| Treatment plant | Treatment level | Discharge volume limit (ML/ day) (As sta ... | Discharge location |
| West Camden | Tertiary (includes disinfection) | 120 | Matahil Creek to the Hawkesbury-Nepean R ... |
| West Hornsby | Tertiary (includes phosphorus and nitrog ... | 154.3 | Waitara Creek to Berowra Creek |
| Winmalee | Tertiary (includes phosphorus and nitrog ... | 330 | Unnamed creek to the Hawkesbury-Nepean R ... |
| Wollongong | Tertiary (includes disinfection) | 320 | Deep water Ocean Outfall approximately 1 ... |
Full Answer
What is the largest water treatment plant in the US?
“The Northeast Water Purification Plant Expansion is currently the largest water treatment project on the planet — not just in the State of Texas, not just in the United States, but on the planet,” said Houston Mayor Sylvester Turner, according to the Houston Chronicle. “Can you imagine this plant just a couple of weeks ago was ...
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
Water Treatment Process: Follow Water Through a Surface Water Treatment Plant
- Coagulation. ...
- Flocculation. ...
- Sedimentation (or Clarification) The water continues on to the sedimentation basin, or clarifier, after the flocs have been formed. ...
- Filtration. ...
- Disinfection. ...
- Chlorination Operations. ...
- Conclusion. ...
What is the purpose of a water treatment plant?
Water treatment
- Drinking water treatment. Water contamination is primarily caused by the discharge of untreated wastewater from enterprises. ...
- Heavy Metals. ...
- Water Treatment Technologies. ...
- Standards. ...
- Industrial water treatment. ...
- Developing countries. ...
- Regulation. ...
- See also
- References. ...
- Further reading. ...
What are the steps of the water treatment process?
- Remove specific contaminants
- Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system
- Improve the taste of drinking water

Where does the water from wastewater treatment plants go?
What happens to the treated water when it leaves the wastewater treatment plant? The treated wastewater is released into local waterways where it's used again for any number of purposes, such as supplying drinking water, irrigating crops, and sustaining aquatic life.
How many wastewater treatment plants are there in the US?
16,000Today, more than 16,000 publicly-owned wastewater treatment plants operate in the United States and its territories.
Where does the wastewater treatment process begin?
The physical process of wastewater treatment begins with screening out large items that have found their way into the sewer system, and if not removed, can damage pumps and impede water flow. A bar screen is usually used to remove large items from the influent and ultimately taken to a landfill.
Where is the largest wastewater treatment plant?
The largest wastewater treatment plants around the globe. 1. Stickney Water Reclamation Plant, Chicago. Capacity: 1.44 billion gallons per day.
Where does wastewater go in Florida?
Most sewers in Florida use gravity to usher waste from homes and businesses to neighborhood lift stations, where it is stored and pumped into pressurized mains, which then take the sewage to the treatment plant. Municipalities have hundreds of miles of these sewer lines buried beneath ground.
How is wastewater treated in Florida?
Domestic wastewater in Florida is treated either by on-site sewage treatment and disposal systems (i.e., OSTDS or septic tanks) or by centralized domestic (municipal) wastewater treatment facilities.
Where does wastewater come from?
Sources of wastewater include homes, shops, offices and factories, farms, transport and fuel depots, vessels, quarries and mines. Water used in toilets, showers, baths, kitchen sinks and laundries in homes and offices is domestic wastewater.
How does wastewater get to the treatment plant?
Sewers collect the wastewater from homes, businesses, and many industries, and deliver it to plants for treatment. Most treatment plants were built to clean wastewater for discharge into streams or other receiving waters, or for reuse.
What happens to poop at the water treatment plant?
During the first stage, all of the waste that accumulates in the city's pipes just sits in a tank for hours. This stage allows the solids to settle at the bottom of the tank. The water at the top of the tank is skimmed off and sent off to be processed. Your poop remains in the sludge that's left over.
Is there still sewage in the ocean?
Sewage Sludge. Although today's environmental regulations in the United States prohibit this practice, sewage sludge is still disposed at sea in some countries. Disease-causing microbes are the primary human health risk in sewage-contaminated waters, and the main cause of recreational beach closures.
Does La dump sewage into the ocean?
Los Angeles beaches reopen almost three days after 17 million gallons of sewage spill into Santa Monica Bay. A mechanical failure “caused untreated sewage to be discharged into the ocean,” according to Los Angeles County Supervisor Janice Hahn.
Does raw sewage go into the sea?
Sewage pollution is released into rivers and the ocean through Combined Sewer Overflows (CSOs).
Q. What are the three stages of wastewater treatment?
Ans: There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process; they are primary, secondary and tertiary process.
