
What is the history of heart disease?
It was in the 1960s and 1970s that treatments like bypass surgery and percutaneous balloon angioplasty were first used to help treat heart disease, according to …
What is the history of heart attack treatment?
But it wasn't until 1982 that PTCA was used as a primary treatment for patients who had a heart attack. By the 1990's, PTCA was the procedure of choice used to treat heart attacks.
How was heart failure treated in the 19th century?
Jan 01, 2001 · Organomercurial diuretics are first used: 1954: Inge Edler and Hellmuth Hertz use ultrasound to image cardiac structures: 1958: Thiazide diuretics are introduced: 1967: Christiaan Barnard performs first human heart transplant: 1987: CONSENSUS-I study shows unequivocal survival benefit of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in severe heart failure: 1995
When were stents first used to treat heart disease?
Paul White in his text, Heart Disease, first published in 1941, was next among the cardiological elite to maintain that one could recover from an infarct and carry on a full life. But progress in defining and diagnosing routinely, during life, the presence, localization, and extent of myocardial infarction came only with the widespread use of the electrocardiogram with the addition of …
When was the first heart surgery performed?
The first procedure done with the use of a heart-lung machine was for closure of an atrial septal defect and was performed by Dr Gibbon in Philadelphia in 1953. [ 8] . Later that year, Dr Lillehei, working in Minneapolis, performed open heart surgery using cross-circulation between the child and a parent.
When was balloon dilatation first used?
Balloon dilatation of the pulmonary valve was first described in the 1950s and became widely used after static balloon dilatation was introduced in 1982 .
When was the EKG invented?
The EKG was invented in the early 1900s and helped physicians to determine if someone was having a heart attack. Before this time all they had was a stethoscope. In the early 1900's, treatment of a MI meant that a person had to be hospitalized and bedridden for a period of 6 weeks. They weren't even allowed to feed themselves.
When was the first CABG performed?
The first successful coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) was performed in the 1960's and this surgery was very successful for the next 20 years. In the 1970s, scientists formulated three medications: beta blockers, ACE inhibitors and thrombolytic therapy to treat heart attacks.
What causes a heart attack?
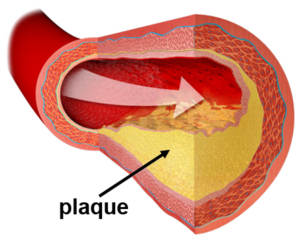
What causes a heart attack? The heart has vessels called coronary arteries. People who are over weight, have high cholesterol, who smoke, have high blood pressure or diabetes have a greater chance of having a buildup of what's called plaque in their coronary arteries. If any of these arteries are blocked, then the heart cannot get blood to that part of the heart, and the person will have a heart attack. Patients having a heart attack will usually primarily complain of chest pain, but there are other symptoms that may not involve chest pain.
What happens if your heart is blocked?
If any of these arteries are blocked, then the heart cannot get blood to that part of the heart, and the person will have a heart attack. Patients having a heart attack will usually primarily complain of chest pain, but there are other symptoms that may not involve chest pain. The treatment of a heart attack, also known as myocardial infarction ...
Can a heart attack cause chest pain?
Patients having a heart attack will usually primarily complain of chest pain, but there are other symptoms that may not involve chest pain. The treatment of a heart attack, also known as myocardial infarction (MI) has evolved tremendously over the years thanks to some very dedicated physicians and researchers.
What is an EKG?
Early Diagnostic Tools and Treatments. The electrocardiogram (EKG) is a device used to monitor the heart's rhythm and determine abnormal patterns. The EKG was invented in the early 1900s and helped physicians to determine if someone was having a heart attack. Before this time all they had was a stethoscope.
When was CABG first used?
Animals were used as practice and the first successful human CABG was completed in the early 1960's.
Who invented the ECG?
Nevertheless, it was the pioneering British clinical investigator, Sir Thomas Lewis, who in the 1920s made the ECG an essential and practical instrument allowing diagnosis not only of disturbances of heart rhythm but also an inadequate blood supply (ischemia) and muscle damage (infarction), the hallmarks of coronary heart disease.
What is angina pectoris?
Angor in the chest– angina pectoris –was depicted in accounts from ancient literature but described as related to coronary artery disease only in the latter part of the eighteenth century. The syndrome of myocardial infarction–prolonged chest pressure or variously referred pain, followed by collapse with rapid death or with survival–was finally and clearly put forward in the early part of the twentieth century. In the English-speaking world, this recognition is mainly attributed to James Herrick, a Chicago internist, because of his effective observations of the clinical and electrocardiographic evolution of the phenomenon. Herrick also documented his views and findings by creating coronary occlusion in animals and became a persistent protagonist of the syndrome at medical meetings in the years following his largely ignored classic JAMA publication in 1912. But others elsewhere, including Obrastzow and Staschesko (1910) in Europe, had similar early insights.
Who is James Herrick?
In the English-speaking world, this recognition is mainly attributed to James Herrick, a Chicago internist, because of his effective observations of the clinical and electrocardiographic evolution of the phenomenon.
Who was Paul Dudley White?
Paul Dudley White, as a youthful clinical fellow from Boston, came to study with the famous clinical investigator, Sir Thomas, in the 1920s and, as did other contemporaries, brought home to the U.S. the apparatus and the popular art of electrocardiology (see Chapter 9). [1]
When was the first CDC conference?
