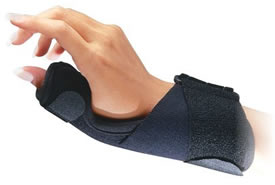
There are a few non-surgical treatment options that may be effective for tendonitis. We usually try these methods before recommending surgery. Immobilization Bracing Splinting Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines Steroid Injection Surgery for Tendonitis
How to cure tendonitis naturally?
The #17 Natural Home Remedies For Tendonitis
- Resting the Tendons. Generally relaxing the body is helpful in healing the body. ...
- Applying Ice to the Affected Area. Ice helps in reducing inflammation in the affected area. ...
- Elevation. ...
- Increase your Activity Level Gradually. ...
- Compression. ...
- Use a Sling or Brace. ...
- Avoid Repetitive Activities. ...
- Stretch Daily. ...
- Epsom Salt. ...
- Olive Oil. ...
Why does tendonitis take so long to heal?
Why Do Tendon Injuries Take So Long To Heal?
- Tendon injuries often develop gradually. Tendons need to be able to transmit forces from muscles to the bones that they attach, however they respond to changes in strength more slowly ...
- Recovery often relies on adherence to a specific rehab program. ...
- Ask your physiotherapist for more information about tendon pain.
How long does it take to recover from tendonitis?
Most damage heals in about two to four weeks, but chronic tendinitis can take more than six weeks, often because the sufferer doesn't give the tendon time to heal. In chronic cases, there may be restriction of motion of the joint due to scarring or narrowing of the sheath of tissue that surrounds the tendon.
Does tendonitis ever go away?
Tendonitis is acute (short-term) inflammation in the tendons. It may go away in just a few days with rest and physical therapy. Tendonitis results from micro-tears in the tendon when it’s overloaded by sudden or heavy force. There is no inflammation in tendonosis, but rather the actual tissue in the tendons is degrading.

What are the common treatments for tendonitis?
As an immediate treatment for overuse tendinopathy, doctors and physical therapists often recommend the RICE program: rest, ice, compression, and elevation of the injured tendon. They may also suggest a short course of aspirin, ibuprofen, or other anti-inflammatory drugs to help inflammation and pain.
What is the best treatment for tendonitis in the wrist?
Management and TreatmentMedication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can reduce pain and inflammation. ... Physical or occupational therapy: Therapists can help you regain strength, mobility and range of motion in your wrist and fingers. ... Rest: The most important treatment for wrist tendinitis is usually rest.More items...•
Which of the following is key to treating tendonitis initially?
Rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications are the primary treatment protocol during early rehabilitation for tendonitis.
How do you treat tendonitis in your arm and wrist?
Common treatments include:splints and compression to give the overworked tendon time to rest and heal.stretching to improve flexibility.hot and cold therapy to reduce swelling.acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)corticosteroid injections to control inflammation.More items...•
How do you treat tendonitis in the hand?
Treatment for tendonitis and tenosynovitis Icing the area to reduce inflammation and pain. Putting a splint on the area to limit movement. Steroid injections to reduce inflammation and pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicine to reduce inflammation and pain.
What is the best treatment for shoulder tendonitis?
How is shoulder tendonitis treated?Rest.Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)Strengthening exercises.Physical therapy.Ultrasound therapy.Corticosteroid shot (injection)Surgery (for severe injuries or tears)
Is ultrasound effective for tendonitis?
A systematic review of physical therapy modalities used for the treatment of shoulder pain suggested ultrasound appeared effective for the treatment of calcific tendonitis [1].
Is heat therapy good for tendonitis?
Heat may be more helpful for chronic tendon pain, often called tendinopathy or tendinosis. Heat can increase blood flow, which may help promote healing of the tendon. Heat also relaxes muscles, which can relieve pain.
What causes tendonitis in the wrist?
In general, repetitive movement and overuse of the hand and wrist can cause tendonitis. Other causes include: 1 Diabetes 2 Inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis 3 Injury to the tendon 4 Sports, such as tennis and racquetball
How to tell if you have tendonitis in your hand?
Other symptoms may include: Grinding sensation when you move the wrist. Swelling from fluid accumulation and inflammation. Warmth and redness.
What is Penn integrated hand program?
Penn Integrated Hand Program surgeons offer effective non-surgical and surgical treatment options for tendonitis. We perform complete assessments of your hand and wrist to determine how severe your condition is.
Can you have tendon surgery under general anesthesia?
