
Medication
9 rows · Dec 24, 2013 · Although there is no established treatment to delay the onset or forestall the progression of HD, ...
Therapy
Medicines can help reduce some of the problems caused by Huntington's disease, but they don't stop or slow down the condition. These include: antidepressants for depression medicines to ease mood swings and irritability medicines to reduce involuntary movements
Self-care
This review offers a detailed overview of the currently approved treatment options for HD and the clinical trials for this neurodegenerative disorder that are underway and concludes by discussing potential disease-modifying treatments that have shown promise in pre-clinical studies, including increasing neurotropic support, modulating autophagy, epigenetic and genetic manipulations, …
See more
Are there any natural treatment for Huntingtons disease?
What types of treatment are there for the Huntingtons disease?
What is the life expectancy of someone with Huntington disease?
How can Huntington disease be treated?
See more

What is the most common treatment for Huntington's disease?
Xenazine (tetrabenazine) is the only medication specifically approved for Huntington's chorea. Others, such as antipsychotics and benzodiazepines, have also demonstrated a benefit and can be used off-label. Physical therapy can help maintain mobility and prevent falls through tailored exercises for the patient.
Can Huntington's disease be cured?
Huntington's disease treatment There is no cure for Huntington's disease. Nothing can stop or reverse the disease's course. The goal of treatment is to help relieve symptoms. This will help you function for as long as possible.Mar 1, 2021
What is the life expectancy for Huntington's disease?
The time from disease emergence to death is often about 10 to 30 years. Juvenile Huntington's disease usually results in death within 10 years after symptoms develop. The clinical depression associated with Huntington's disease may increase the risk of suicide.Apr 14, 2020
Is Huntington's painful?
A large worldwide study on the prevalence of pain in Huntington's Disease (HD). The outcomes are pain interference, painful conditions and analgesic use. The prevalence of pain interference increases up to 42% in the middle stage of HD. The prevalence of painful conditions and analgesic use decrease as HD progresses.
What were your first symptoms of Huntington's disease?
The first symptoms of Huntington's disease often include:difficulty concentrating.memory lapses.depression – including low mood, a lack of interest in things, and feelings of hopelessness.stumbling and clumsiness.mood swings, such as irritability or aggressive behaviour.
What triggers Huntington disease?
Huntington's disease is a progressive brain disorder caused by a single defective gene on chromosome 4 — one of the 23 human chromosomes that carry a person's entire genetic code. This defect is "dominant," meaning that anyone who inherits it from a parent with Huntington's will eventually develop the disease.
What are the 5 stages of Huntington's disease?
5 Stages of Huntington's DiseaseHD Stage 1: Preclinical stage.HD Stage 2: Early stage.HD Stage 3: Middle stage.HD Stage 4: Late stage.HD Stage 5: End-of-life stage.Oct 23, 2020
Can you live a normal life with Huntington's disease?
Huntington's disease makes everyday activities more difficult to do over time. How fast it progresses varies from person to person. But the average lifespan after diagnosis is 10 to 30 years. HD itself is not fatal.Jun 1, 2020
What is the first treatment for Huntington's disease?
If you have severe muscle stiffness that causes pain or inhibits your movements, medication adjustment is usually the first type of treatment, because some of the antipsychotic medication used in the treatment of Huntington’s disease can cause muscle stiffness. 6 . Physical therapy may help as well.
How to reduce Huntington's symptoms?
And, as your behavioral symptoms and mood changes emerge, keeping a familiar schedule and avoiding unexpected or sudden changes in your life can help reduce the impact of these symptoms on your day-to-day life. The Signs and Symptoms of Huntington's Disease.
What is the best medication for chorea?
Oral medications used to reduce chorea are taken daily or several times per day. Xenazine (tetrabenazine) and Austedo (deutetrabenazine) are both approved for reducing chorea in Huntington’s disease. 1 These medications are believed to work by interaction with neurotransmitters in the brain.
What to do when a home care nurse comes to check in?
As a caregiver, you might feel some relief if you have a home care nurse come to check in your loved one, help with medications, and provide advice about safety and care in your home. You may also want to reach out for help about how to make decisions regarding your loved one’s living situation.
What is the difference between occupational therapy and speech therapy?
Occupational therapy is focused on maintaining skills, such as self-care. Speech therapy can help you speak clearly if your muscle control is becoming impaired and interfering with your ability to speak in an understandable way. Swallow therapy is very important as Huntington’s disease advances.
