Full Answer
What are the treatments for HPV?
However, there are treatments for the health problems that HPV can cause: Genital warts can be treated by your healthcare provider or with prescription medication. Cervical precancer can be treated. Other HPV-related cancers are also more treatable when diagnosed and treated early.
How much AHCC does it take to cure HPV?
Based on the best available scientific evidence, 3 grams of HPV cure AHCC. Daily AHCC appears to be an effective AHCC HPV dosage for the eradication of HPV. Treatment with this supplement makes the virus dormant in the body, so to achieve continuous suppression, it is important to continue taking the supplement indefinitely.
How often should I have an HPV test?
For persons aged 30–65 years, a cytology test every 3 years, an HPV test alone every 5 years, or a cytology test plus an HPV test (cotest) every 5 years is recommended. Cotesting can be done by either collecting one sample for the cytology test and another for the HPV test or by using the remaining liquid cytology material for the HPV test.
How to get tested for HPV infection?
HPV infection 1 Diagnosis. Your doctor might be able to diagnose HPV infection by looking at your warts. 2 Treatment. Warts often go away without treatment, particularly in children. 3 Clinical trials. Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments,... 4 Preparing for your appointment. You'll likely start by seeing your primary care provider.

How much does it cost for HPV treatment?
How much does the HPV vaccine cost? Each dose of the vaccine can cost about $250. Luckily, many health insurance companies cover the HPV vaccine. There are also programs that help some people without insurance get the vaccine for low or no cost.
Can HPV be fully treated?
There's no treatment for HPV. Most HPV infections do not cause any problems and are cleared by your body within 2 years. Treatment is needed if HPV causes problems like genital warts or changes to cells in the cervix.
What is the best treatment for HPV?
HPV treatment optionsHPV usually does not need treatment. ... According to one study , the most effective treatment for genital warts is surgical removal. ... Cryotherapy is a procedure where a doctor freezes off genital warts. ... For home treatment, a doctor may recommend Condylox and Imiquimod.
Is HPV treatment covered by insurance?
Most insurance companies provide coverage for both the Pap test and the HPV test. Most states also cover Pap and HPV testing through their Medicaid programs for low-income women. Most large insurance plans usually cover the costs of HPV vaccines as well.
Can you clear HPV after 30?
There is no cure for HPV, but 70% to 90% of infections are cleared by the immune system and become undetectable. HPV peaks in young women around age of sexual debut and declines in the late 20s and 30s. But women's risk for HPV is not over yet: There is sometimes a second peak around the age of menopause.
How long does HPV take to clear?
For 90 percent of women with HPV, the condition will clear up on its own within two years. Only a small number of women who have one of the HPV strains that cause cervical cancer will ever actually develop the disease.
Can HPV 16 go away?
Progression depends on the type of HPV strain and on the unique characteristics of the individual who is infected. The longer the virus is present, the higher the potential for a cancer to develop. The good news is that more than 90% of HPV 16 and 18 infections go away within 6 to18 months of initial exposure.
Is HPV permanent?
In most cases, your body can produce antibodies against the virus and clear the virus within one to two years. Most strains of HPV go away permanently without treatment. Because of this, it isn't uncommon to contract and clear the virus completely without ever knowing that you had it.
What happens if you test positive for HPV?
If you get a positive HPV test, your physician has detected one or more high risk strains of the virus on the Pap test of your cervix. If the virus stays with you for a long time, it can cause cell changes that can lead to several types of cancer.
Do I need a colposcopy if I have HPV?
If you test positive for HPV 16/18, you will need to have a colposcopy. If you test positive for HPV (but did not have genotyping performed or had genotyping and tested negative for 16/18), you will likely have a colposcopy.
How often should I get a Pap smear if I have HPV?
every 5 years with high-risk HPV testing alone. every 5 years with Pap and high-risk HPV cotesting. every 3 years with a Pap test alone.
Is HPV a STI or STD?