However, if the tendon damage is more complex, the procedure may be carried out under general anesthesia. Our hand surgeons are experts in orthopaedics and plastic surgery, giving you the full spectrum of care that you need to heal.
Can tendonitis affect hand function?
Without proper diagnosis and treatment, tendonitis can become a long-term issue that may limit your hand function. That's why prompt evaluation and the development of an appropriate treatment plan by our specialists are important to ensure the best possible results.
Is tendon repair surgery minimally invasive?
The surgery is minimally invasive, allowing patients to go home on the same day, experience a quicker recovery time and have a lower risk of side effects and complications. During the procedure, our surgeons will make a small incision in your wrist, hand or finger to locate and repair the damaged tendon.
Can you have surgery on your thumb?
If any of the tendons in your hand are damaged and non-surgical treatment is not helping, surgery may be needed to repair them and help restore movement in the affected fingers or thumb. In many cases, our surgeons will use local anesthesia while the patient is awake when performing surgery for tendonitis.
What is wrist tendonitis?
Wrist tendonitis (sometimes spelled "tendinitis") is when the tendons in your hand or arm inflame. The inflammation causes pain and other symptoms.
Why is stretching important for tendonitis?
Stretching also enhances blood flow. This is particularly important with wrist tendinosis. That's because the added circulation brings in nutrients to the tendon that are important to the long-term healing process. Circulation also helps eliminate cellular debris as new collagen replaces worn out components of the tendon.
What is the term for a straining of the wrist?
Both wrist tendonitis and wrist tendinosis occur with chronic, forceful straining of your wrist, hand or fingers. Certain occupations and activities are infamous for such straining (see below).
What is the term for a swollen hand tendons?
Wrist tendonitis is acute trauma to the hand tendons causing swelling and inflammation.
What causes the wrist to flex?
Flexor tendons pull and cause the wrist to flex, and the fingers to close or grip. They're located on the palm side of the hand. They also help rotate the wrist.
What are the tendons in your hand?
Tendons are ropy structures that attach the muscles in your forearm to your fingers . There are two basic types of tendons of the wrist and hand: flexors and extensors (see image below). Both types pull on your fingers, but in different directions, causing a different motion.
How long does it take for a tendon to heal?
The major treatment goals for wrist tendinosis are to break the cycle of injury and promote proper collagen placement in the tendon. Healing can take 2-6 months, depending on severity.
What are the most effective treatments for tendonitis?
Previously, doctors advised patients to take anti-inflammatory tablets such as ibuprofen. Remember, they used to believe that acute inflammation played a key role. However, recent evidence suggests that medications like ibuprofen may slow down the healing process. Nevertheless, a short course of ibuprofen can help with acute tendon pain.
What features are common in tendonitis from a tendonitis specialist?
Generally, people with tendonitis report pain arising from their tendon. Often, pain occurs with an activity that stresses the tendon such as running for Achilles tendons or knee tendons or playing tennis or golf for elbow tendons. Usually, pain ‘warms up’ with activity but often gets worse when you cool down.
What is tendonitis?
Tendons are rope-like collagen proteins bundled together to form fibrils. The primary function of tendons is to transmit forces from muscle to bone for movement. In tendonitis, there is a breakdown of collagen proteins of the tendon. Overload of the tendons either gradually or due to sudden stress can cause tendonitis. Aging and diseases such as obesity and diabetes can also contribute to tendonitis. A tendonitis specialist understands the importance of finding those factors that have led to tendonitis.
How does physical therapy help with tendonitis?
How physical therapy improves pain in tendonitis is unknown. However, we think that exercise works by stimulating collagen proteins in the tendon or increasing muscle strength. Positive effects occur irrespective of the type of exercise. For example, in Achilles pain, concentric loading which forces your muscle to shorten while they contract has ...
Why do we need sound waves for tendonitis?
The sound waves stimulate the body’s own healing capacity. Injections for tendonitis are used to improve healing of tendons. A recent review of different injections used in tendinopathy co-authored by Dr Masci suggests that there are no clear favourites.
How to strengthen calf muscles?
An example of strengthening for the calf: First, strengthening sessions every 3rd day consisting of seated and standing calf raises on a step. Second, exercises should be performed with a single leg. Third, aim for 3 sets of 8-10 repetitions. Finally, you should add weight to your body (eg add 2.5 kg) every week to stimulate calf strength.
What are the causes of tendonitis?
