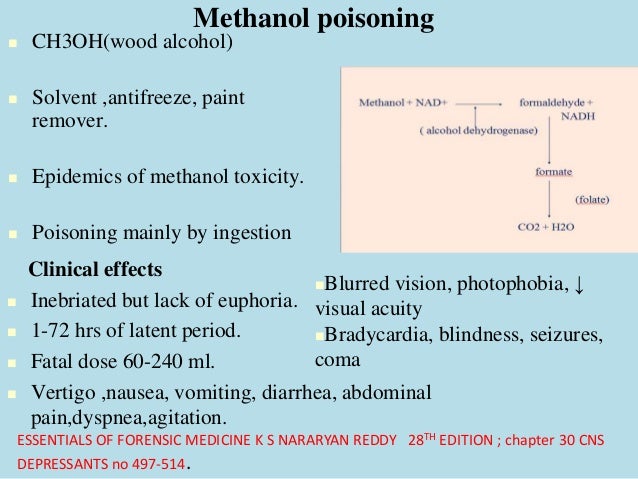
Both drugs act to reduce the action of alcohol dehydrogenase on methanol by means of competitive inhibition. Ethanol, the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, acts as a competitive inhibitor by more effectively binding and saturating the alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme in the liver, thus blocking the binding of methanol.
Full Answer
Why is ethanol a good fuel?
2 specific different reasons why ethanol is used to treat methanol poisoning? Uncategorized. One antidote therapy for methanol ingestion is using ethanol by delaying methanol metabolism until the methanol is eliminated from the patient’s system either naturally or via dialysis. Like methanol, ethanol is metabolized by antidiuretic hormone (ADH) , but the enzyme’s affinity for …
What are the symptoms of ethanol poisoning?
· Alcohol dehydrogenases are enzymes which catalyze the breakdown of alcohols and, in the case of methanol poisoning, allow for the breakdown of methanol to formic acid. Ethanol or fomepizole are typically administered to prevent the metabolism of methanol because they act as competitive inhibitors to alcohol dehydrogenases, meaning they bind to alcohol …
Why is methanol toxic, but not ethanol?
· Abstract. Twelve cases of methanol poisoning are reviewed. The clinical presentation and biochemical features are described and the results of treatment with alkali, ethanol and dialysis reported. The outcome of methanol poisoning appears to be related more to the interval between the time of ingestion and the start of therapy and to the degree of acidosis …
How to test if alcohol has methanol?
· Ethylene glycol (EG) and methanol are responsible for life-threatening poisonings. Fomepizole, a potent alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) inhibitor, is an efficient and safe antidote that prevents or reduces toxic EG and methanol metabolism. Although no study has compared its efficacy with ethanol, fomepizole is recommended as a first-line antidote.
See more
In addition to supportive measures, ethylene glycol and methanol poisoning are treated with fomepizole (4-methylpyrazole), which inhibits alcohol dehydrogenase and prevents formation of toxic metabolites (see Fig.12.10). 32 If fomepizole is unavailable, intravenous ethanol can be used to prevent the formation of toxic metabolites. Ethanol has more than a 10-fold greater …

Why do you give ethanol for methanol poisoning?
Ethanol, the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, acts as a competitive inhibitor by more effectively binding and saturating the alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme in the liver, thus blocking the binding of methanol.
Why is ethanol used as an antidote?
Treatment with ethanol Ethanol occupies the active site of the enzyme, thereby reducing production of toxic metabolites as demonstrated in many case reports/series on methanol or ethylene glycol poisoning 29, 30, 51, 52, 53.
Is ethanol an antidote for methanol?
A 10% ethanol solution administered intravenously is a safe and effective antidote for severe methanol poisoning.
What is the best antidote for methanol poisoning?
Although both ethanol and fomepizole are effective, fomepizole is the preferred antidote for methanol poisoning.
Why is ethanol used in medicine?
Ethanol is used as a solvent to dissolve the active ingredient in some medicines or as an extraction solvent in herbal medicinal products. Ethanol has also been used as an antimicrobial preservative, possessing bactericidal and fungicidal activity.
Which antidote can be given post exposure to methanol?
ANTIDOTE: Fomepizole and ethanol are effective antidotes against methanol toxicity. Fomepizole or ethanol should be administered as soon as possible once the patient/victim has been admitted to a medical care facility.
Why is methanol poisonous but not ethanol?
Methanol is not toxic itself, but it is metabolised to a very toxic substance: formic acid and/or formate. In the absence of ethanol, it takes about 12-24 hours to produce enough formate for symptoms of poisoning to appear.
What's the difference between ethanol and methanol?
Methanol and ethanol are alcohol variants. Methanol contains only one carbon and ethanol contains two carbon in each molecule. Both substances can be used as energy sources, but methanol primarily serves as a research subject, and its use as a motor fuel has been mostly phased out in the United States.
How is methanol exposure treated?
Treatment can include administration of ethanol or fomepizole, both inhibitors of the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase to prevent formation of its metabolites, and hemodialysis to remove methanol and formate.
Which drug is used for methanol poisoning?
Conclusions: Fomepizole appears to be safe and effective in the treatment of methanol poisoning.
What is the antidote of methanol and ethylene glycol?
Ethylene glycol (EG) and methanol are responsible for life-threatening poisonings. Fomepizole, a potent alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) inhibitor, is an efficient and safe antidote that prevents or reduces toxic EG and methanol metabolism.
Which substance may be used to treat ethylene glycol or methanol toxicity?
Currently, there are two antidotes used to block ADH-mediated metabolism of EG and methanol: ethanol and fomepizole.
Is methanol poisoning rare?