What is physical therapy?
5 . Physical therapy is focused on improving your muscle strength, control, and coordination.
Why is swallow therapy important?
Swallow therapy is very important as Huntington’s disease advances. Eating safety involves learning how to chew and swallow with better muscle control, and also selecting food and liquids that aren’t choking hazards.
How to help someone with Huntington's disease?
Help with everyday tasks. Daily tasks such as getting dressed, moving around your house and eating can be frustrating and exhausting if you have Huntington's disease. An occupational therapist can look at activities you find difficult and see if there's another way you can do them.
What are some ways to reduce Huntington's disease?
These include: antidepressants for depression. medicines to ease mood swings and irritability. medicines to reduce involuntary movements. Some of these medicines aren't licensed for Huntington's disease, ...
What are some ways to get a wheelchair accessible?
putting in ramps so an area can be accessed in a wheelchair. fitting a stairlift. installing grab rails – for example, by the stairs or beside the bed. using electric can openers, electric toothbrushes and kitchen utensils with large handles that are easier to hold.
How to help with weight loss?
alternative ways of communicating – such as electronic speech devices or picture charts. a high-calorie diet to help prevent weight loss. ways to make food easier to chew and swallow. At some point, a feeding tube that goes directly into your stomach may be needed.
Is there a cure for Huntington's disease?
There's currently no cure for Huntington's disease or any way to stop it getting worse. But treatment and support can help reduce some of the problems caused by the condition. In many areas, there are Huntington's disease clinics run by a specialist doctor and nurse, who can offer treatment and support and refer you to other specialists if needed.
Can a physiotherapist help with movement problems?
Getting around can be difficult if you have problems with co-ordination and balance, but even regular walking with the use of aids like walking sticks can be beneficial. A physiotherapist can also help with movement problems. They may recommend things like: an exercise plan.
What is Huntington's disease?
Treatments for Huntington’s disease. Huntington’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, caused by inheritable mutations in the huntingtin ( HTT) gene. The mutation produces a toxic form of the HTT protein that aggregates in and ultimately kills nerve cells.
What are some examples of anti-inflammatory treatments for Huntington's disease?
Examples of experimental anti-inflammatory therapies include VX15/2503 and laquinimod. Neuroprotective therapies aimed at reducing nerve cell death in the brain are also an option. Examples include Huntexil (prodopidine) and SBT-20.
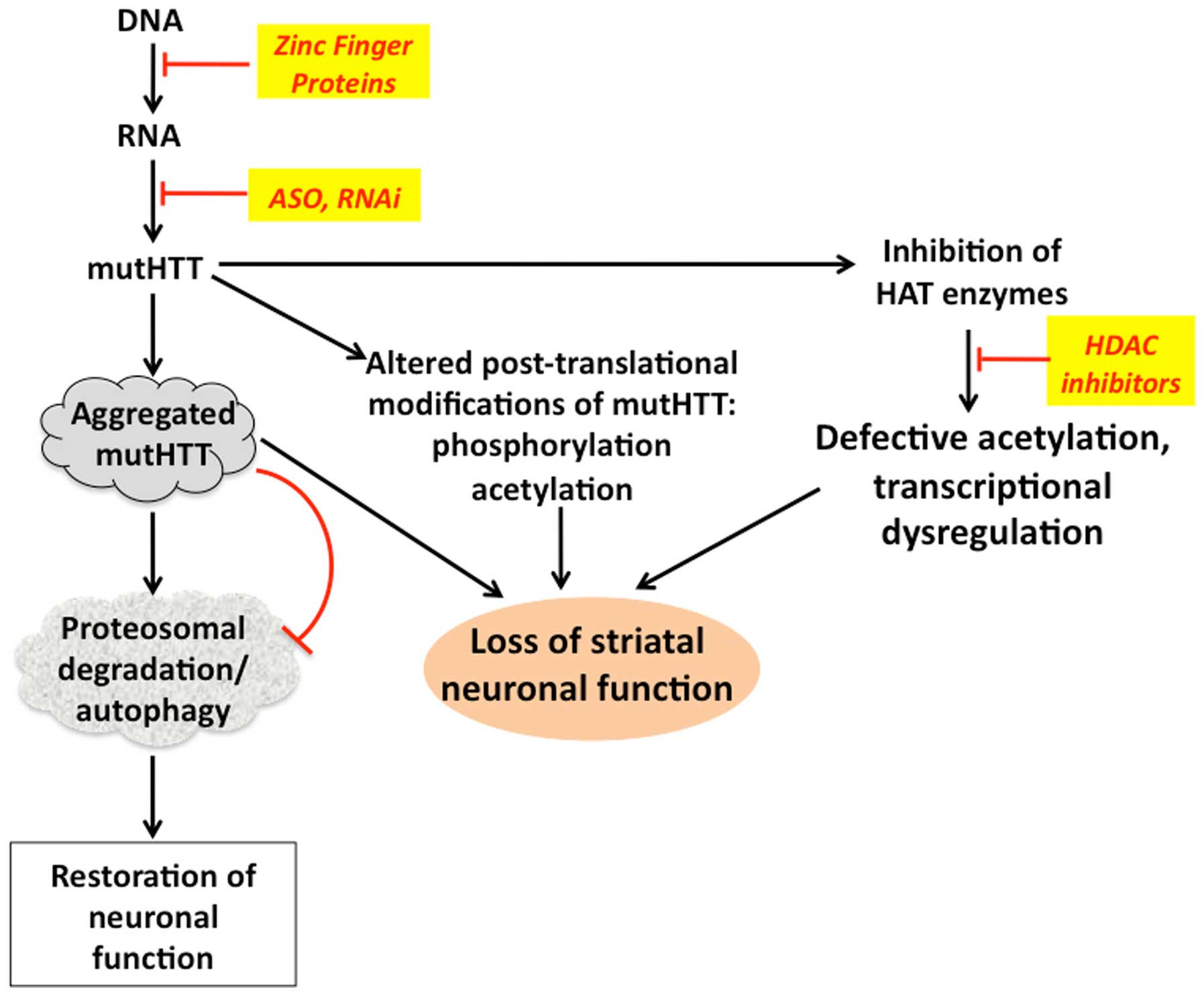