Aging and diseases such as obesity and diabetes can also contribute to tendonitis. A tendonitis specialist like Dr Masci understands the importance of finding those factors that have led to tendonitis.
Drugs used to treat Tendonitis
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
What is the best treatment for tendonitis in the knee?
The best treatments for knee tendonitis include knee support, over-the-counter pain medications, rest, ice and other home care measures. Tendonitis, or tendinitis, is the inflammation of a tendon. A tendon is a thick cord made up of tiny fibers that connect muscles to bones.
What is knee tendonitis?
Knee tendonitis or jumper's knee, a common , often sports-related injury characterized by inflammation of your patellar tendon. This tendon connects your kneecap ( patella) to your shinbone (tibia). Knee tendonitis is caused by a repeated strain that leads to micro-tears in your tendon. These micro-tears cause inflammation and pain, weaken your tendon, and, if left untreated, can lead to larger tears in your tendon.
How to tell if you have tendonitis?
Symptoms of knee tendonitis include: 1 Pain above or below the kneecap 2 Tenderness behind the lower part of your kneecap 3 Pain that occurs with specific activities and stops with rest 4 Swelling, may be accompanied by heat or redness 5 Chronic pain in severe cases, in spite of resting the joint 6 Crackling or grating sensation when moving the tendon
What does it feel like to move a knee tendon?
Crackling or grating sensation when moving the tendon. Some symptoms of knee tendonitis are similar to those of more severe conditions like osteoarthritis, tendon tears, and fractures. You should see a doctor if your symptoms don’t go away after a few days.
How do you know if you have tendonitis in your knee?
Main symptoms. Symptoms of knee tendonitis include: Pain above or below the kneecap. Tenderness behind the lower part of your kneecap. Pain that occurs with specific activities and stops with rest. Swelling, may be accompanied by heat or redness. Chronic pain in severe cases, in spite of resting the joint.
How to diagnose knee tendonitis?
Knee tendonitis is diagnosed in a medical exam with your orthopedic or sports medicine doctor. Your doctor will take a full medical history to understand your normal activity level, the kind of sports you play, and your symptoms and when they occur. They will then go over some remedies that reduce the pain.
What sports can cause patellar tendonitis?
If you play high-impact sports such as volleyball, basketball, or tennis, you may be at a higher risk of developing patellar tendonitis. Running, squatting, and jumping are some of the exercises that put excessive stress on the tendons in the knee.
What are the treatments for tendinopathy?
Based on the authors’ knowledge of the field and an extensive literature review, we evaluated the following treatment options: NSAIDS; exercise-based physical therapy; physical therapy modalities including iontophoresis, phonophoresis, ultrasound, transverse friction massage, and low-level laser therapy; corticosteroid injections ; glyceryl trinitrate patches; shock wave therapy; sclerotherapy; surgery; growth factor treatment; and stem cell treatment . Our goal was to provide a comprehensive and up-to-date review of these treatment options with recommendations based on the best level of evidence available.
How to treat Achilles tendon?
(A) The patient starts in a single-leg standing position with the weight on the forefoot and the ankle in full plantar flexion. (B) The Achilles is then eccentrically loaded by slowly lowering the heel to a dorsiflexed position. (C) The patient then returns to the starting position using the arms or contralateral leg for assistance to avoid concentric loading of the involved Achilles tendon.
What is ESWT therapy?
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) has been advocated for treating a number of soft tissue conditions, including plantar fasciitis, lateral epicondylitis, calcific and noncalcific tendonitis of the supraspinatus, and tendinopathy of the Achilles tendon. It is FDA-approved for plantar fasciitis and lateral epicondylitis only. ESWT entails delivering a series of low-energy shock waves directly over the painful area of the tendon. The mechanism by which ESWT would provide pain relief or enhance tendon healing is not clear. Ohtori et al. [121] reported the administration of a single session of low-energy shock waves to rat skin resulted in nearly complete degeneration of epidermal sensory nerve fibers. The fibers began to regenerate in 14 days. By applying a second session of shock waves at 14 days, the nerve fiber regeneration was delayed to 42 days [175]. There is also evidence tenocytes release growth factors in response to ESWT that may promote tendon healing. Chen et al. [33] reported administering shock waves to a rat Achilles tendinopathy model resulted in increased tenocyte proliferation and increased expression of transforming growth factor-beta1 and insulin growth factor 1.
What is sclerotherapy in tendinopathy?
