
ECT may be less risky than alternate pharmacologic treatment or non-treatment of mental illness during pregnancy. Children and Adolescents should receive ECT only when it is evident that other viable treatments have been ineffective or if other treatments cannot be administered safely. (APA pp. 31-52)
Full Answer
What if a patient refuses ECT treatment?
treatment. Q. When is ECT an appropriate treatment? A. ECT is generally recommended for people with severe depression (accom-panied by psychosis, suicidal intent, or refusal to eat), especially if it is resistant to medications. It is also used for mania that has not improved with medica-
When is ECT used as the initial treatment of choice?
It is recommended that for children under the age of 13, concurrence by two consultants, at least one being independent, who are experienced in the treatment of children be obtained before ECT is administered . Any modifications to the standard ECT treatment regimen must be clinically documented at the time of ECT.
What is the difference between electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) and ongoing treatment?
If appropriate, information about alternative treatments and the consequences of not having ECT should be discussed and recorded. If appropriate, consent to ECT should be sought prior to each treatment and recorded. The issue of perceived coercion merits further study.
Can ECT be used to treat serious mental illness?
Previous research suggests that electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)—the criterion standard for the treatment of severe depression—is not as effective when the patient has comorbid borderline personality disorder (BPD). The ECT outcomes of patients with and without BPD were compared in a retrospective chart review to test this claim.
When should ECT not be used?
Do not use electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) routinely for people with moderate depression but consider it if their depression has not responded to multiple drug treatments and psychological treatment.
Who should not get ECT?
Not everyone is a candidate for treatment even if they believe ECT could help them. For example, children under age eleven cannot undergo ECT for mental health disorders. People with heart conditions and people who cannot handle short-acting sedatives or muscle relaxers should not undergo ECT treatments.
Can ECT treatments make you worse?
ECT can't prevent future depression, or fix any ongoing stresses or problems that are contributing to how you're feeling. Some people have very bad experiences of ECT, for example because they feel worse after treatment or are given it without consent.
Why is ECT a controversial treatment?
Reasons for Controversy Three reasons are given for the aversion: 1) ECT is considered old-fashioned and politically incorrect; 2) it is forced on the patient; and 3) the memory disturbances are so severe and persistent that no rational human being would undergo this procedure, no matter how well-intended.Mar 1, 2004
What are the indications for ECT?
ECT is used mainly to treat severe depression, but is also indicated for patients with other conditions, including bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, catatonia, and neuroleptic malignant syndrome.Sep 16, 2021
Does ECT damage the brain?
Despite many scientific and governmental authorities having concluded that ECT does not cause brain damage, there is significant evidence that ECT has indeed caused brain damage in some patients, both historically and recently, and evidence that it always causes some form or degree of brain damage.
Is ECT worth the risk?
Risk Assessment of Electroconvulsive Therapy in Clinical Routine: A 3-Year Analysis of Life-Threatening Events in More Than 3,000 Treatment Sessions. Background: Extensive research has reported that electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can be highly effective in approximately 80% of patients suffering from depression.Nov 23, 2021
Can ECT be harmful?
As a result, many laypeople regard ECT as a hazardous, even barbaric, procedure. Yet most data suggest that when properly administered, ECT is a relatively safe and often beneficial last-resort treatment for severe depression, among other forms of mental illness.
What are the negative effects of ECT?
The most common side effects of ECT on the day of treatment include nausea, headache, fatigue, confusion, and slight memory loss, which may last minutes to hours. These risks must be balanced with the consequences of ineffectively treated severe psychiatric disorders.
Why is ECT not ethical?
ECT is not safe: it produces varying amounts of memory loss and other adverse effects on cognition in nearly everyone who receives it, typically lasting weeks or months after the last treatment (as well as many other adverse consequences, from ocular effects to postictal psychosis).Oct 1, 2003
What are the ethical concerns surrounding electroconvulsive therapy?
The present practice of ECT meets standards for beneficence, non-maleficence, and autonomy. In many nations, however, the principle of justice is not respected, leading to unavailability of ECT, increased suffering and prolonged illness.
Is electric shock therapy ethical?
ECT research is ethically justified and should always continue to be conducted with the highest ethical standards. ECT research entails few ethical peculiarities such as involving multiple sessions were capacity to consent can change.May 13, 2016
What are the guidelines for ECT?
Guidelines: Providers should assure review of medical conditions that may substantially increase risk during the delivery of ECT. A medical history and physical examination are essential before prescribing of ECT to determine risk factors and minimize risks.
What should providers identify for ECT?
Guidelines: Providers should identify principal diagnostic indications and other diagnostic indications for the use of ECT. When identifying persons for possible ECT, a current psychiatric evaluation and diagnosis should be part of the required procedures.
What are the approaches to minimizing risks?
Approaches to minimizing risks may include modifications in patient management, changes in patient preparation or adjustments in treatment delivery technique. The decision to administer ECT to special populations of patients should include an appraisal of specific risks and benefits for the individual patient.
What should be included in a patient's monitoring?
and should also include patient self-reporting.