Q. What is the process of a wastewater treatment plant?
Ans: The process of wastewater treatment plant is as follows: 1. Primary treatment: It is the initial stage. Waste water is passed through rotating...
Q. What are the four stages of wastewater treatment?
Ans: The four stages of wastewater treatment are: 1. Physical water treatment 2. Biological water treatment 3. Chemical treatment 4. Sludge treatment
Q. What are the two types of wastewater treatment?
Ans: There are two wastewater treatment plants, (i) chemical or physical treatment plants, (ii) biological wastewater treatment plants.
Q. What are the types of wastewater treatment?
Ans: Types of wastewater treatment system are; A. Effluent treatment plants B. Sewage treatment plants C. Common and combined effluent treatment pl...
Q. What are the main sources of wastewater?
Ans: The main sources of wastewater are Domestic wastewater, agricultural wastewater, industrial wastewater, petroleum.
What is wastewater treatment plant?
A wastewater treatment plant is a facility in which a combination of various processes ( e.g., physical, chemical and biological) are used to treat industrial wastewater and remove pollutants (Hreiz et al., 2015).
How is wastewater treatment plant design based?
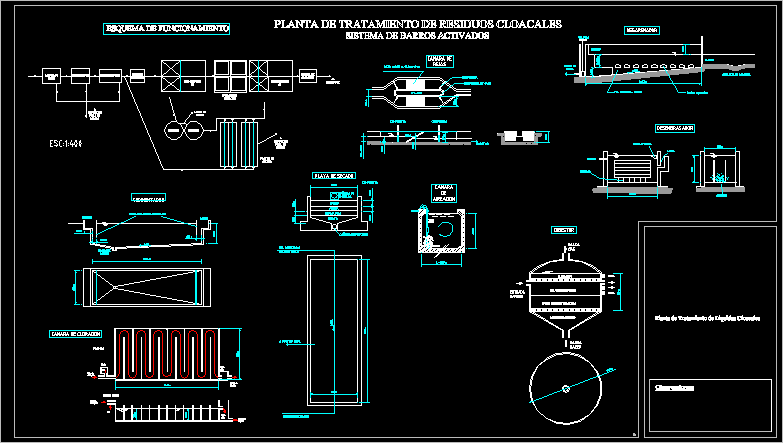
Wastewater treatment plant design is based on the selection and sequencing of various unit operations. A schematic illustrating integration of processes capable of treating a variety of wastewaters is shown in Figure 1. Selection of a combination of processes depends on the characteristics of the wastewaters; the required effluent quality (including potential future restrictions); costs; and, availability of land. As previously indicated, treatment methods can be classified as pretreatment/primary treatment; secondary treatment; tertiary treatment; sludge treatment/stabilization; and, ultimate disposition or reuse treatment technologies for residuals.
What is WWTP in wastewater treatment?
WWTPs are a significant point source for AMRDs and antimicrobials. WWTPs are relatively nutrient-rich, heavily contaminated environments that receive waste from a variety of AMRD-loaded environments, including hospitals, industrial and agricultural sites and release both solid and liquid by-products that can disseminate AMRDs. Influent can be contaminated with a variety of pollutants, including antimicrobial agents, pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and heavy metals, which can accumulate within WWTPs. Many microbial and chemical contaminants in wastewater cannot be degraded by the treatment process or inactivated through disinfection of the effluent. For those contaminants that can be degraded, the resulting metabolites may still have antimicrobial or selective activity. WWTP effluent and solid waste products not only have a high prevalence of AMRDs but also release selective agents into the receiving environments ( Jury et al., 2011 ).
What is reclaimed water?
Reclaimed wastewater is usually clean enough to be used for irrigation, but usually contains higher (~1.5 times) concentrations of dissolved solids than the source water. Also, chlorine-disinfected reclaimed water can contain significant trace amounts of disinfection by-products such as trihalomethanes and haloacetic acids.
How did the treatment plant get to net zero?
It made its operations and equipment more efficient (cutting energy consumption), but mostly it got to net zero by producing renewable energy on site. This is the fats, oils and grease receiving station.
What is the purpose of sodium hypochlorite in wastewater treatment?
The wastewater is then disinfected with sodium hypochlorite to remove any disease-causing organisms and ensure that water leaving the plant meets the water quality standards set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Following the treatment, the water is discharged to the Columbia River.
What is the mass of solids in a sedimentation tank called?
The remaining solids are minute particles that fall to the bottom of a sedimentation tank. The particles form a mass of solids called biosolids or sludge.
Where is DWA water delivered?
Once treated to all state and federal recycled water standards, DWA delivers the recycled water for irrigation of the City's municipal golf courses, nearby Demuth Park, Palm Springs High School and other locations.
Where does sewage come from?
