Medication
To find the right prescription medication to help you sleep, your doctor generally should:
- Ask questions to get a clear picture of your sleep patterns
- Order tests to rule out any underlying conditions that may be causing difficulty sleeping
- Discuss options for taking prescription sleeping medication, including how often and when to take it and in what form, such as pills, oral spray or dissolving tablets
Therapy
The results of this study showed that daridorexant may potentially be effective and safe in treating insomnia in older adults. This was a small study with only 58 participants. The next step will be to do a study including more people. This will give a better idea of how well daridorexant works and how safe it is.
Self-care
- Types of prescription sleeping pills. Prescription sleeping pills may help you fall asleep easier or stay asleep longer — or both. ...
- Side effects of prescription sleeping pills. ...
- Antidepressants with a sedating effect. ...
- Side effects of antidepressants with a sedating effect
- Safety considerations. ...
- Taking sleeping pills. ...
Nutrition
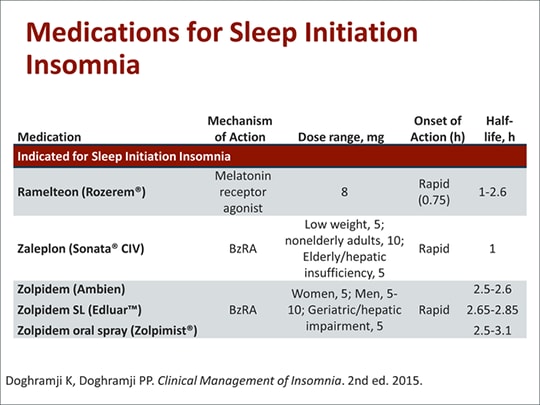
Some of the most common sleep aids and their respective half-lives, in parentheses, include:
- Benadryl or diphenhydramine (3.4 to 9.2 hours)
- Unisom or doxylamine (10 hours)
- Ambien, Ambien CR, or zolpidem (2.5 to 3.1 hours)
- Lunesta or eszopiclone (6 hours)
- Sonata or zaleplon (1 hour)
- Silenor or doxepin (15.3 hours for parent drug, 31 hours for metabolites)
- Belsomra or suvorexant (12 hours)
See more
What is the best long term sleep medication?
Is there a safe and effective medication for insomnia?
What is a good med Ro take for insomnia?
How long does insomnia last after taking Benadryl?

What sleeping pills are approved for long-term use?
The three drugs approved are eszopiclone, ramelteon, and zolpidem extended release.
Which medications are FDA approved for insomnia?
Currently, five BZDs are FDA-approved for the treatment of insomnia: triazolam (Halcion, Pfizer), estazolam (ProSom, Abbott), temazepam (Restoril, Mallinckrodt), quazepam (Doral, Questcor), and flurazepam. All of these agents are Schedule IV controlled substances because of their potential for abuse or dependence.
What is the best long-term treatment for insomnia?
Sleeping pills may help when stress, travel or other disruptions keep you awake. For long-term insomnia, behavior changes learned in behavioral therapy is usually the best treatment.
What is the best medication for sleep maintenance insomnia?
The AASM recommends the following pharmacotherapies1: For sleep maintenance insomnia: suvorexant, eszopiclone, zolpidem, temazepam, doxepin. For sleep onset insomnia: eszopiclone, zaleplon, zolpidem, triazolam, temazepam, ramelteon.
Drugs used for Insomnia
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Alternative treatments for Insomnia
The following products are considered to be alternative treatments or natural remedies for Insomnia. Their efficacy may not have been scientifically tested to the same degree as the drugs listed in the table above. However there may be historical, cultural or anecdotal evidence linking their use to the treatment of Insomnia.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
What is the best treatment for insomnia?
Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) can help you control or eliminate negative thoughts and actions that keep you awake and is generally recommended as the first line of treatment for people with insomnia. Typically, CBT-I is equally or more effective than sleep medications.
What is the therapy for learning insomnia?
Also called paradoxical intention, this therapy for learned insomnia is aimed at reducing the worry and anxiety about being able to get to sleep by getting in bed and trying to stay awake rather than expecting to fall asleep. Light therapy.
How does sleep restriction work?
Sleep restriction. This therapy decreases the time you spend in bed and avoids daytime naps, causing partial sleep deprivation, which makes you more tired the next night. Once your sleep has improved, your time in bed is gradually increased. Remaining passively awake.
How to get rid of insomnia?
If these measures don't work, your doctor may recommend cognitive behavioral therapy, medications or both , to help improve relaxation and sleep.
What is the diagnosis of insomnia?
Diagnosis. Depending on your situation, the diagnosis of insomnia and the search for its cause may include: Physical exam. If the cause of insomnia is unknown, your doctor may do a physical exam to look for signs of medical problems that may be related to insomnia. Occasionally, a blood test may be done to check for thyroid problems ...
How to reduce anxiety at bedtime?
Relaxation techniques. Progressive muscle relaxation, biofeedback and breathing exercises are ways to reduce anxiety at bedtime. Practicing these techniques can help you control your breathing, heart rate, muscle tension and mood so that you can relax. Sleep restriction.
What are the side effects of sleeping pills?
Ramelteon (Rozerem) Zaleplon (Sonata) Zolpidem (Ambien, Edluar, Intermezzo, Zolpimist) Prescription sleeping pills can have side effects, such as causing daytime grogginess and increasing the risk of falling, or they can be habit-forming, so talk to your doctor about these medications and other possible side effects.
What are some medications that help you sleep?
