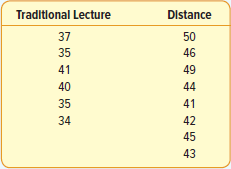
Alternatively, open the test workbook using the file open function of the file menu. Then select Two Way from the Analysis of Variance section of the analysis menu. Select the columns marked "Treatment 1", "Treatment 2","Treatment 3" and "Treatment 4" in one action when prompted for data.
Full Answer
How do you interpret a two-way ANOVA?
Complete the following steps to interpret a two-way ANOVA. Key output includes the p-value, the group means, R 2, and the residual plots. To determine whether each main effect and the interaction effect is statistically significant, compare the p-value for each term to your significance level to assess the null hypothesis.
Are the three p values produced by two-way ANOVA corrected for comparison?
Note that the three P values produced by two-way ANOVA are not corrected for the three comparisons. It would seem logical to do so, but this is not traditionally (ever?) done in ANOVA.
How do you do a two factor ANOVA with multiple values?
Enter sample data directly Balanced two Factor ANOVA with Replication - several values per cell. The data should be separated by Enteror ,(comma). ANOVA without Replication - one value per cell. The tool ignores empty cells or non-numeric cells.
How does StatsDirect handle multiple comparisons in two way ANOVA?
StatsDirect extends this to two way ANOVA by using the treatment group mean square from two way ANOVA for multiple comparisons. Treatment effects must be fixedfor this use of multiple comparisons to be valid.
How do you find the number of treatments in a two-way ANOVA?
The total number of treatment groups is the product of the number of levels for each factor. The within variance is the within variation divided by its degrees of freedom.
How do you determine the number of treatments in ANOVA?
The F statistic is in the rightmost column of the ANOVA table and is computed by taking the ratio of MSB/MSE....The ANOVA Procedure= sample mean of the jth treatment (or group),= overall sample mean,k = the number of treatments or independent comparison groups, and.N = total number of observations or total sample size.
What are treatments in ANOVA?
In the context of an ANOVA, a treatment refers to a level of the independent variable included in the model.
How do you calculate the SSE in two-way ANOVA?
SS (AB) = SS Total − SS Error − SS (A) − SS(B) SS Error = S iΣ jΣ k (y ijk − y̅ ij. ) SS Total = Σ iΣ jΣ k (y ijk − y̅...)...Adj SS.TermDescriptiony...overall mean of all observationsy .j.mean of the j th factor level of factor By ij.mean of observations at the i th level of factor A and the j th level of factor B4 more rows
How do you find treatments in statistics?
2:584:15What is a Statistical Treatment? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou might also be asked for a statistical treatment when writing a thesis or conducting anMoreYou might also be asked for a statistical treatment when writing a thesis or conducting an experiment. Basically it means to summarize your results. You'll want to include measurements.
How do you calculate TSS in ANOVA?
TSS = ∑ i , j ( y i j − y ¯ . . ) 2. It can be derived that TSS = SST + SSE . We can set up the ANOVA table to help us find the F-statistic.
What does it mean to find the treatment?
0:565:33How to Compute the Treatment Means Difference Confidence IntervalYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo plus or minus the T value times the square root of the mean standard error of the ANOVA. TableMoreSo plus or minus the T value times the square root of the mean standard error of the ANOVA. Table times 1 over n sub 1 plus 1 over n sub.
What is a treatment in statistics?
The term “statistical treatment” is a catch all term which means to apply any statistical method to your data. Treatments are divided into two groups: descriptive statistics, which summarize your data as a graph or summary statistic and inferential statistics, which make predictions and test hypotheses about your data.
What is a treatment variable in statistics?
the independent variable, whose effect on a dependent variable is studied in a research project.
How is SSE calculated?
To calculate the sum of squares for error, start by finding the mean of the data set by adding all of the values together and dividing by the total number of values. Then, subtract the mean from each value to find the deviation for each value. Next, square the deviation for each value.
How is SS treatment calculated?
0:112:13The Sums of Squares Treatment in ANOVA (Module 2 2 6) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo another way we can write the sums of squares for treatment is to say the number of people in eachMoreSo another way we can write the sums of squares for treatment is to say the number of people in each group the n sub J multiplied by the deviation between the group mean for the group J.
How do you calculate the SSE in two-way ANOVA quizlet?
How do you calculate the SSE in two-way ANOVA? By subtracting SST and SSB from SS total.
What is the difference between a one-way and a two-way ANOVA?