2001: CDC convenes The First National CDC Prevention Conference on Heart Disease and Stroke on August 22–24, 2001, in Atlanta, Georgia.
What is the CDC's public health program?
CDC’s public health activities to combat heart disease and stroke include the following: 1984: The Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, a state–based telephone health survey, begins in 15 states, with all 50 states participating by 1993. High blood pressure and high blood cholesterol are standard topics in the BRFSS.
What is the leading killer of men and women?
Heart disease and stroke are among the nation’s leading killers for both men and women and among all racial and ethnic groups. CDC’s public health activities to combat heart disease and stroke include the following:
How to treat heart disease?
You can lower your risk of heart disease by eating a low-fat and low-sodium diet, getting at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise on most days of the week, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol intake. Medications.
What tests are needed to diagnose heart disease?
The tests you'll need to diagnose your heart disease depend on what condition your doctor thinks you might have. Besides blood tests and a chest X-ray, tests to diagnose heart disease can include: Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). An ECG is a quick and painless test that records the electrical signals in your heart.
What is the best test for heart disease?
Besides blood tests and a chest X-ray, tests to diagnose heart disease can include: Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). An ECG is a quick and painless test that records the electrical signals in your heart. It can spot abnormal heart rhythms.
Can heart disease be detected without an appointment?
Some types of heart disease will be discovered without an appointment — for example, if a child is born with a serious heart defect, it will be detected soon after birth. In other cases, your heart disease may be diagnosed in an emergency situation, such as a heart attack.
What is a CT scan?
Cardiac computerized tomography (CT) scan. In a cardiac CT scan, you lie on a table inside a doughnut-shaped machine. An X-ray tube inside the machine rotates around your body and collects images of your heart and chest. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
What is the recommended LDL level?
Most people should aim for a low-density lipoprotein (LDL) level below 130 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), or 3.4 millimoles per liter (mmol/L). If you have other risk factors for heart disease, you should aim for an LDL level below 100 mg/dL (2.6 mmol/L).
Why is physical activity important?
Physical activity helps you achieve and maintain a healthy weight and control diabetes, high cholesterol and high blood pressure — all risk factors for heart disease. If you have a heart arrhythmia or heart defect, there may be some restrictions on the activities you can do, so talk to your doctor.
Can you develop heart disease from a family history?
If you have a family health history of heart disease , you are more likely to develop heart disease yourself. Different types of heart disease and related conditions, like high blood pressure and high blood cholesterol, can run in families.
What to include in a family history?
Include your parents, sisters, brothers, children, grandparents, grandchildren, aunts, uncles, nieces, and nephews. Make sure you include both your mother’s and father’s sides of the family. Note which relatives have had heart disease, related conditions, or procedures and the age at which they were diagnosed or treated.
What is an external icon?
external icon. Heart bypass. external icon. or other heart surgery. Based on this information, your doctor may suggest steps to prevent or treat heart disease. If you have been diagnosed with heart disease or related conditions, it is important to tell your family members.
Surgical Developments
- The organized study of congenital heart disease (CDH) began with the establishment of Dr Helen Taussig’s pediatric cardiology clinic at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore in 1930[1] and the publication of Dr Maude Abbott’s incredible atlas describing 1000 CHD cases in 1936.[2] The first surgical procedure was ligation of a patent ductus arteriosus...
Interventional and Diagnostic Techniques
- Interventional techniques went hand in hand with surgical advances. Although balloon dilatation of the pulmonary valve was described in 1953 by Rubio-Alvarez and colleagues,[10] the procedure did not become widely used until Kan and colleagues[11] introduced static balloon dilatation in 1982. Balloon atrial septostomy, developed in 1966 by Drs Rashkind and Miller,[12] promoted mi…
Canadian Contributions
- Canadians have been at the forefront of improvements for patients with congenital heart disease, beginning with Dr Maude Abbott of Montreal, who wrote the Atlas of Congenital Heart Disease already mentioned. Dr Wilfred Bigelow[16] of the Toronto General Hospital determined how to use total body hypothermia for open heart surgery in 1953. The first open heart procedures in Canad…
Further Developments
- In the early days of cardiac surgery, intracardiac repairs could only be performed on older children. Congenital heart lesions frequently resulted in too much or too little blood flow to the lungs. Infants and young children with reduced blood flow to the lungs were palliated with arterial shunts, either Blalock-Taussig (subclavian artery to pulmonary artery), Potts (descending aorta t…
Adult Congenital Heart Disease Care in BC
- As in the past, many children born with congenital heart disease today will require multiple operations as they grow to adulthood for various reasons, including scarring and narrowing of arteries or veins and insertion or replacement of conduits and valves. Patients with moderate to severe disease are rarely cured and face a lifetime of repeat surgical and interventional procedur…
Summary
- Many advances have followed the first successful ligation of a patent ductus arteriosus in 1938. Intracardiac repair became possible with the development of cardiopulmonary bypass technology in the 1950s, while lengthier surgeries became possible after the development of deep hypothermia with circulatory arrest in the 1970s. Interventional techniques have accompanied s…
Competing Interests
- None declared. This article has been peer reviewed. Dr Kiess is director of the Pacific Adult Congenital Heart (PACH) clinic, Division of Cardiology, St. Paul’s Hospital. She is also a clinical professor in the Division of Cardiology at the University of British Columbia.