9 medications/ pills to help you sleep. You can take a number of medications to fight insomnia and help you sleep. Such medications include: 1. Benzodiazepines. These types of medications, which may include triazolam (Halcion) and emazepam (Restoril), are the best type of medication that stays longer in the system.
What hormone is used to treat insomnia?
Melatonin is a widely studied hormone in the treatment of insomnia. It is a hormone produced by the pineal glands in the body but is also found in some plants. Its produced by the body to control sleep wake cycles. Currently there are synthetic melatonin in the market for insomnia treatment.
What are the side effects of sleeping pills?
Most of the sleep medications have different side effects. As such, it is advisable to have prior knowledge of the potential side effects of the medication you have about to take. However, these side effects vary based on the prescription and the type of the sleeping pills. The common ones include: 1 Light headedness or dizziness that leads to falls 2 Headaches 3 Gastrointestinal issues like nausea and diarrhea 4 Extended drowsiness for medications, which help you stay asleep 5 Allergic reactions 6 Sleep-associated behaviors 7 Performance and memory problems
What is Belsomra used for?
Belsomra is used for the treatment of insomnia. Its efficiency is pegged on the drug’s ability to block the hormone responsible for the promotion of wakefulness. FDA approves the use of Belsomra for the treatment of individuals with insomnia resulting from challenges of staying asleep or total failure to fall asleep.
What is insomnia related to?
Research indicates that insomnia affects over 10% of adult Americans. It is associated with a feeling of irritability, sadness, and anxious and can account for people’s anxiety and depression.
What is the best herb to use for insomnia?
Chamomile is the most widely used herb extract as a sleeping aid. It is taken in tea, or pills to cure insomnia. It may also be used as a sachet in the bed to induce a good night sleep. This herb enables one to get sleep in the short term or long term.
How long does eszopiclone help you sleep?
Eszopiclone (Lunesta) Lunesta is a great medication for anyone who wants to fall asleep quickly. It can help you sleep for a period of up to 8 hours. To avoid grogginess, it is advisable to take the medication whenever you have the time for a full night’s sleep. 5.
Abstract
Chronic insomnia disorder, which affects 6–10% of the population, is diagnostically characterized by ongoing difficulties with initiating or maintaining sleep occurring at least three times per week, persisting for at least 3 months, and associated with daytime impairment.
Introduction
Insomnia disorder is described by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) International Classification of Sleep Disorders, Third Edition, as having frequent and persistent difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep that results in general sleep dissatisfaction despite adequate opportunity for sleep.
Pathophysiology of Insomnia
Several models of insomnia etiology and pathophysiology have been proposed, most of which suggest that both external stressors as well as internal psychologic factors have a role.
Nonpharmacologic Treatments for Chronic Insomnia
As regards behavioral and psychological treatments for chronic insomnia, clinical practice guidelines from the AASM and the American College of Physicians (ACP) both indicate that standard-of-care should be to at least provide cognitive behavioral therapies for insomnia (CBT-I) as first-line nonpharmacologic treatment.
Conclusions
Several advances in the nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic treatment options for chronic insomnia have occurred recently.
Acknowledgments
Medical writing assistance was provided by Christina McManus of Envision Pharma Group. Services provided by Envision Pharma Group complied with international guidelines for Good Publication Practice (GPP3).
Funding Statement
Funding for medical writing assistance was provided by Eisai Inc., who was not involved in any aspects of manuscript preparation.
What is the best medication for insomnia?
Antidepressants such as trazodone (25-100 mg), doxepin (10-50 mg), amitriptyline (10 -50 mg), imipramine (10-75 mg), and mirtazapine (5-15 mg) are commonly used for insomnia due to their sedative properties, however the evidence for their use is less convincing. Atypical antipsychotics. Most of the atypical antipsychotics (quetiapine, ...
How long does melatonin last?
Its half-life is ~5-10 hours, but is much longer in elderly. Most over the counter products contain diphenhydramine or a similar sedating antihistamine, including products such as Unisom, Tylenol PM, and Nyquil. Melatonin is used for circadian rhythm sleep disorders and is less effective for chronic insomnia.
What are some atypical antipsychotics?
Atypical antipsychotics. Most of the atypical antipsychotics (quetiapine, olanzapine and ziprasidone), except for risperidone, improve total sleep time and/or sleep efficiency in healthy subjects and schizophrenic patients.
Is diphenhydramine good for elderly?
Diphenhydramine or other classical anti-histamines have sedative properties, but they are generally not preferred in the elderly due to anticholinergic properties and drug interactions . Diphenhydramine (25-100 mg) has been shown to increase sleep duration but not quality (as it does not affect sleep architecture).
Is melatonin safe for insomnia?
Melatonin is used for circadian rhythm sleep disorders and is less effective for chronic insomnia. It has short half-life (45-60 min), has been used in doses ranging from 0.3 to 20 mg, is not FDA approved, and does not have any significant effects on either sleep onset latency or sleep efficiency.
Is Choral Hydrate more toxic than benzodiazepines?
Choral Hydrate has moderate short term efficacy but is more toxic than benzodiazepines. Barbiturates are effective in short term treatment, but tolerance develops rapidly. Once commonly used for insomnia, these drugs are no longer used except in rare circumstances. Antihistamines and over-the-counter drugs.
Can benzodiazepines be used for insomnia?
Non-Specific Drug Treatment: Benzodiazepines have been successfully used for short term insomnia as they improve sleep quality, total sleep time and reduce night-time awakenings, although there are no systematic studies on long-term use and rare studies in palliative care. All drugs are dosed orally, at bedtime.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
Preparing For Your Appointment