HPV is a very common STI. Among 15- to 59-year-olds, 2 in 5 (40%) people will have HPV. There are many different types of HPV; most do not cause any health problems. HPV is a different virus than HIV or (HSV) herpes.
How to treat HPV in the cervix?
If you have an abnormal HPV or Pap test, your gynecologist will perform a procedure called a colposcopy. Using an instrument that provides a magnified view of the cervix (colposcope), your doctor will look closely at the cervix and take samples (biopsy) of any areas that look abnormal.
What is the best treatment for warts?
Salicylic acid. Over-the-counter treatments that contain salicylic acid work by removing layers of a wart a little at a time. For use on common warts, salicylic acid can cause skin irritation and isn't for use on your face. Imiquimod. This prescription cream might enhance your immune system's ability to fight HPV.
What does a doctor do if you have HPV?
If you have HPV, your doctor will want to make sure you don’t develop any problems from it . If you’re a woman, your doctor may swab cells from your cervix, just like when you get a Pap test, and send them to a lab for testing. This analysis looks for genetic material, or DNA, of HPV within the body's cells.
Why do you need a Pap test for HPV?
If your doctor finds that you have a type of HPV that can lead to cancer, they may suggest you get Pap tests more often to watch for signs of abnormal cell changes in the genital area. Abnormal cell changes in the cervix may be a warning sign cervical cancer.
How to remove a wart from a spherical object?
Your doctor can also prescribe other types of wart-removal treatments. Among the options: 1 Cryotherapy freezes off of the wart with liquid nitrogen. 2 Trichloracetic acid is a chemical that’s put on the surface of the wart. 3 They can remove the cells surgically, with a scalpel. 4 They can burn off warts using an electric current (electrocautery). 5 A laser can vaporize the warts.
How long does it take for genital warts to grow?
HPV types 6 and 11, which are linked to genital warts, tend to grow for about 6 months, then stabilize. Sometimes, visible genital warts go away without treatment. If you need treatment, your doctor can prescribe a cream that you can use at home. There are two options:
How long does it take for podofilox to kill warts?
There are two options: Podofilox ( Condylox) Imiquimod ( Aldara, Zyclara) You’d use podofilox for about 4 weeks. It destroys the wart tissue. Research shows that about 45% to 90% of warts clear up, but sometimes the warts come back. Imiquimod boosts the immune system so it fights off the virus.
Does cryotherapy remove warts?
It often clears the warts, but not always permanently. Your doctor can also prescribe other types of wart-removal treatments. Among the options: Cryotherapy freezes off of the wart with liquid nitrogen. Trichloracetic acid is a chemical that’s put on the surface of the wart.
Do warts go away?
Warts on moist surfaces respond better to treatments that go right on them, compared with warts on drier surfaces. If your warts don't go away after several treatments, your doctor might have more tests done to see if something else is going on.
Screening Recommendations
Recommendations for cervical cancer screening in the United States are based on systematic evidence reviews by major medical and advocacy organizations, including USPSTF ( 174 ), ACS ( 177 ), and ACOG ( 175 ).
Counseling
Persons might believe the cytology (Pap test) or HPV test screens for conditions other than cervical cancer, or they might be confused by abnormal results ( 1252 – 1254 ).
Promoting Cervical Cancer Screening
Clinics can use the evidence-based interventions in the Community Preventive Services Task Force guidelines to promote cervical cancer screening in their communities ( https://www.thecommunityguide.org/findings/cancer-screening-multicomponent-interventions-cervical-cancer external icon ).
Key Messages About Cervical Cancer Screening
When counseling persons about cervical cancer screening, the provider should discuss the following:
Management of Sex Partners
The benefit of disclosing a positive HPV test to current and future sex partners is unclear. The following counseling messages can be communicated to sex partners:
Screening Recommendations in Special Populations
Persons who are pregnant should be screened at the same intervals as those who are not. A swab, Ayre’s spatula, or cytobrush can be used for obtaining cytology test samples during pregnancy ( 1268 – 1270 ).