Sewage comes from various types of structures such as residences, institutions, hospitals and commercial and industrial establishments. In Palm Springs, it is collected and transported via a network of pipes and pump stations to the treatment plant.
What is wastewater treatment plant?
Wastewater treatment plant is the process of removing contaminants from wastewater and converting it into effluent that can be recycled into the water cycle. Once returned to the water cycle, the effluent has an acceptable environmental impact or is reused for a variety of purposes. A wastewater treatment plant is where the treatment ...
How does a sewage treatment plant filter wastewater?
The wastewater that enters the sewage treatment plant is first filtered through bar screens, a process known as screening. The bar screen separates large trash objects from the wastewater, such as rags, sticks, cans, plastic bags, napkins, sanitary towels, and so on. As a result, screening removes large pieces of trash from the wastewater.
What is the solid component of sewage?
The majority of the solid organic matter (faeces, for example) settles as sludge on the sloping bottom of the sedimentation tank. As a result, the solid component of sewage is known as sludge .
Why is activated sludge returned to the aeration tank?
Some of the activated sludge is returned to the aeration tank to boost the population of aerobic bacteria and accelerate the cleaning of watery waste. The digester tank receives the remaining activated sludge. The water in the second sedimentation tank contains very little organic material and suspended matter.
What is WWTP in water treatment?
WWTP is an abbreviation for Waste-Water Treatment Plant. A wastewater treatment plant is also referred to as a sewage treatment plant. A modern wastewater treatment plant treats wastewater or sewage through a series of physical, chemical, and biological processes until it becomes fit to be discharged into the environment.
Where is sludge removed from sedimentation tanks?
The sludge is removed from the bottom of the first sedimentation tank and placed in a large, closed tank known as the digester tank. Many different types of anaerobic bacteria decompose the organic matter in sludge in the digester tank to produce biogas.
What is a WWTP?
A wastewater treatment plant is a facility that treats wastewater, making it considerably cleaner and safer to be released into water bodies. A wastewater treatment plant is a place where wastewater from homes and other buildings is collected and processed. WWTP is an abbreviation for Waste-Water Treatment Plant.
1. Waste water – What is it and its types ?
Wastewater or sewage is water that has been adversely affected in quality by containing wastes from residential, commercial, and industrial processes. Waste water encompass a wide range of hazardous dissolved toxins and chemicals, whiles others contain particles, sediments and suspended matter of all sizes.
2. What is Waste Water Treatment and why it is required ?
Waste water treatment is the process of converting wastewater – water that is no longer needed for use and that can be discharged back into the natural environment.
3. Types of waste water treatment process or methods
Some of the important types of wastewater treatment plants are as follows: 1. Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP) 2. Sewage Treatment Plants (STP) 3.
5. Waste Water Recycling
Water resources are depleting day by day and hence recycling and reuse of wastewater is extremely important to preserve our precious resources for domestic, agriculture, commercial and industries.
How is wastewater drained to the WWTP?
1. Firstly, wastewater is drained to the WWTP by gravity through the main sewer system of the size of a car. Having such size, objects you could hardly imagine reach the WWTPs, ranging from mattresses, fridges, tree branches to wallets disposed of by thieves in order to get rid of the evidence. 2.
What is wastewater water?
Wastewater can be divided into two major groups: Sewage water is all wastewater used in domestic dwellings (e. g. originating from toilets, showers or sinks). Industrial wastewater originates from production, industrial and commercial activities, and has a different chemical composition to sewage water.
How long does it take for sludge to dry out?
9. Sludge, digested and dewatered to the optimal degree, is finally disposed of at the dump. In about a month, sludge is adequately dried out and ripe. If it complies with agricultural standards, it can be reused for fertilisation of industrial crops.
What is the first stage of wastewater treatment?
The first mechanical stage is called preliminary treatment or rather pre-treatment. Water flows through gravel chamber for settling out the grit from water. Afterwards, gravel is disposed of at the dump. Water further reaches the bar screens used to remove large objects from the wastewater.
What is wastewater in agriculture?
What is wastewater? It is used water originating from domestic, industrial, agricultural, and medical or transport activities. Used water becomes wastewater upon the change of its quality, composition and/or temperature. However, wastewater does not include water released from ponds or reservoirs for fish farming.
What is the purpose of bar screens in wastewater treatment?
Water further reaches the bar screens used to remove large objects from the wastewater. At first come the coarse screens and then the fine screens which remove smaller objects such as matches, cigarette butts or undigested foods. 3. After the removal of large objects, grit is to be removed from the wastewater.
Is wastewater treatment a difficult process?
Wastewater treatment is certainly a difficult process with noble goal which requires work of qualified experts. If you are interested in wastewater treatment or need guidance, don’t hesitate to contact Hydrotech’s experts. They will gladly and professionally advise you.