Methanol poisoning is actually rare, but when it occurs, many people are often involved simultaneously, hence the special place of methanol poisonings in clinical toxicology. Examples of mass poisonings include the Atlanta outbreak, which involved 323 people, of whom 41 died [16], and the Kristiansand outbreak with 70 people involved and 3 deaths ...
Is methanol a toxic substance?
Ingestion of greater than 100 mg/kg of methanol should be deemed potentially toxic. Therefore, even a single swallow of windshield washer fluid, with 40% methanol, is to be considered dangerous. Methanol is less inebriating than ethanol or ethylene glycol, so patients may appear well shortly after ingestion.
Is methanol poisoning a contraindication to organ donation?
As for the heart, it seems also that methanol poisoning is not an absolute contraindication to organ donation. There is no clear evidence that methanol or its toxic metabolites may provoke direct injury to the myocardium.
Can ethanol cause hypoglycemia?
Hypoglycemia may occur as was described for ethanol. After several hours, profound metabolic acidosis, with a wide anion gap (see Chapter 111, Metabolic Acidosis), is common. Clinical evidence of toxicity may be further delayed if ethanol has also been ingested.
How long does it take for methanol to cause an anion gap?
Methanol intoxication is accompanied by the production of formaldehyde and formic acid; production of the latter leads to a profoundly elevated anion gap, which usually develops 12 to 24 hours after ingestion . Although controversial, formic acid seems to be the earliest cause of anion-gap elevation, although lactic and other organic acids may contribute to this disturbance. Additionally, multiple-organ failure results in decreased hepatic lactate utilization. In untreated patients, as methanol is metabolized, an early osmolal gap and normal or slightly elevated anion gap is followed by a decrease in the osmolal gap with an increase in the anion gap. Treatment includes correction of the profound academia with bicarbonate administration, use of fomepizole or ethanol to inhibit the metabolism of methanol, and hemodialysis to correct the profound acidemia and remove the toxic compounds. Methanol is further discussed in Chapter 32.
Can methanol cause vision loss?
Methanol intoxication may cause partial visual loss to irreversible blindness. In less severe cases, central and centrocecal scotomas predominate. Hyperemic disc swelling and some edema of the peripapillary retina may be seen. No pupillary reaction indicative of a poor visual prognosis. Vision may improve within a week of discontinuation of methanol. Vision occasionally may worsen weeks after first improving. The optic disc gradually become pale and may acquire cupping that mimics that in glaucoma. Retinal arteries may also be attenuated.
Does fomepizole slow the metabolism of ethylene glycol?
As with methanol intoxication, fomepizole and ethanol will slow the metabolism of ethylene glycol to its more toxic metabolites. 159 The indications for the use of one of the antidotes have been outline by the AACT. These indications include a plasma ethylene glycol concentration of greater than 20 mg/dl, a recent ingestion of ethylene glycol, and an osmolar gap greater than 10 mOsm/kg or a high clinical suspicion and two of the following: pH of less than 7.3, serum bicarbonate of less than 20 mEq/L, osmolar gap of greater than 10 mOsm/kg, or urinary oxalate crystals (see Table 51-7 ). 147 The dosing schedule of each antidote is the same as that for methanol intoxication and is listed in Tables 51-8 and 51-9. 106
What is the treatment for methanol poisoning?
Treatment can include administration of ethanol or fomepizole, both inhibitors of the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase to prevent formation of its metabolites, and hemodialysis to remove methanol and formate.
Is methanol a poison?
Methanol intoxication is an uncommon but serious poisoning. Its adverse effects are due primarily to the impact of its major metabolite formic acid and lactic acid resulting from cellular hypoxia.
What enzyme catalyzes methanol?
Figure 1 Metabolism of methanol. Methanol undergoes serial oxidation: methanol is catalyzed by the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase to formal dehyde and then formaldehyde is catalyzed by the enzyme formaldehyde dehydrogenase to formic acid. Folinic acid given to a patient will accelerate the conversion to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
What enzyme is used to oxidize methanol?
Methanol undergoes serial oxidation: methanol is catalyzed by the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase to formaldehyde and then formaldehyde is catalyzed by the enzyme formaldehyde dehydrogenase to formic acid. Folinic acid given to a patient will accelerate the conversion to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
How long was fomepizole dialyzed?
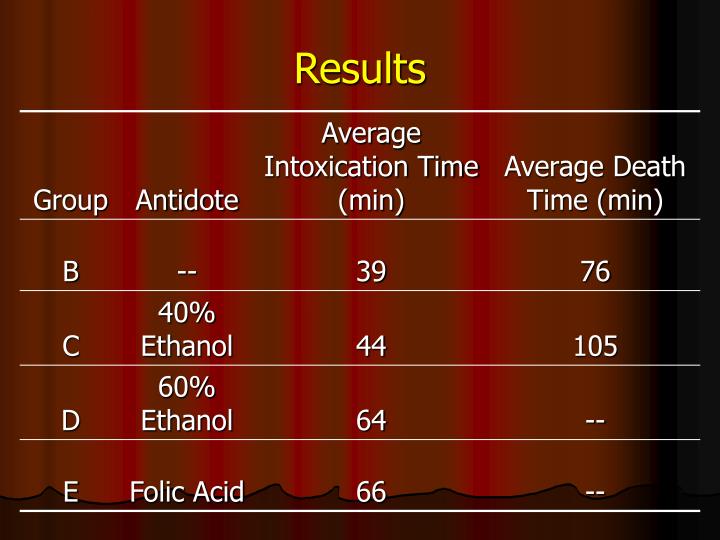
The patient initially was given fomepizole and dialyzed for 4 hours. Additional doses of fomepizole were given and dialysis was repeated during the hospitalization. With treatment, acid-base parameters and serum osmolality ( Table 1) returned to normal and the patient was discharged.