
Monoclonal antibody therapy
Monoclonal antibody therapy is a form of immunotherapy that uses monoclonal antibodies (mAb) to bind monospecifically to certain cells or proteins. This may then stimulate the patient's immune system to attack those cells. Alternatively, in radioimmunotherapy a radioactive dose localiz…
Who can get Regeneron treatment?
Jan 06, 2022 · Individuals qualify for monoclonal antibody treatment if: they have tested positive for COVID-19, and; it has been 10 days or less since symptoms first started, and; they have other health conditions that put them at higher risk. Monoclonal antibody treatment is most effective when given early—and the sooner it is given, the better.
How soon should you get monoclonal antibodies?
1-877-332-6585. If you are at risk for serious COVID-19 and you have tested positive for COVID-19 or have been in close contact with someone who has tested positive, you may want to consider a monoclonal antibody (mAb) treatment. You may qualify for a mAb treatment ( bebtelovimab) for this promising COVID-19 treatment depending on your age, health history, and how long you …
What are the dangers of monoclonal antibodies?
Apr 13, 2022 · April 13, 2022 16:39 Updated Follow All monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapies are in limited supply, and not everyone will be eligible for treatment. A prescription from a healthcare provider is required to receive any mAb therapy. Variants, like Omicron, may have an impact on the effectiveness of mAb therapies.
Can everyone get Regeneron?
Dec 21, 2021 · Who is eligible for monoclonal antibody treatment? If you believe you are at high risk for progression of severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or …
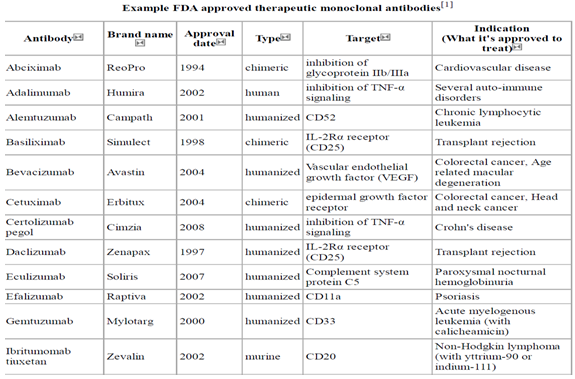
Who could benefit from monoclonal antibody therapy to prevent COVID-19?
See full answerVaccines are the best way to protect against COVID-19. But some people with weakened immune systems do not produce enough antibodies after vaccination, and others are severely allergic to the vaccine. The FDA recently authorized Evusheld, a pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) monoclonal antibody therapy developed by AstraZeneca, which should help prevent COVID-19 in these populations.To be eligible for Evusheld, individuals must be 12 years or older and have a moderately to severely weakened immune system, or have a history of severe adverse reactions to the COVID-19 vaccine or its components. In addition, the therapy cannot be given to someone with a current SARS-CoV-2 infection, or who has been recently exposed to someone who is infected. Evusheld is given as two consecutive shots, and evidence suggests it can help prevent symptomatic infection for at least six months.Apr 1, 2022
How do monoclonal antibodies work against COVID-19?
Monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 may block the virus that causes COVID-19 from attaching to human cells, making it more difficult for the virus to reproduce and cause harm. Monoclonal antibodies may also neutralize a virus.Mar 31, 2022
Is there a monoclonal antibody therapy for post COVID-19 exposure?
FDA authorizes bamlanivimab and etesevimab monoclonal antibody therapy for post-exposure prophylaxis (prevention) for COVID-19 | FDA.Sep 16, 2021
How many types of monoclonal antibody COVID-19 treatments are there in the US?
In the United States, there are three anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody treatments with FDA Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the treatment of COVID-19: bamlanivimab plus etesevimab, casirivimab plus imdevimab,, and sotrovimab.
What is a monoclonal antibody?
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-produced molecules that act as substitute antibodies that can restore, enhance or mimic the immune system's attack on cells.Mar 31, 2022
Can I get the COVID-19 vaccine if I was treated with monoclonal antibodies or convalescent plasma?
If you were treated for COVID-19 symptoms with monoclonal antibodies or convalescent plasma, you should wait 90 days before getting a COVID-19 vaccine.
Is there an antibody cocktail for COVID-19?
The treatment, bamlanivimab and etesevimab administered together, was granted FDA emergency use authorization in February. Eli Lilly and the FDA stipulated that the antibody cocktail is authorized as a COVID-19 prophylaxis only for individuals who have been exposed to the virus.Sep 16, 2021
Is it possible to develop immunity to COVID-19 after being exposed?