Human Papillomavirus Tests for Cervical Cancer Screening
Clinical tests for HPV are used for the following: cervical cancer screening as a primary test, cervical cancer screening with a cytology test, triage of some abnormal cervical cytology results, follow-up after abnormal screening test results, follow-up after a colposcopy in which no CIN 2 or CIN 3 is found, and follow-up after treatment of cervical precancers.
How long does it take for HPV to clear?
What to Do If You Have HPV. In most cases, the immune system will be able to clear human papillomavirus (HPV) on its own within 18 to 24 months, usually with no long-term consequences, though that is not always the case. 1 . Because there are no drugs available to treat an active HPV infection, HPV treatment involves resolving HPV symptoms ...
How to check for HPV?
If a woman tests positive for cervical HPV infection but has a normal Pap smear, the doctor may do one of two things: 4 1 Schedule another round of tests in 12 months. If the results are normal, you can return to normal screening. If they are not, additional testing will be needed. 2 Perform an HPV test to identify the two high-risk HPV strains (HPV 16 and HPV 18) that account for 70% of all cervical cancers. 5 If the results are negative (meaning you have not been infected with these specific viruses), you can be retested in 12 months as a safeguard. If the results are positive, additional testing will be needed.
What is the best treatment for warts?
Cryotherapy (freezing warts with liquid nitrogen) Electrocautery (using electricity to burn warts away) Surgery. Laser therapy. Trichloracetic acid (applied topically to gradually remove a wart) Genital warts should never be considered normal, and you should not treat them at home without first seeing a doctor.
What is the treatment for dysplasia?
For persons with moderate- to high-grade dysplasia, treatment would involve the removal of affected tissue using either a loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP), cone biopsy, cryotherapy, or other surgical techniques. 11 . It is important to remember that dysplasia is not cancer.
Can HPV be treated with drugs?
Because there are no drugs available to treat an active HPV infection, HPV treatment involves resolving HPV symptoms and monitoring for any changes in the skin or mucosal cells ; in addition to causing genital warts, more than 30 of the approximately 150 viruses that make up HPV are linked to cervical, anal, and other cancers.
Do genital warts cause health problems?
Though unsightly and uncomfortable, genital warts generally do not pose any major health risk. Most are caused by two low-risk strains, known as HPV 6 and HPV 11, which account for around 90% of all genital wart outbreaks. 8
What percentage of cancer is caused by HPV?
According to the CDC, other types of cancers have been attributed to HPV, such as 70 percent of oropharyngeal cancer, 90 percent of anal cancer, and 70 percent of vaginal and vulvar cancer (2). There are 100 different types of HPV, many of which do not cause cancer.
How many cancers are caused by HPV?
The human papillomavirus, otherwise known as HPV, is a common virus that contributes to an estimated 630,000 new cancer cases annually worldwide (1). Cancer of the cervix represents over 80 percent of the cases caused by the virus. According to the CDC, other types of cancers have been attributed to HPV, such as 70 percent of oropharyngeal cancer, ...
How long does it take for HPV to disappear from a Pap?
HPV often disappears from Pap test results within about two years, often without any treatment. While this scenario happens in the majority of cases, it does not always occur that way. In some instances of HPV infections, the virus stays dormant and surfaces many years later.
What age can you get HPV?
HPV Vaccination Recommendations. The CDC recommends HPV vaccination for girls and boys ages 11 to 12. It can also be given to anyone 26 and under who has not been adequately vaccinated and administered to children as young as 9 if needed. Some people up to age 45 are also eligible. 4 .
How many cancers are caused by HPV?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 36,000 new cancer diagnoses each year can be attributed to prior HPV infection. 2 These include: Cervical cancer. Anal cancer. Penile cancer.
How long does it take for HPV to clear?