The only difference between one-way and two-way ANOVA is the number of independent variables . A one-way ANOVA has one independent variable, while...
How is statistical significance calculated in an ANOVA?
In ANOVA, the null hypothesis is that there is no difference among group means. If any group differs significantly from the overall group mean, t...
What is a factorial ANOVA?
A factorial ANOVA is any ANOVA that uses more than one categorical independent variable . A two-way ANOVA is a type of factorial ANOVA. Some exa...
What is the difference between quantitative and categorical variables?
Quantitative variables are any variables where the data represent amounts (e.g. height, weight, or age). Categorical variables are any variables...
What is an ANOVA test?
An ANOVA tests the null hypothesis that there is no difference among the mean values for the different treatment groups. Although it is possible to conduct an ANOVA by hand, no one in their right mind having access to computer software would do so. Setting up an ANOVA using RStudio is quite easy.
What is the purpose of ANOVA?
The fundamental principle in ANOVA is to determine how many times greater the variability due to the treatment is than the variability that we cannot explain.
How to find the mean square?
The " Mean square " is calculated by dividing the sum of squares by the degrees of freedom for that source. The mean square is analogous to the variance (i.e. the square of the standard deviation) of a distribution. Thus a large mean square represents a large variance, and vice versa.
What are differences caused by experimental treatment?
Differences caused by an experimental treatment can be thought of as just one part of the overall variability of measurements that originates from many sources. If we measured the strength of the response of cockroach retinas when stimulated by light, we would get a range of measurements. Some of the variability in measurements could be due to ...
What is a two way ANOVA?
A two-way ANOVA (“analysis of variance”) is used to determine whether or not there is a statistically significant difference between the means of three or more independent groups that have been split on two variables (sometimes called “factors”). When to use a two-way ANOVA.
What are the assumptions for a two way ANOVA?
For the results of a two-way ANOVA to be valid, the following assumptions should be met: 1. Normality – The response variable is approximately normally distributed for each group. 2. Equal Variances – The variances for each group should be roughly equal. 3.
What is the null hypothesis?
The null hypothesis is that there is no interaction between columns (data sets) and rows. More precisely, the null hypothesis states that any systematic differences between columns are the same for each row and that any systematic differences between rows are the same for each column. Often the test of interaction is the most important of the three tests. If columns represent drugs and rows represent gender, then the null hypothesis is that the differences between the drugs are consistent for men and women.
Does treatment have the same effect in males and females?
The treatment has about the same effect in males and females. The graph on the right, in contrast, shows a huge interaction. the effect of the treatment is completely different in males (treatment increases the concentration) and females (where the treatment decreases the concentration). In this example, the treatment effect goes in ...
When to use adjusted R2?
Use adjusted R 2 when you want to compare models that have different numbers of predictors. R 2 always increases when you add a predictor to the model, even when there is no real improvement to the model. The adjusted R 2 value incorporates the number of predictors in the model to help you choose the correct model.
How to determine if an interaction effect is statistically significant?
Step 2: Assess the means. Step 3: Determine how well the model fits your data. Step 4: Determine whether your model meets the assumptions of the analysis.
How to determine if an interaction is significant?
Step 1: Determine whether the main effects and interaction effect are statistically significant 1 The null hypothesis for a main effect is that the response mean for all factor levels are equal. 2 The null hypothesis for an interaction effect is that the response mean for the level of one factor does not depend on the value of the other factor level.
