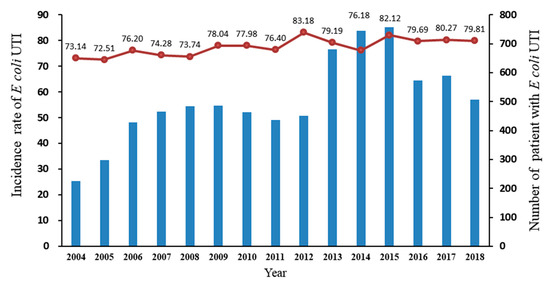
- Escherichia coli or better known as E. coli, is the bacterium responsible for over 80 percent of common UTI cases.
- The standard treatment for most urinary tract infections is antibiotics. However, some E. coli strains are resistant to most antibiotic drugs. These strains are called extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing E. coli.
- When lower urinary tract infections are properly treated on time, complications rarely occur. However, when UTIs are left untreated, serious complications may happen.
How to get rid of UTI in 24 hours?
The standard treatment for most urinary tract infections is antibiotics. However, some E. coli strains are resistant to most antibiotic drugs. These strains are called extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing E. coli. When lower urinary tract infections are properly treated on time, complications rarely occur.
Can an uti go away on its own?
Feb 06, 2022 · Treatment For A Uti Caused By E Coli The first line of treatment for any bacterial infection is antibiotics . If your urinalysis comes back positive for germs, a doctor will likely prescribe one of several antibiotics that works to kill E. …
What antibiotics are used to treat E coli?
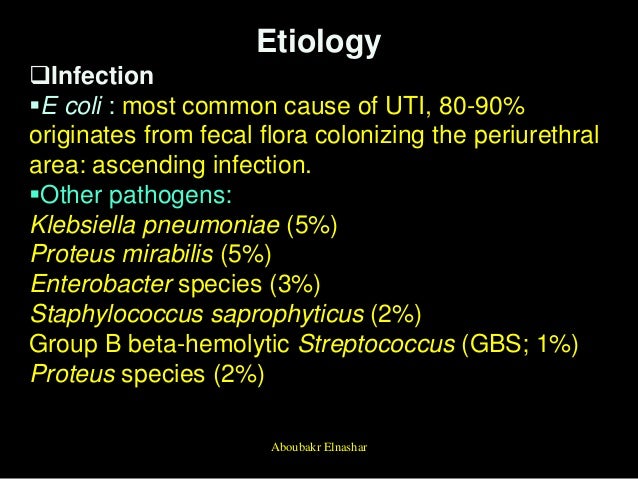
Feb 09, 2018 · However, among bacteria causing UTIS, E. coli is considered as the most predominant cause of both community and nosocomial UTIs. Antibiotics commonly recommended for treatment of UTIs include co-trimoxazole (trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole), nitrofurantoin, ciprofloxacin and ampicillin [ 3, 10 ].
What is the best treatment for an uti patient?
What is the best antibiotic for E. coli UTI?
coli is considered as the most predominant cause of both community and nosocomial UTIs. Antibiotics commonly recommended for treatment of UTIs include co-trimoxazole (trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole), nitrofurantoin, ciprofloxacin and ampicillin [3, 10].Feb 9, 2018
What antibiotics treat E. coli infection?
Which medications in the drug class Antibiotics are used in the treatment of Escherichia coli (E coli) Infections?Antibiotics. ... Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Bactrim DS, Septra DS, Sulfatrim) ... Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) ... Levofloxacin (Levaquin) ... Amoxicillin (Moxatag) ... Aztreonam (Azactam)More items...
How did I get E. coli in my urinary tract?
E. coli often gains entry into the urinary tract via stool. Women are particularly at risk for UTIs because their urethra sits close to the anus, where E. coli is present.Dec 16, 2019
How serious is E. coli in urine?
E. coli normally lives harmlessly in the human intestinal tract, but it can cause serious infections if it gets into the urinary tract. In women, the trip from the anus to the urethra is a short one. This is the reason why "wiping front to back" after using the toilet is helpful in preventing UTI.
What is the best treatment for a UTI?
Treatment for a UTI caused by E. coli. The first line of treatment for any bacterial infection is antibiotics. If your urinalysis comes back positive for germs, a doctor will likely prescribe one of several antibiotics that works to kill E. coli, since it’s the most common UTI culprit.
What bacteria are responsible for UTI?
Other bacteria that cause a UTI. While infection with E. coli accounts for most UTIs, other bacteria can also be the cause. Some that might appear in a urine culture include: Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Why are women at risk for UTIs?
Women are particularly at risk for UTIs because their urethra sits close to the anus, where E. coli is present. It’s also shorter than a man’s, giving the bacteria easier access to the bladder, where the majority of UTIs occur, and the rest of the urinary tract.
What is the UTI in the urinary tract?
A urinary tract infection (UTI) occurs when germs (bacteria) invade the urinary tract. The urinary tract is made up of your kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. The ureters are the tubes connecting the kidneys to the bladder. The urethra is the tube carrying urine from the bladder to outside your body.
How common are UTIs?
UTIs are incredibly common. In fact, 6 to 8 million cases are diagnosed each year in the United States. While men aren’t immune, women are 30 times. Trusted Source.
Can you send urine to a lab for a recurrent infection?
In some cases, especially if you don’t seem to be improving with treatment or you get recurrent infections, a doctor may send your urine out to a lab to be cultured. This can pinpoint exactly what bacteria is causing the infection and what antibiotic effectively fights it.
Can UTIs be treated with antibiotics?
Takeaway. UTIs are some of the most common infections doctors see. Most are caused by E. coli and are successfully treated with a round of antibiotics. If you have symptoms of a UTI, see a doctor. Most UTIs are uncomplicated and don’t cause any lasting harm to your urinary tract.
