Medication
Rabies is an overwhelmingly fatal disease, with only a few documented survivors. There is no effective curative treatment for rabies once clinical signs have appeared. All cases of suspected rabies exposure should be treated immediately to prevent the onset of clinical symptoms and death. Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) consists of wound treatment, the administration of rabies vaccines based on WHO recommendations, and if indicated, the administration of rabies immunoglobulin (See table below).
Will there ever be an effective rabies treatment?
What happens if rabies goes untreated? Rabies is almost always fatal if it is left untreated. In fact, once someone with rabies starts experiencing symptoms, they usually do not survive. This is why it is very important to seek medical attention right away following an animal bite, especially if the bite is from a wild animal.
What happens if rabies is untreated?
This treatment includes extensive washing and local treatment of the wound followed by a course of a potent and effective rabies vaccine. When given in time, PEP can stop the rabies virus from entering the central nervous system and, in turn, prevent the onset of rabies symptoms.
Can you cure rabies?
Why is rabies not curable? During infection of the brain, the permeability of the barrier can increase, allowing immune cells and antibodies through to help clear the infection. However, during infection with rabies virus, the blood brain barrier locks down, meaning nothing can get through, even antiviral drugs.25 Has anyone been cured rabies?
Why is rabies not curable?

What do they give humans for rabies?
Postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) consists of a dose of human rabies immune globulin (HRIG) and rabies vaccine given on the day of the rabies exposure, and then a dose of vaccine given again on days 3, 7, and 14.
Can rabies be stopped in humans?
Rabies in humans can be prevented either by eliminating exposures to rabid animals or by providing exposed persons with prompt local treatment of wounds combined with appropriate passive and active immunization.
How long can a human live with rabies?
Death usually occurs 2 to 10 days after first symptoms. Survival is almost unknown once symptoms have presented, even with intensive care. Rabies has also occasionally been referred to as hydrophobia ("fear of water") throughout its history.
Can you survive rabies with treatment?
As we know rabies has approximately 100% mortality rate but by using the aggressive treatment approach (like Milwaukee protocol), the patient may survive. Rabies can be effectively prevented by using adequate postexposure vaccine prophylaxis and rabies immunoglobulin (in category-3) after bite of a rabid animal.
What to do after a rabies bite?
In addition to seeking medical attention right after an animal bite (especially from a bat, fox, or skunk), the wound should be cleaned immediately and thoroughly.
What is the weakened form of rabies?
The Rabies Vaccine. Like all vaccines, rabies vaccines contain a weakened form of the virus that is incapable of causing disease or reproducing. In response to the vaccine, your body produces antibodies that target and kill the rabies virus.
What is PEP in rabies?
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) is the only treatment strategy known to prevent rabies-related deaths. 4 This treatment includes extensive washing and local treatment of the wound followed by a course of a potent and effective rabies vaccine.
What is the first category of exposure to rabies?
The guidelines identify three categories of rabies exposure. The first category is defined as "touching or feeding animals, licks on intact skin," but post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) is recommended only for category 2 and category 3 exposure. 8.
What animals are most likely to get rabies?
2 The rabies virus may also be spread by such animals as foxes, skunks, and raccoons. Across the globe, over 90 percent of human rabies cases result from virus transmission by domestic dogs. 3 .
How long does it take to die from rabies?
Once symptoms set in, however, death from respiratory failure usually occurs within seven days —even if treatment is given.
Can rabies cause nausea?
Swelling. Itching. In rare cases, patients may experience symptoms like headache, nausea, abdominal pain, muscle aches, and dizziness. Before receiving the rabies vaccine, let your doctor if you’ve ever had a serious allergic reaction to a dose of rabi es vaccine.
Incubation
Incubation is the time before symptoms appear. It usually lasts from 2–3 months and varies from 1 week to 1 year, depending on where the virus entered the body and the number of viral particles involved. The closer the bite is to the brain, the sooner the effects are likely to appear.
Coma and death
A person may enter a coma, and most people then die within 3 days. During the coma stage, even with supportive therapy, virtually no person survives rabies.
Why does rabies cause a fear of water?
People used to call rabies hydrophobia because it appears to cause a fear of water. The reason is that the infection causes intense spasms in the throat when a person tries to swallow. Even the thought of swallowing water can cause spasms, making it appear that the individual is afraid of water.
Rabies vaccine
Doctors do not offer the rabies vaccine routinely. Instead, they reserve it for those at high risk of rabies exposure, such as laboratory staff working with the virus that causes the disease, veterinarians, and people likely to receive animal bites. These individuals may receive regular vaccinations.
Individual precautions
Individuals should follow some safety rules to reduce the chance of contracting rabies.
How do you get rabies?
Rabies is transmitted through direct contact with the saliva or brain tissue of an infected animal.
Is a rabies vaccine available for humans?
Yes, rabies vaccines ( RabAvert, Imovax) are available for humans. The vaccine is given by an injection into the muscle, and it consists of four shots. Most people only need the rabies vaccine if they’ve had exposure to a rabid animal.
How do you prevent rabies from becoming an infection?
Prompt medical attention is vital for preventing a rabies infection. If you’ve been bit by a rabid animal — or even an animal that might have rabies — you’ll need post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) to help protect yourself. About 55,000 people in the U.S. get PEP every year.
Can you treat rabies once symptoms of an infection develop?