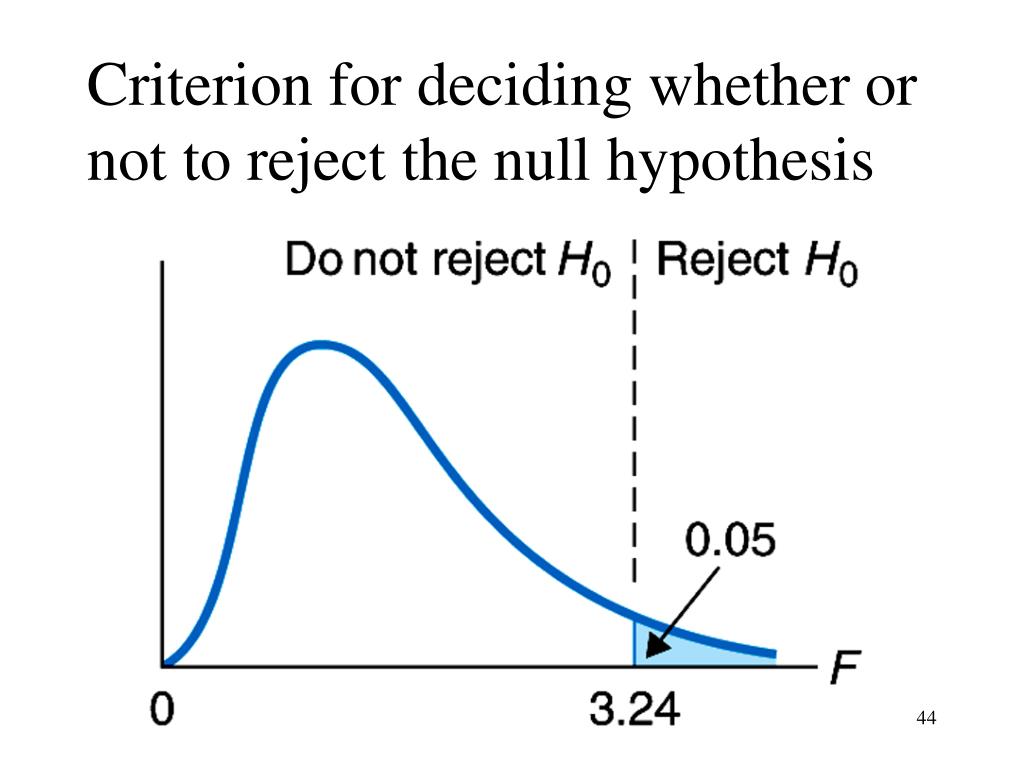
What happens if the p-value is greater than the significance level?
If the p-value is greater than the significance level you selected, the effect is not statistically significant. If the p-value is less than or equal to the significance level you selected, then the effect for the term is statistically significant. The following shows how to interpret significant main effects and interaction effects.
What is the null hypothesis for an interaction effect?
The null hypothesis for a main effect is that the response mean for all factor levels are equal. The null hypothesis for an interaction effect is that the response mean for the level of one factor does not depend on the value of the other factor level. The statistical significance of the effect depends on the p-value, as follows: ...
What is R2 in statistics?
R2 is the percentage of variation in the response that is explained by the model. The higher the R2 value, the better the model fits your data. R2 is always between 0% and 100%.
Why use residuals versus fits plot?
Use the residuals versus fits plot to verify the assumption that the residuals are randomly distributed and have constant variance. Ideally, the points should fall randomly on both sides of 0, with no recognizable patterns in the points.
Adj MS
The calculations for the mean square for the factors, interaction, and error follow:
Adj SS
The sum of squared distances. SS Total is the total variation in the data. SS (A) and SS (B) are the amount of variation of the estimated factor level mean around the overall mean. These statistics are also known as the sum of squares for factor A or factor B. SS Error is the amount of variation of the observations from their fitted values.
Fitted mean
The fitted means are least squares estimates. For a factor level, the least squares mean is the sum of the constant coefficient and the coefficient for the factor level.
F-value
The F statistic depends on the term in the test. For factor A, the F-statistic is as follows:
Pooled standard deviation
The pooled standard deviation is equivalent to S, which is displayed in the output. The formula follows:
P-value – Analysis of variance table
The degrees of freedom for the F statistic that you use to calculate the p-value depend on the term that is in the test.
R-sq (adj)
Accounts for the number of predictors in your model and is useful for comparing models with different numbers of predictors.
When to Use A Two-Way Anova
Two-Way Anova Assumptions
- For the results of a two-way ANOVA to be valid, the following assumptions should be met: 1. Normality – The response variable is approximately normally distributed for each group. 2. Equal Variances – The variances for each group should be roughly equal. 3. Independence – The observations in each group are independent of each other and the observat...
Two-Way ANOVA: Example
- A botanist wants to know whether or not plant growth is influenced by sunlight exposure and watering frequency. She plants 40 seeds and lets them grow for two months under different conditions for sunlight exposure and watering frequency. After two months, she records the height of each plant. The results are shown below: In the table above, we see that there were fiv…
Additional Resources
- The following articles explain how to perform a two-way ANOVA using different statistical softwares: How to Perform a Two-Way ANOVA in Excel How to Perform a Two-Way ANOVA in R How to Perform a Two-Way ANOVA in Python How to Perform a Two-Way ANOVA in SPSS How to Perform a Two-Way ANOVA in Stata