cutaneous nocardiosis have been described: Superficial skin infection. Lymphocutaneous infection. Mycetoma (click on the link for details) Disseminated and/or pulmonary nocardiosis can also spread to involve the skin; in these cases Nocardia asteroides is often responsible.
Is nocardia a gram positive bacterium?
Nocardia is partially acid-fast, aerobic, gram-positive, branching filamentous bacillus bacterium that is found ubiquitously in soil, fresh and salt water, decomposing vegetation, other organic matter and marine water 1). There are more than 100 Nocardia species defined. However, approximately 30 of these carry significance to human disease. Nocardia species cause serious pulmonary infections (with occasional brain abscesses) in immunocompromised patients, primarily those with cell-mediated immunity abnormalities 2). Nocardiosis is a rare infection caused by several species of Nocardia bacteria and have two main clinical forms, disseminated and/or pulmonary infection and cutaneous infection. Nocardiosis most commonly occurs after Nocardia bacterium has been introduced into the respiratory tract, but it may be acquired through direct inoculation into the skin 3). Classically, Nocardia manifests as an opportunistic infection in immunocompromised hosts and can impact nearly every part of the human body including skin and skin structures, the pleural or pulmonary system, or it can be a disseminated disease impacting other organ systems 4). However, Nocardia bacteremia is rarely reported, even for severely immunocompromised patients with underlying malignancies 5).
Is pulmonary nocardiosis a disease?
Pulmonary nocardiosis and disseminated forms of the infection are opportunistic diseases occurring mainly in patients deficient in T cell-mediated immunity 9). Patients with the greatest susceptibility to this include those with solid organ transplant and hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients, HIV-infected patients, patients taking corticosteroids chronically, or patients with ongoing malignant processes. Primary cutaneous nocardiosis may occur in immunocompetent patients who have experienced a direct inoculation of the microorganism into the skin structures from a traumatic event. This is seen most commonly in those working in rural areas involving in agricultural activities. While rare, post-surgical wound infections may occur if non-sterile equipment is used. Pulmonary forms of nocardiosis are induced via aerosolized inoculation of the bacterium into the airways. Dissemination throughout the remainder of the body may occur from either of these initial inoculations 10).
Is nocardiosis fatal?
Prognosis of nocardiosis is variable. It depends upon the organ infected, duration, immunological state of the person, and severity of the infection. Approximately 10% of cases of uncomplicated pulmonary disease are fatal. The case-fatality rate increases with disseminated disease or brain abscesses, particularly in patients with impaired immunity. Cutaneous nocardiosis is rarely fatal, but long-lasting mycetomal infection can be significantly disfiguring.
How long does nocardiosis last?
Nocardiosis may last from several months to years.
What is the cause of nocardiosis?
Nocardiosis is caused by Nocardia asteroides, a bacterium that is carried up into the air from the ground and may be inhaled. Other species of the same family of bacteria such as Nocardia brasiliensis, Nocardia caviae, and Nocardia farcinica, are also known to cause disease.
How many cases of nocardiosis are diagnosed in the USA each year?
Nocardiosis occurs worldwide. Those affected tend to be older adults, and males are more often affected than are females. In the USA, about 500 to 1,000 new cases of nocardiosis are diagnosed each year.
What are the symptoms of nocardiosis?
Symptoms may include chest pain, cough, bloody sputum, sweats, chills, weakness, lack of appetite, weight loss and difficult or labored breathing. Nocardiosis symptoms are similar to those of pneumonia and tuberculosis.
Is it possible to have nocardial infections if your immune system is not functioning properly?
People whose immune systems are not functioning properly (immunocompromised) are at risk for nocardial infections. People whose immune systems are functioning properly but who are taking immunosuppressive drugs as part of the routine for organ transplantation are at greater than normal risk as well.
What is a nocardia?