After being exposed to rabies, it takes time for rabies to travel to your brain. This is known as the incubation period and can last weeks to months. This time can vary depending on the initial location of exposure.
Is there any ongoing research for rabies treatments?
Recently, the FDA released guidance for drug manufacturers to use to help develop monoclonal antibody cocktails — a type of new anti-rabies treatment. Monoclonal antibodies are biologic medications that act as artificial antibodies. The term cocktails refers to multiple monoclonal antibody medications being used at the same time.
The bottom line
Rabies is a disease that is preventable with prompt medical care, but it’s almost always fatal when it reaches your brain. Treating rabies once it reaches your brain is difficult because it’s hard to get medications into your brain.
How does WHO promote human rabies prevention?
WHO continues to promote human rabies prevention through the elimination of rabies in dogs, dog bite prevention strategies , and more widespread use of the intradermal route for PEP which reduces volume and therefore the cost of cell-cultured vaccine by 60% to 80%.
How much does rabies cost?
Globally rabies causes an estimated cost of US$ 8.6 billion per year. 40% of people bitten by suspect rabid animals are children under 15 years of age. Immediate, thorough wound washing with soap and water after contact with a suspect rabid animal is crucial and can save lives.
What is the importance of education on dog bite prevention?
Education on dog behaviour and bite prevention for both children and adults is an essential extension of a rabies vaccination programme and can decrease both the incidence of human rabies and the financial burden of treating dog bites.
How long does it take for rabies to die?
Death occurs after a few days due to cardio-respiratory arrest. Paralytic rabies accounts for about 20% of the total number of human cases.
What is PEP in rabies?
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) is the immediate treatment of a bite victim after rabies exposure. This prevents virus entry into the central nervous system, which results in imminent death. PEP consists of: Extensive washing and local treatment of the bite wound or scratch as soon as possible after a suspected exposure;
How long does it take to flush a rabies wound?
This first-aid measure includes immediate and thorough flushing and washing of the wound for a minimum of 15 minutes with soap and water, detergent, povidone iodine or other substances that remove and kill the rabies virus.
How many people get rabies shots every year?
Every year, more than 29 million people worldwide receive a post-bite vaccination. This is estimated to prevent hundreds of thousands of rabies deaths annually. Globally, the economic burden of dog-mediated rabies is estimated at US$ 8.6 billion per year.
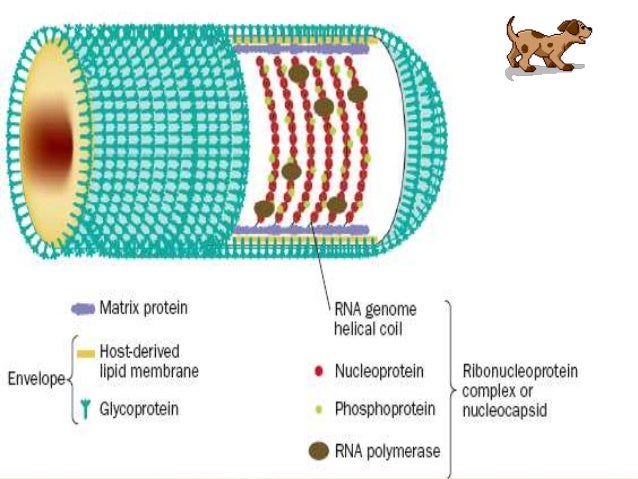
Abstract
Rabies is an acute, fatal, neurological disease that affects almost all kinds of mammals. Vaccination (using an inactivated rabies vaccine), combined with administration of rabies immune globulin, is the only approved, effective method for post-exposure prophylaxis against rabies in humans.
1. Introduction
Rabies is an ancient neurological disease caused mainly by the rabies virus (RABV) and is almost invariably fatal once clinical symptoms develop. Currently, rabies continues to pose a serious public health threat in most areas of the world, especially in the developing countries of Asia and Africa.
2. Brief History of Classical Rabies Vaccines
Rabies is one of the oldest infectious diseases and has been known to mankind for more than 4000 years [ 11 ]. However, it was not until 1885 that Louis Pasteur developed the first RABV vaccine from the spinal cord of rabbits infected with rabies that was air-dried for inactivation.
3. Live-Attenuated Virus-Based Rabies Vaccines
Unlike most other vaccines, however, rabies vaccines are designed to be prophylactic and administered primarily in a post-exposure manner. Due to the extremely high mortality of rabies, only inactivated rabies vaccines were approved for human rabies control.
4. Other Novel Modalities for Rabies Control and Prevention
Although live-attenuated virus-based vaccines represent the most promising approach for rabies control and treatment, some other novel modalities have also been investigated for their potential role in rabies treatment, such as protein and peptide vaccine, nucleic acid-based vaccine, RNA interference (RNAi), and RIG, coupled with BBB permeability enhancing agents such as monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1).
5. Conclusions
Rabies continues to pose a severe burden to public health and is ranked one of the most fatal diseases. It causes tens of thousands of human deaths annually, particularly in developing countries. Currently, dogs remain the main source of rabies and are responsible for almost 99% of fatal rabies cases in humans.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Yongxin Yu (National Institutes for Food and Drug Control) for the generous technical assistance and advice. We also acknowledge support from Jincai Wang (Shenzhen Weiguang Biological Products Co., Ltd.). This work was financially supported by the Guangdong Engineering Technology Research and Development Center.