Some studies estimate that 50 percent of those infected with HPV will clear the virus within eight months— and 90 percent will be cured within two years. It's only when your immune system isn’t able to fight off the infection that some strains of HPV can persist and possibly lead to cancer.
What are the best vitamins to fight HPV?
“I would tank up on certain vitamins,” Landa said. “Several vitamins have been shown to increase the likelihood of clearing the HPV.”. “The first one is B vitamins— especially Folic acid and B12.
What is the most common STI in the US?
The human papillomavirus, or HPV, is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI) in the United States. In fact, it's so common that nearly all sexually active men and women get it at some point in their lives.
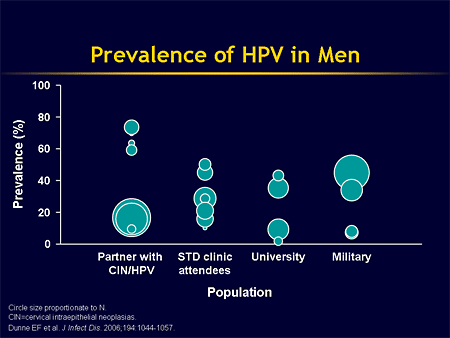
Is there a test for HPV in men?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved an HPV test for women over 30 years old, but there is currently no HPV test for men.
How much will the HPV vaccine cost?
For people not covered by medical insurance, the expense of HPV vaccination normally consists of shot administration costs and the expense of the 3 needed dosages of the vaccine at about $125 each, for an overall of $400 to $500.
What should be included in the expense?
The HPV vaccination will require 3 shots to work as intended. The 2nd shot is provided 2 months after the very first, and the last shot is offered 6 months after the initial one. The vaccine is practically one hundred percent efficient in protecting you against the 4 targeted strains of HPV.
Extra expenses to take into account
HPV vaccination can be done at a regular doctor’s office; otherwise, the doctor consultation fee or copay will be an extra expense. According to a CDC fact check, the HPV vaccine supplies protection for a minimum of 5 years, and more research is being done to see if it offers protection for even longer periods of time.
Discount rates to take advantage of
Eligible ladies 18 and younger can get the HPV vaccination free of charge through the Vaccines for Children program. Or, for eligible females older than 18, Merck provides Gardasil through its patient help program.
Looking for human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine
Talk to your kid’s pediatrician or your family physician.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle
Prescriptions
- Genital warts and anal warts are caused by human papillomavirus. There are roughly 40 different low-risk HPV types that can cause genital warts, the vast majority of which are caused by HPV6 and HPV11.9 The HPV types that cause genital warts rarely cause cancer. Even so, they can be itchy, painful, or unsightly.9 Most genital warts will resolve on their own without treatment withi…
Surgery and Specialist-Driven Procedures
- Specialist procedures, including surgery, are sometimes used to treat genital warts that are not responsive to at-home treatments. The same applies to HPV-related changes in cells that can lead to cancer, referred to as dysplasia.
Vaccination
- Scientists have long been trying to develop a therapeutic vaccine that can prevent high-risk HPV from causing cancer. Despite advances in research, there are currently no therapeutic HPV vaccines approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).22 This doesn't mean that the current preventive vaccine, called Gardasil-9, doesn't play a role in people who already have HPV…
Summary
- There is no cure for human papillomavirus (HPV). The treatment is instead focused on managing the conditions that HPV can cause. This includes genital and HPV warts. These conditions may be treated with topical prescription drugs or removed with procedures like cryotherapy, laser therapy, electrocautery, and surgery. There are also procedures used to treat HPV-related dysplasia (cha…
A Word from Verywell
- While an HPV diagnosis can be distressing, it helps you catch any problems before they become serious or even life-threatening. By and large, treatments for HPV-associated conditions have few complications. Many of the treatments are covered, at least in part, by health insurance. Patient assistance and co-pay assistance programsare also available to reduce your out-of-pocket cost…