Polidocanol is not FDA-approved although other sclerosing agents are. The rationale behind using sclerotherapy in tendinopathy is based on the finding that there is a proliferation of small blood vessels in areas of tendinopathy. Nerve fibers appear to travel in close proximity to these areas of neovascularization [24, 95, 97]. It is possible these nerve fibers are the pain generators in tendinopathy. In theory, injecting a sclerosing agent into the areas of neovascularization could not only sclerose the vessels, but also may eradicate the pain-generating nerve fibers. These injections are performed under Doppler ultrasound guidance (Fig. 3A–C).
Does ESWT help with lateral epicondylitis?
Variable results have been demonstrated with the use of ESWT in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis. There have been reports of improved pain and function compared to control groups using ESWT in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis [135, 142]. However, the majority of studies evaluating ESWT for the treatment of lateral epicondylitis report no improvement using this modality compared to controls [35, 68, 91, 165]. Two systematic reviews have investigated this issue and have concluded ESWT provides little or no benefit in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis [22, 29]. Similar, contradictory findings are seen with the use of ESWT in the treatment of Achilles tendinopathy. One study reported ESWT comparable to eccentric training and superior to a wait-and-see policy for the treatment of Achilles tendinopathy in a randomized clinical trial [143]. In contrast, another randomized, double-blind clinical trial reported no difference between patients treated with ESWT and sham ESWT in the treatment of Achilles tendinopathy [40]. Of note, this study also reported two episodes of Achilles tendon rupture in the ESWT group and questioned the safety of this treatment modality for the Achilles tendon in older patients.
Can NSAIDs help Achilles tendonitis?
NSAIDs do not seem nearly as effective in treating lateral epicondylitis or Achilles tendinopathy [13, 64, 71, 106]. The only study to look at the effectiveness of NSAIDS for the treatment of lateral epicondylitis in the long term reported no difference between placebo and naproxen treatment groups at 1-year followup [71]. A systematic review of NSAID use for lateral epicondylitis identified data to support the use of local NSAIDs with a decrease in pain in the short term (2 weeks) [64]. However, there is little evidence to support or refute the use of topical or oral NSAIDs in the long term. In addition, long-term NSAID use increases the risk of gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, and renal complications associated with these medications. Overall, a short course of NSAIDs appears a reasonable option for the treatment of acute pain associated with tendon overuse, particularly about the shoulder. There is no clear evidence that NSAIDS are effective in the treatment of chronic tendinopathy in the long term.
Can corticosteroid injections be used for tendinopathy?
Corticosteroid injections have been a mainstay in the treatment of tendinopathy. Despite their widespread use, there is some controversy as to their usefulness and safety in this setting. Our literature search identified 19 controlled trials and systematic reviews with mixed results regarding corticosteroid injections in the treatment of tendinopathy [2, 8, 9, 11, 12, 43, 71, 73, 86, 114, 133, 149, 159, 160, 172, 180, 187, 193, 194]. Several studies report good short-term pain control (≤ 6 weeks) with corticosteroid injections in patients with lateral epicondylitis and shoulder impingement [46, 71, 160, 188]. The long-term efficacy of corticosteroid injections for tendinopathy has not been demonstrated. Corticosteroid injections for lateral epicondylitis do not provide any long-term benefit (6–12 months) compared with placebo, NSAIDs, or physical therapy in randomized, controlled studies [71, 159, 160, 188]. Mixed results have been published with regard to the long-term benefits of subacromial corticosteroid injections for rotator cuff tendinopathy. Several well-controlled studies report a small but statistically significant level of improvement in the short term using corticosteroids in the treatment of shoulder impingement [3, 25, 133]. In contrast, several authors have reported no major benefit with corticosteroid injections over control patients in the treatment of shoulder impingement [9, 187]. An extensive systematic review evaluating the efficacy of corticosteroid injections in the treatment of rotator cuff disease recently reported little or no evidence to support the use of corticosteroid injections for these patients [86].
What is the inflammation of the Achilles tendon?
Achilles tendonitis refers to the inflammation of the Achilles tendon, the thick connective tissue running between the calf muscle and the heel bone. Achilles tendonitis is caused by putting repetitive strain on the tendon— more like your body’s way of telling you that you’ve pushed it too hard.
How long does cortisone last?
Cortisone shots can provide pain relief up to several months. However, they are not recommended for any type of tendonitis that has already lasted over three months (chronic tendonitis). Mounting research evidence suggests that repeated injections into the tendon can weaken it, rendering you susceptible to rupture.
