Why do we need water treatment?
Drinking water sources are subject to contamination and require appropriate treatment to remove disease-causing agents. Public drinking water systems use various methods of water treatment to provide safe drinking water for their communities.
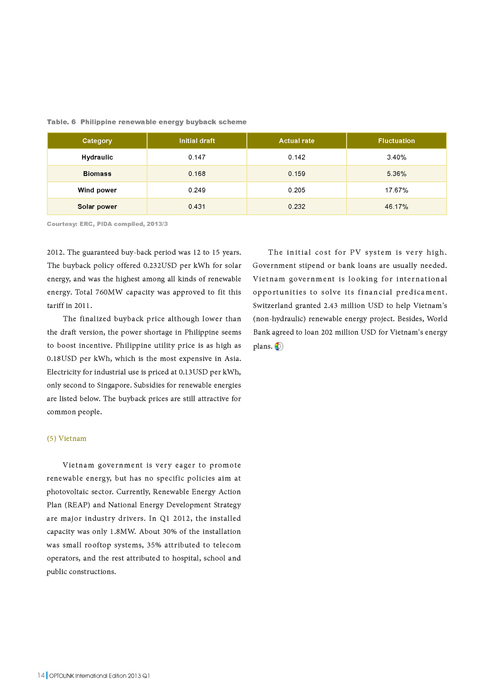
What are the top 7 methods of water treatment?
Top 7 Methods of Water Treatment. 1 Coagulation / Flocculation. Coagulation is adding liquid aluminum sulfate or alum and/or polymer to raw or untreated water. The resulting mixture ... 2 Sedimentation. 3 Filtration. 4 Disinfection. 5 Sludge Drying. More items
Why does surface water require more treatment and filtration?
Typically, surface water requires more treatment and filtration than ground water because lakes, rivers, and streams contain more sediment and pollutants and are more likely to be contaminated than ground water. Some water supplies may also contain disinfections by-products, inorganic chemicals, organic chemicals, and radionuclides.
What is the first step in water treatment?
Coagulation and flocculation are often the first steps in water treatment. Chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water. The positive charge of these chemicals neutralizes the negative charge of dirt and other dissolved particles in the water.
What are the 4 steps of water treatment?
4 Steps of Community Water TreatmentCoagulation and Flocculation. ... Sedimentation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection.
What are the 5 steps of water treatment?
The 5 major unit processes include chemical coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection (described below). There are chemicals added to the water as it enters the various treatment processes.
What are the 3 parts of the water treatment process?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.
What is not removed during water treatment?
Biological stages in wastewater treatment plants are not able to remove substances such as drugs, found in the wastewater of medical centers, or halogenated compounds and cyanides from industrial wastewater.
What is water treatment process?
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, including being safely returned to the environment.
What is the first step in water treatment?
The first step is coagulation, which involves adding chemicals to the water. That causes small particles to adhere to one another, or coagulate. The second step is called flocculation, in which larger particles called flocc form after coagulation.
What are the types of water treatment?
Four Common Water Treatment Methods:Reverse Osmosis Water Filtration. Reverse Osmosis is a process where water pressure is employed to force water through a semi-permeable membrane. ... Ultraviolet Water Sterilization and Filtration. ... Filtration. ... Distillation.
What are the 7 methods of water treatment?
Top 7 Methods of Water TreatmentCoagulation / Flocculation. Coagulation is adding liquid aluminum sulfate or alum and/or polymer to raw or untreated water. ... Sedimentation. When water and flocs undergo the treatment process, they go into sedimentation basins. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection. ... Sludge Drying. ... Fluoridation. ... pH Correction.
What are the three stages in the treatment of water give the objectives of each stage?
The three stages of wastewater treatment are known as primary, secondary and tertiary. Each stage purifies water to a higher level. In some applications, only one or two stages are necessary. The level of treatment necessary depends on the water's intended use case, and what environment it will be discharged into.
What materials Cannot be removed from wastewater?
When wastewater arrives at the treatment plant, it contains many solids that cannot be removed by the wastewater treatment process. This can include rags, paper, wood, food particles, egg shells, plastic, and even toys and money.
What is removed in wastewater treatment?
Suspended solids that pass through screens and grit chambers are removed from the sewage in sedimentation tanks.
What is removed during wastewater treatment?
As sewage enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen, which removes large floating objects such as rags and sticks that might clog pipes or damage equipment. After sewage has been screened, it passes into a grit chamber, where cinders, sand, and small stones settle to the bottom.
Why are pathogens removed from water?
Usually, the pathogens that are removed from the water are removed because they are attached to the dissolved substances that are removed by coagulation. In the picture below, the coagulants have been added to the water, and the particles are starting to bind together and settle to the bottom.
What is the most widely used water treatment technology?
Many water treatment plants use a combination of coagulation, sedimentation, filtration and disinfection to provide clean, safe drinking water to the public. Worldwide, a combination of coagulation, sedimentation and filtration is the most widely applied water treatment technology, and has been used since the early 20th century.
Why is coagulation important in water treatment?
It is, however, an important primary step in the water treatment process, because coagulation removes many of the particles, such as dissolved organic carbon, that make water difficult to disinfect. Because coagulation removes some of the dissolved substances, less chlorine must be added to disinfect the water.
What is added to ferric chloride?
If ferric chloride is used, iron and chloride are added. And if aluminum sulphate is used, aluminum and sulphate are added. The majority of municipal water treatment plants use aluminum sulphate as the coagulation chemical. Generally, water treatment facilities have the coagulation process set up so that the coagulant chemicals are removed with ...
What is residual water?
Residuals are the by-products that remain in the water after substances are added and reactions occur within the water. The particular residuals depend on the coagulant that is used. If ferric sulphate is used, iron and sulphate are added to the water. If ferric chloride is used, iron and chloride are added.
What is slow sand filtration?
that are used. Slow sand filtration removes bacteria, protozoa and viruses, and produces. essentially clean water, though it is still advisable to use a disinfectant as a precautionary. measure.
How is fine sand removed from water?
Particles with a diameter greater than 100 microns (or 0.1 millimetre), such as fine sand, are removed through sand filtration. As the pore size decreases, a greater proportion of material is retained as the water passes through the filter.
What is the purpose of a water filter?
Filtration. In filtration, water passes through a filter, which is made to take away particles from the water. Such filters are composed of gravel and sand or sometimes crushed anthracite. Filtration gathers together impurities that float on water and boosts the effectiveness of disinfection.
Why is water so undrinkable?
This brings about an undrinkable solution, since it can contain deadly bacteria and viruses, among other disease-causing agents.