In addition, the hope is that people who've been exposed to COVID-19 also develop an immunity to it. When you have immunity, your body can recognize and fight off the virus. It's possible that people who've had COVID-19 can get sick again -- and maybe infect other people.Jan 21, 2022
Should I get the COVID-19 vaccine if I had COVID-19?
Yes, you should be vaccinated regardless of whether you already had COVID-19.
Which drug is approved by FDA to treat COVID-19?
Veklury (Remdesivir) is an antiviral drug approved for use in adults and pediatric patients [12 years of age and older and weighing at least 40 kilograms (about 88 pounds)] for the treatment of COVID-19 requiring hospitalization.Mar 31, 2022
How many types of COVID-19 vaccines are available in the US?
Three COVID-19 vaccines are authorized or approved for use in the United States to prevent COVID-19. Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna (COVID-19 mRNA vaccines) are preferred. You may get Johnson & Johnson's Janssen COVID-19 vaccine in some situations.
What is the first drug that was approved by the FDA to treat COVID-19?
Remdesivir is the first drug approved by the FDA for treatment of hospitalized COVID patients over the age of 12.Jan 25, 2022
What is the purpose of monoclonal antibody therapy?
The goal of this therapy is to help prevent hospitalizations, reduce viral loads and lessen symptom severity.
What are monoclonal antibodies?
However, monoclonal antibodies are mass-produced in a laboratory and are designed to recognize a specific component of this virus — the spike protein on its outer shell .
What antibodies interfere with the virus?
By targeting the spike protein, these specific antibodies interfere with the virus' ability to attach and gain entry into human cells. The two monoclonal antibody therapies currently available are the bamlanivimab and a combination of the casirivimab and imdevimab.
WHAT IS A MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY?
Your body naturally makes antibodies to fight infection. However, your body may not have antibodies designed to recognize a novel (or new) virus like SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
How Can I Get Monoclonal Antibodies?
To receive a mAb you should be referred for treatment by your healthcare professional and directed to available infusion locations. If you do not have a healthcare provider, call the Combat COVID Monoclonal Antibodies Call Center at 1-877-332-6585 to find out who to talk with about your symptoms and treatment.
WHAT IF I DO NOT QUALIFY FOR MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY TREATMENT?
Your healthcare professional may decide you do not qualify for mAb treatment. There could be several reasons for this. You may not meet all eligibility criteria or you may have an underlying health condition that disqualifies you for mAb treatment.
WHAT CAN I EXPECT FROM TREATMENT (INFUSION)?
The mAb treatment is usually offered at an infusion center because the treatment is given through an intravenous (IV) infusion or shots. Depending on the mAb treatment you receive, the whole process takes about 1-3 hours, depending on the treatment..
CAN MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY TREATMENT MAKE ME SICK?
Antibody treatments do not contain any live SARS-CoV-2, so there is no risk you will get COVID-19 from mAb treatment. However, the antibody treatment may have side effects:
Monoclonal antibody treatment in Colorado
A treatment is becoming more widely available statewide for people who test positive for COVID-19 and have mild to moderate symptoms but are at high risk of becoming severely ill: monoclonal antibodies.
Larimer County providers offering monoclonal antibody treatment
If you are not fully vaccinated and have been exposed to COVID-19, here are the organizations the state says you should contact to see if you're eligible for monoclonal antibody treatment:
What are monoclonal antibodies, and how do they work?
Monoclonal antibodies are lab-made antibodies that work by binding to bacteria, cancer cells or viruses the way natural antibodies do, stopping them from infecting more cells. The first monoclonal antibody therapy was approved more than 30 years ago and has been used for other diseases, including cancer .
Who's eligible?
The monoclonal antibody made by GlaxoSmithKline and Vir Biotechnology ( sotrovimab) is authorized for people 12 and up who are at risk of getting severely sick from COVID-19 within 10 days of their symptoms starting. People eligible include adults age 65 and up and people living with diabetes, asthma or other medical conditions.
Why did the FDA stop the use of some monoclonal antibodies?
The virus that causes COVID-19 has mutated over time, and the newest variant causing a wave of infections, omicron, has reduced the effectiveness of some COVID-19 treatments, including the monoclonal antibodies made by Eli Lilly and Regeneron.
How do I get treatment? Is it free?
In January, it was announced that the US government would purchase an additional 600,000 doses of sotrovimab, up from its November agreement. This means the drug itself is free, but you may have to pay the administration fee depending on your insurance.
Do monoclonal antibodies interfere with the coronavirus vaccines?
If you were treated with monoclonal antibodies and you haven't been vaccinated yet, you should wait 90 days after your treatment to get the shot, according to the CDC. This recommendation is until more is known about how the antibody response from the treatment affects the immune response from getting vaccinated.