How many seizures should a provider treat per week?
Guidelines: Providers should address the following: Frequency of treatments, including the usual number of weekly treatments (generally, 3 per week), variations in frequency, and review of frequency, based on patient response. In general, the use of more than one adequate seizure per treatment session is discouraged.
Does ECT diminish with age?
The efficacy of treatment does not diminish with advancing age. ECT may have a lower risk of complications than some forms of pharmacotherapy in the elderly. Pregnant women and nursing mothers may receive ECT during all trimesters of pregnancy, puerperium and nursing.
Is ECT a primary or secondary treatment?
ECT may be considered as a primary treatment (or first-line treatment) for persons exhibiting syndromes such as: severe major depression, acute mania, mood disorders with psychotic features, and catatonia.
How often do you get ECT?
In the United States, ECT treatments are generally given two to three times weekly for three to four weeks — for a total of six to 12 treatments. Some doctors use a newer technique called right unilateral ultrabrief pulse electroconvulsive therapy that's done daily on weekdays.
What is ECT used for?
ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. Treatment-resistant depression, a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications or other treatments. Severe mania, a state of intense euphoria, agitation or hyperactivity ...
What is ECT in medical terms?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure, done under general anesthesia, in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure. ECT seems to cause changes in brain chemistry that can quickly reverse symptoms of certain mental health conditions.
Why is electroconvulsive therapy used?
Why it's done. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. Treatment-resistant depression, ...
How long after ECT can you drive?
However, some people may be advised not to return to work, make important decisions, or drive until one to two weeks after the last ECT in a series, or for at least 24 hours after a single treatment during maintenance therapy.
Is it safe to take ECT?
Risks. Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: Confusion. Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there. Rarely, confusion may last several days or longer.
What is the treatment for ECT?
This typically means psychotherapy and/or medication or, in some circumstances, ongoing ECT treatments.
What is ECT therapy?
What is Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)? Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment most commonly used in patients with severe major depression or bipolar disorder that has not responded to other treatments. ECT involves a brief electrical stimulation of the brain while the patient is under anesthesia.
How often is TMS given?
TMS is usually administered four or five times a week for four-to-six weeks. Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) was developed as a treatment for seizure disorders but can also be used to treat depression that has not responded to other therapies.
What are the side effects of ECT?
The most common side effects of ECT on the day of treatment include nausea, headache, fatigue, confusion, and slight memory loss, which may last minutes to hours.
How long does a seizure last after a brain surgery?
The patient's brain is stimulated with a brief controlled series of electrical pulses. This causes a seizure within the brain that lasts for approximately a minute. The patient is asleep for the procedure and awakens after 5-10 minutes, much as from minor surgery.
Is ECT effective for mental health?
ECT’s effectiveness in treating severe mental illnesses is recognized by the American Psychiatric Association, the American Medical Association, the National Institute of Mental Health, and similar organizations in Canada, Great Britain and many other countries. Although ECT can be very effective for many individuals with serious mental illness, ...
Is ECT good for depression?
Extensive research has found ECT to be highly effective for the relief of major depression. Clinical evidence indicates that for individuals with uncomplicated, but severe major depression, ECT will produce substantial improvement in approximately 80 percent of patients. It is also used for other severe mental illnesses, ...
How long does an ECT procedure last?
How long is an ECT procedure? A single ECT session usually lasts one hour. This includes the time the patient will be in the treatment room (approximately 15-20 minutes) and the time spent in the recovery room (approximately 20-30 minutes). Typically, ECT (whether inpatient or outpatient) is given two to three times a week for a total ...
How does ECT work?
Why does ECT work? No one is sure how ECT helps certain psychiatric disorders. It may promote changes in how brain cells communicate with each other at synapses and it may stimulate the development of new brain cells. ECT may flood the brain with neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which are known to be involved in conditions like ...
How long does it take to drive after ECT?
Usually this takes about 20 to 25 minutes. Patients who are given ECT on an outpatient basis must have someone drive them home after the procedure and stay with them until they go to sleep at night. People should not drive in the 24 hours following ECT.