Nocardia. Nocardia as found on a brain biopsy. Nocardia is a genus of weakly staining Gram-positive, catalase-positive, rod-shaped bacteria. It forms partially acid-fast beaded branching filaments (acting as fungi, but being truly bacteria). It contains a total of 85 species.
How many species of nocardia are there?
It contains a total of 85 species. Some species are nonpathogenic, while others are responsible for nocardiosis. Nocardia species are found worldwide in soil rich in organic matter. In addition, they are oral microflora found in healthy gingiva, as well as periodontal pockets.
What are the virulence factors of nocardia?
Nocardial virulence factors are the enzymes catalase and superoxide dismutase (which inactivate reactive oxygen species that would otherwise prove toxic to the bacteria), as well as a "cord factor" (which interferes with phagocytosis by macrophages by preventing the fusion of the phagosome with the lysosome ).
What are the nocardial virulence factors?
Nocardial virulence factors are the enzymes catalase and superoxide dismutase (which inactivate reactive oxygen species that would otherwise prove toxic to the bacteria), as well as a "cord factor" (which interferes with phagocytosis by macrophages by preventing the fusion of the phagosome with the lysosome ).
What is the best medium for nocardia isolation?
Nocardia isolation from biological specimens can be performed using an agar medium enriched with yeast extract and activated charcoal (BCYE), the same used for Legionella species. Selective media for mycobacteria or fungi can also be inoculated.
How long does Linezolid last?
Antibiotic therapy is continued for six months (in immunocompetent people) to a year (in immunosuppression ), and may need to be continued indefinitely. Proper wound care is also critical.
Does trimethoprim cause nocardia?
People who take trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for other reasons, such as prevention of Pneumocystis jirovecii infection, appear to have fewer Nocardia infections, although this protective effect has been considered unreliable, and some studies have disputed it altogether.
Why has nocardia increased?
In the last 2 decades, Nocardia infections have increased significantly, likely as a result of improved detection and identification methods and an expanding immunocompromised population.
What is the first line of treatment for nocardia?
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is the first-line treatment for Nocardia infections. In patients with a sulfa allergy, imipenem, ceftriaxone, or linezolid are options for first-line therapy. In cases of localized skin infection or stable patients with pneumonia, monotherapy is adequate; in cases of severe pulmonary infection, CNS involvement, ...
How does nocardia spread?
The primary route of transmission of Nocardia is inhalation from environmental sources. Depending on the organ transplanted and the immunosuppressive regimen used, Nocardia infections in SOT recipients varies between <1% and 3.5%. Nocardia commonly affects the lung, brain, and skin and may cause disseminated infection, ...
What is the best treatment for nocardial infection?
The primary treatment of nocardial infections is antibiotic therapy , although surgical debridement may also be required. However, there have been no controlled clinical trials comparing treatment regimens for nocardiosis; therefore, antibiotic therapy selection should consider the site and severity of disease, the potential drug interactions and adverse effects, and species of Nocardia involved. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing is strongly recommended, as inter- and intra-species susceptibility patterns can vary. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is the first-line treatment for Nocardia infections. In patients with a sulfa allergy, imipenem, ceftriaxone, or linezolid are options for first-line therapy. In cases of localized skin infection or stable patients with pneumonia, monotherapy is adequate; in cases of severe pulmonary infection, CNS involvement, or disseminated infection, 2 agents (such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, or imipenem plus amikacin) should be used for initial therapy. In cases of life-threatening disease, 3 drugs can be considered.
Does trimethoprim reduce the rate of nocardial infection?
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole used daily for the prevention of pneumonia in the first 6 months post-transplantation, also reportedly reduces the rate of nocardial infection in recipients of SOT via prevention of the primary Nocardia infection and prevention of relapse after treatment. However, there are no definitive data on the dose and duration of prophylaxis. Previous studies have used one double-strength trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole tablet daily, a double-strength tablet 3 times weekly, and other dosing regimens sometimes indefinitely. In terms of secondary prophylaxis, azithromycin has been used successfully.
