Find a Monoclonal Antibody Treatment Location
- Barnstorm Theater 2720 Brownwood Blvd, The Villages, FL 32163 Hours: Monday: 9 AM to 5 PM Tuesday: 9 AM to 5 PM Wednesday: 9 AM to 5 PM Thursday: 9 ...
- Bay County Fairgrounds 2230 E. ...
- CB Smith Park 900 N Flamingo Rd, Pembroke Pines, FL 33028 Hours: Monday: 9 AM to 5 PM Tuesday: 9 AM to 5 PM Wednesday: 9 AM to 5 PM ...
How effective is the monoclonal treatment?
Monoclonal Antibody Treatment for COVID-19 Eligibility: Talk with your healthcare provider to find out if you qualify for a COVID-19 treatment. You may be eligible if you: have recently tested positive for COVID-19, have been in close contact with someone who has tested positive, are immunocompromised, or have had a severe adverse reaction to a ...
What are the dangers of monoclonal antibodies?
Jan 06, 2022 · “Some people will still be hospitalized for COVID-19. The most effective thing you can do is get vaccinated and to wear a mask.” If you think you may qualify for monoclonal antibody therapy and want to ask about getting treatment, contact your health care provider. If you live in Utah, you may fill out this questionnaire to see if you qualify.
How safe is monoclonal antibodies?
Apr 07, 2022 · March 08, 2022 18:48 Updated Follow All monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapies are in limited supply, and not everyone will be eligible for treatment. A prescription from a healthcare provider is required to receive any mAb therapy. Variants, like Omicron, may have an impact on the effectiveness of mAb therapies.
Does Medicare cover monoclonal antibodies?
Preventative Monoclonal Antibody Therapy: EvuSheld. Preventative monoclonal antibody therapy locations are marked with a blue pin on the locator map. AstraZeneca’s Evusheld is authorized for pre-exposure prophylaxis (prevention) of COVID-19 in certain populations age 12 and older. Specifically, it is for:

What is a monoclonal antibody for COVID-19?
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-produced molecules that act as substitute antibodies that can restore, enhance or mimic the immune system's attack on cells. Monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 may block the virus that causes COVID-19 from attaching to human cells, making it more difficult for the virus to reproduce and cause harm. Monoclonal antibodies may also neutralize a virus.Mar 31, 2022
Is there an antibody cocktail for COVID-19?
The treatment, bamlanivimab and etesevimab administered together, was granted FDA emergency use authorization in February. Eli Lilly and the FDA stipulated that the antibody cocktail is authorized as a COVID-19 prophylaxis only for individuals who have been exposed to the virus.Sep 16, 2021
How long do COVID-19 antibodies last?
At this time, it is unknown for how long antibodies persist following infection and if the presence of antibodies confers protective immunity.Jan 31, 2022
How many types of monoclonal antibody COVID-19 treatments are there in the US?
In the United States, there are three anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody treatments with FDA Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the treatment of COVID-19: bamlanivimab plus etesevimab, casirivimab plus imdevimab,, and sotrovimab.
Are antibiotics effective in preventing or treating COVID-19?
Antibiotics do not work against viruses; they only work on bacterial infections. Antibiotics do not prevent or treat COVID-19, because COVID-19 is caused by a virus, not bacteria. Some patients with COVID-19 may also develop a bacterial infection, such as pneumonia.Mar 31, 2022
What antiviral drugs are available for treatment of COVID-19?
Remdesivir is the only drug that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of COVID-19. Ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid), molnupiravir, and certain anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have received Emergency Use Authorizations from the FDA for the treatment of COVID-19.Feb 24, 2022
How long do antibodies last in people who have mild COVID-19 cases?
A UCLA study shows that in people with mild cases of COVID-19, antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 — the virus that causes the disease — drop sharply over the first three months after infection, decreasing by roughly half every 36 days. If sustained at that rate, the antibodies would disappear within about a year.
How long does it take for antibodies to develop after exposure to COVID-19?
It can take days to weeks after an infection for your body to make antibodies.Feb 24, 2022
Do people produce COVID-19 antibodies after infection?
Most people who've recovered from COVID-19 do make antibodies against the virus.Jan 21, 2022
What is the first drug that was approved by the FDA to treat COVID-19?
Remdesivir is the first drug approved by the FDA for treatment of hospitalized COVID patients over the age of 12.Jan 25, 2022
Which drug is approved by FDA to treat COVID-19?
Veklury (Remdesivir) is an antiviral drug approved for use in adults and pediatric patients [12 years of age and older and weighing at least 40 kilograms (about 88 pounds)] for the treatment of COVID-19 requiring hospitalization.Mar 31, 2022
How many types of COVID-19 vaccines are available in the US?