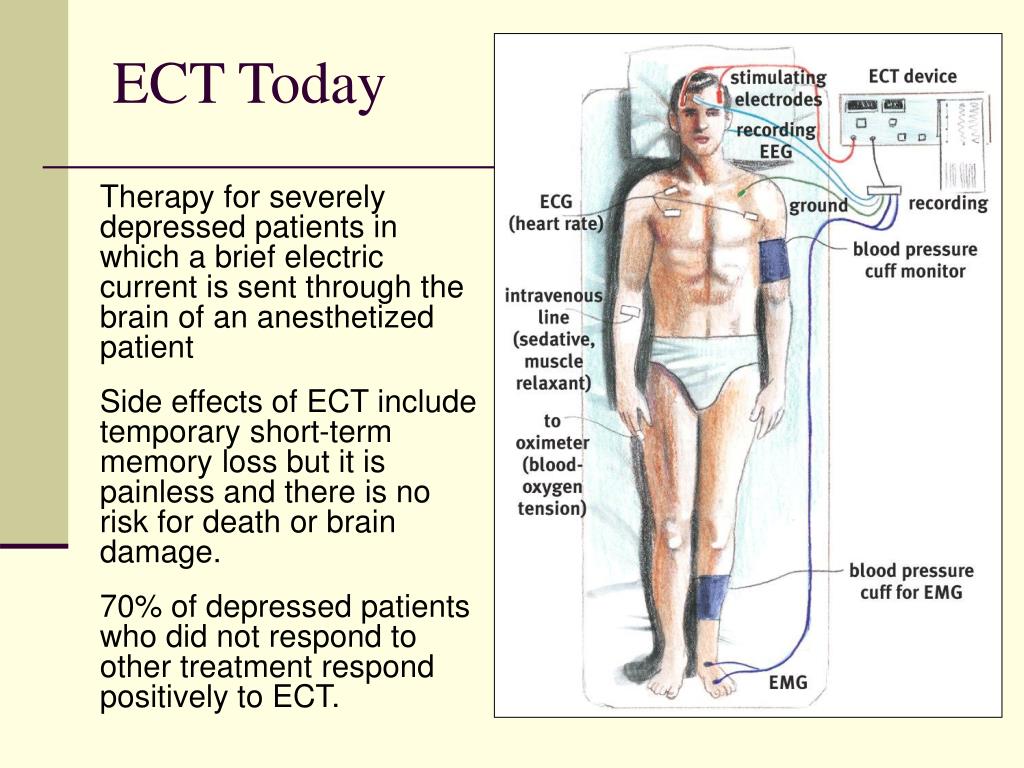
What are the two electrodes used for?
Two of these electrodes are for monitoring the brain waves. The other two are for delivering a short, controlled set of electrical pulses for a few seconds. The electrical pulses must produce a generalized seizure to be effective.
How long does it take to sleep before ECT?
During the procedure, the patient receives a short acting anesthetic agent which puts the patient to sleep for approximately 5-10 minutes.
How can families help with ECT?
Families can help by providing a gentle reminder of the day and date and that feeling confused is to be expected. Family members should inform the nurse of any concern they have about their loved one. View a Powerpoint Presentation for Families about ECT.
Can memories be lost after ECT?
Memories formed closer to the time of ECT are at greater risk of being lost while those formed long before ECT are at less risk of being lost. The ability to form new memories is also impaired after a course of ECT treatments but this ability usually makes a full recovery in the weeks and months following the last treatment.
What is ECT treatment?
D. Encourage high-caloric diet throughout the ECT course of treatment. ANS: A. ECT is an intervention for major depression that often includes suicidal ideations as a symptom. Continued suicide assessment is needed because mood improvement due to ECT may cause the client to act on suicidal ideations.
What is electroconvulsive therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy is the induction of a grand mal seizure through the application of electrical current to the brain for the purpose of decreasing depression. A chronically depressed and suicidal client is admitted to a psychiatric unit. The client is scheduled for electroconvulsive therapy (ECT).
How often should a nurse monitor pulse and blood pressure after electroconvulsive therapy?
ANS: A. Immediately after electroconvulsive therapy a nurse should monitor pulse, respirations, and blood pressure every 15 minutes for the first hour, during which time the client should remain in bed.
How long does it take for an electroconvulsive patient to sleep?
After the treatment, most clients will awaken within 10 to 15 minutes and will be confused and disoriented. Some clients will sleep for 1 to 2 hours.
Is ECT a first line treatment?
In view of its efficacy and speed of action, ECT may be a first-line treatment for life-threatening depression and a second line treatment for patients with major depressive disorder who do not respond or respond incompletely to antidepressant drugs.
Is electroconvulsive therapy still used?
Curative electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) remains a very useful treatment, still irreplaceable for some specific rare cases, as long as other brain stimulation methods, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation, remain experimental.
Overview
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure, done under general anesthesia, in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure. ECT seems to cause changes in brain chemistry that can quickly reverse symptoms of certain mental health conditions. ECT often works when other treatments are unsuccessful and when the full course o…
Why It's Done
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: 1. Severe depression,particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. 2. Treatment-resistant depression,a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications o…
Risks
- Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: 1. Confusion.Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there. Rarely, confusion may last several days or longer. Confusion is generally more noticeable in older adults....
How You Prepare
- Before having your first ECT treatment, you'll need a full evaluation, which usually includes: 1. Medical history 2. Complete physical exam 3. Psychiatric assessment 4. Basic blood tests 5. Electrocardiogram (ECG) to check your heart health 6. Discussion of the risks of anesthesia These exams help make sure that ECT is safe for you.
What You Can Expect
- The ECT procedure takes about five to 10 minutes, with added time for preparation and recovery. ECT can be done while you're hospitalized or as an outpatient procedure.
Results
- Many people begin to notice an improvement in their symptoms after about six treatments with electroconvulsive therapy. Full improvement may take longer, though ECT may not work for everyone. Response to antidepressant medications, in comparison, can take several weeks or more. No one knows for certain how ECT helps treat severe depression and other mental illness…