What is gene silencing therapy?
Gene silencing therapies act to reduce the levels of toxic HTT protein being produced. It is hoped that this could slow the progression ...
What is the best treatment for a person with a psychiatric disorder?
Occupational therapy and speech therapy can also help deal with communication issues that may arise due to the disease affecting the muscles of the mouth and throat. Psychiatric problems may be managed using anti-depressants, antipsychotics, and mood-stabilizing medications.
Can Huntington's disease slow the progression of the disease?
It is hoped that this could slow the progression of the disease, and not just manage the symptoms. Neuroinflammation is an abnormal immune response that is common in Huntington’s disease and can lead to further damage and cell death in the brain.
Is Huntington's disease still being developed?
Many of these have now progressed to the clinical trial stage in humans, and more are still being developed.
Does Xenazine help with Huntington's disease?
Xenazine (tetrabenazine) is the only medication specifically approved for Huntington’s chorea. Others, such as antipsychotics and benzodiazepines, have also demonstrated a benefit and can be used off-label. Physical therapy can help maintain mobility ...
Treatment
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
Specialist to consult
Home Remedies and Lifestyle
- No treatments can alter the course of Huntington's disease. But medications can lessen some symptoms of movement and psychiatric disorders. And multiple interventions can help a person adapt to changes in his or her abilities for a certain amount of time. Medications will likely evolv…
Prescriptions
- Managing Huntington's disease is demanding on the person with the disorder, family members and other in-home caregivers. As the disease progresses, the person will become more dependent on caregivers. A number of issues will need to be addressed, and strategies to cope with them will evolve.
Surgeries and Specialist-Driven Procedures
- A number of strategies may help people with Huntington's disease and their families cope with the challenges of the disease.
Emerging Treatment
- If you have any signs or symptoms associated with Huntington's disease, you'll likely be referred to a neurologist after an initial visit to your family doctor. A review of your symptoms, mental state, medical history and family medical history can all be important in the clinical assessment of a potential neurological disorder.
Complementary and Alternative Medicine
A Word from Verywell
- There are a number of prescription therapies used to alleviate some of the symptoms of Huntington’s disease. These treatments do not reverse the disease itself or stop its progression. You might need several different medications to manage each of the different symptoms, and sometimes one or more of your medications may exacerbate the effects of Huntington’s diseas…