Three COVID-19 vaccines are authorized or approved for use in the United States to prevent COVID-19. Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna (COVID-19 mRNA vaccines) are preferred. You may get Johnson & Johnson's Janssen COVID-19 vaccine in some situations.
What are monoclonal antibodies?
Our bodies naturally make antibodies to fight infections. However, if you haven’t received the COVID-19 vaccine or had a previous COVID-19 infection, your body will not have antibodies designed to recognize a new virus like SARS-CoV-2.
How does monoclonal antibody therapy help?
Monoclonal antibody therapy is a way of treating COVID-19 for people who have tested positive, have had mild symptoms for seven days or less, and are at high risk for developing more serious symptoms.
Who is eligible for monoclonal antibody therapy?
Given that COVID-19 vaccination provides strong protection against severe disease and need for hospitalization, monoclonal antibody therapy is an option for certain high-risk patients with COVID-19.
Monoclonal Antibody Therapy
Glaxo Smith Kline’s monoclonal antibody Sotrovimab is authorized for the treatment of mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in:
Preventative Monoclonal Antibody Therapy: EvuSheld
Preventative monoclonal antibody therapy locations are marked with a blue pin on the locator map.
WHAT IS A MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY?
Your body naturally makes antibodies to fight infection. However, your body may not have antibodies designed to recognize a novel (or new) virus like SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
How Can I Get Monoclonal Antibodies?
To receive a mAb you should be referred for treatment by your healthcare professional and directed to available infusion locations. If you do not have a healthcare provider, call the Combat COVID Monoclonal Antibodies Call Center at 1-877-332-6585 to find out who to talk with about your symptoms and treatment.
WHAT IF I DO NOT QUALIFY FOR MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY TREATMENT?
Your healthcare professional may decide you do not qualify for mAb treatment. There could be several reasons for this. You may not meet all eligibility criteria or you may have an underlying health condition that disqualifies you for mAb treatment.
WHAT CAN I EXPECT FROM TREATMENT (INFUSION)?
The mAb treatment is usually offered at an infusion center because the treatment is given through an intravenous (IV) infusion or shots. Depending on the mAb treatment you receive, the whole process takes about 1-3 hours, depending on the treatment..
CAN MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY TREATMENT MAKE ME SICK?
Antibody treatments do not contain any live SARS-CoV-2, so there is no risk you will get COVID-19 from mAb treatment. However, the antibody treatment may have side effects:
About the Treatment
Antibodies are proteins that exist in our immune system. They recognize and defend against harmful viruses and bacteria.
Fruita Clinic
We are located at 401 Kokopelli Blvd, in the Kokopelli Plaza Shopping Center just off Interstate 70 (I-70) in Fruita.
What antibody is used to block the virus?
Monoclonal antibodies against COVID-19 attach to the virus to block it from entering human cells. The monoclonal antibody protein also “marks” the virus to be broken down by the immune system and cleared from the body.
What is the function of antibodies?
Antibodies are proteins that exist in our bodies as part of our immune system to recognize and defend against harmful viruses and bacteria. Monoclonal antibodies are made in a laboratory and designed to target a specific virus or bacteria.
Can monoclonal antibodies cause nausea?
Most people tolerate monoclonal antibody infusions very well. Some people may experience infusion-related side effects, such as nausea and dizziness, that are short-lived and go away on their own. As with any medication, there is the potential for mild or more severe allergic reactions, which are uncommon.
What is monoclonal antibody?
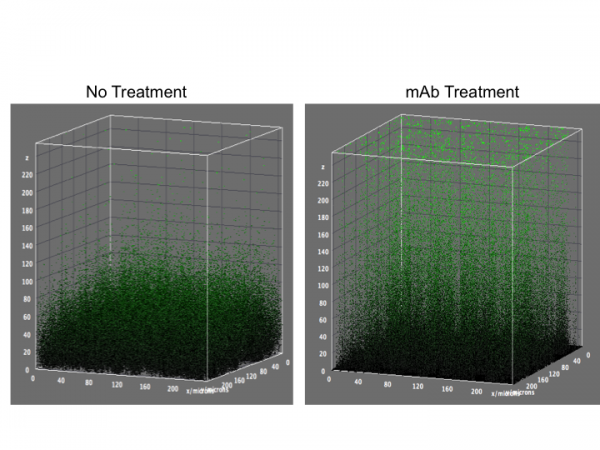
Monoclonal antibodies are synthetic antibodies that mimic the immune system’s response to an infection. Initial data shows that mAb treatment reduces the risk of hospitalization and death in COVID-19 patients and slows down progression of the virus in the community.
Can you use bamlanivimab and etesevimab together?
In addition, FDA recommends that health care providers nationwide use alternative authorized monoclonal antibody therapies, as described below, and not use bamlanivimab and etesevimab administered together at this time.