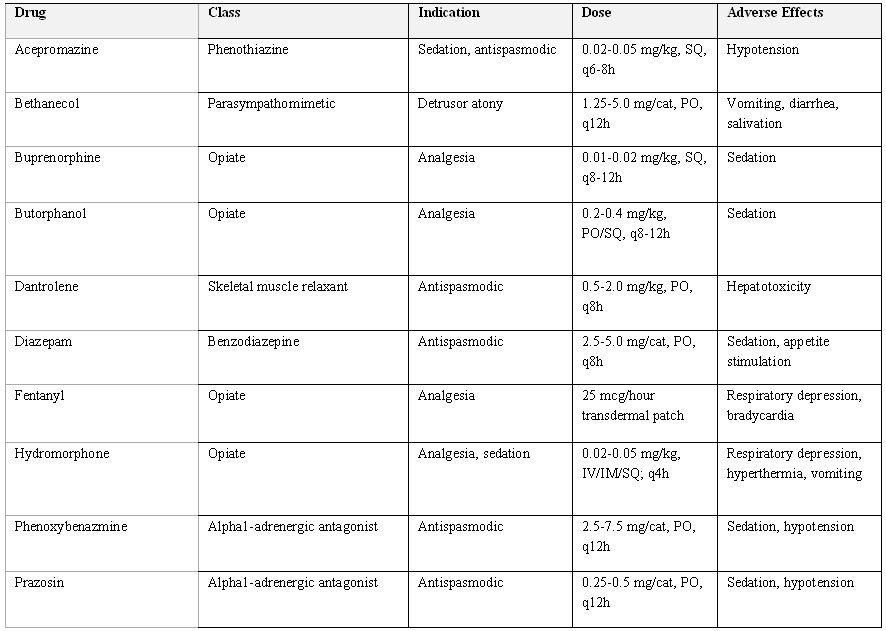
Sedatives may be administered to relax the urethral muscle allowing stones to pass If stones are logged in the urethral process the urethral process may be sniped off to allow urination In some cases depending upon the location of the stone in the urethra and the integrity of the bladder, surgery may be necessary to save the animals life
How to get rid of urethral stones in cattle?
TREATMENT FOR URINARY STONES. Sedatives may be administered to relax the urethral muscle allowing stones to pass. If stones are logged in the urethral process the urethral process may be sniped off to allow urination. In some cases depending upon the location of the stone in the urethra and the integrity of the bladder, surgery may be necessary to save the animals life.
What is the best treatment for urolithiasis in cattle?
Urethrotomy: The urethral calculus to be removed is located by evaluation of radiographs, palpation of the os penis and its relationship to the calculus, and/or passing a catheter in the urethra until it contacts the stone, removing the catheter and using it …
How do you prevent urinary calculi in horses?
Laser lithotripsy is best utilized when there are urethral calculi or small numbers of cystic calculi. Stones that develop in the kidney may be removed by a nephrotomy, although most do not require surgical removal. Ureteral stones, if causing a blockage to urine flow, may be removed by a ureterotomy. Alternatively to ureterotomy, a ureteral stenting procedure can be performed to …
What is urinary calculi and how can it kill an animal?
Jun 06, 2011 · The addition of hay or some other type of long fiber to the animal's diet is absolutely critical to help avoid Urinary Calculi. This is a big problem with some show-animal producers because they tend to take animals off long fiber and push concentrates. Urinary Calculi requires immediate medical attention.
How is urethral stone treated?
How are ureteral stones treated?Shock wave lithotripsy: During this procedure, you are set up with a machine that produces focused shock waves to break up the stones. ... Ureteroscopy: The urologist feeds a long tube with an eyepiece, called an ureteroscope, into your urethra (the hole where urine leaves your body).More items...•Sep 18, 2017
What are the treatment options for urinary calculi?
TreatmentDrinking water. Drinking as much as 2 to 3 quarts (1.8 to 3.6 liters) a day will keep your urine dilute and may prevent stones from forming. ... Pain relievers. Passing a small stone can cause some discomfort. ... Medical therapy. Your doctor may give you a medication to help pass your kidney stone.May 5, 2020
How is urinary calculi treated in cattle?
Acidification of the urine with ammonium chloride will help dissolve the phosphate stones that occur in feedlot cattle. Surgery is the surest cure if used soon after the problem is first discovered.
How do you treat urinary calculi in sheep?
Remove feed from the lambs or kids for 24 hours and apply oral doses of ammonium chloride (1 oz per . 5 lbs of body wt) can acidify the urine and dissolve the crystals. The oral treatment should be continued for at least a week due to probability that there are multiple calculi in the bladder.
What medicine is used to dissolve kidney stones?
Your doctor may prescribe potassium citrate to help prevent kidney stones from growing larger or returning. Potassium citrate can also be used to help dissolve and prevent uric acid kidney stones.
How do you treat a 10mm kidney stone?
Medical therapy for kidney stones Most evidence suggests that stones less than 10 mm in diameter have a reasonable chance of passing through the urinary tract spontaneously. You may be offered medical expulsive therapy (MET) using an alpha blocker medication, such as tamsulosin.Jul 18, 2019
What causes urinary calculi in cattle?
“If the animal isn't drinking enough water, urine becomes concentrated,” he says. “If the diet leads to high mineral content in the urine, this makes a double problem. Mineralized salts may crystallize or clump together into stones.Jan 6, 2015
How do you treat a UTI in cattle?
Treatment of Bovine Cystitis and Pyelonephritis The treatment of choice for pyelonephritis caused by Corynebacterium spp is penicillin (22,000 IU/kg, IM, twice a day) or trimethoprim-sulfadoxine (16 mg combined/kg, IM, twice a day) for ≥3 weeks.
How do you treat struvite stones?
Since struvite stones are caused by bacteria, doctors may use a mixture of antibiotics and surgery to remove the stones and kill the bacteria creating them. Surgical methods include shock wave lithotripsy (SWL) or percutaneous nephrolithotomy or nephrolithotripsy.Jun 7, 2021
How long does it take for ammonium chloride to work?
This medication should take effect within 1 to 2 hours; however, effects may not be noted outwardly and therefore laboratory tests may need to be done to evaluate this medication's effectiveness.
How can urinary calculi be prevented?
The high acid concentration of the urine makes it easier for uric acid stones to form. To prevent uric acid stones, cut down on high-purine foods such as red meat, organ meats, and shellfish, and follow a healthy diet that contains mostly vegetables and fruits, whole grains, and low fat dairy products.
What causes urinary calculi in sheep?
The primary cause of urinary calculi is feeding concentrate diets which are excessive in phosphorus and magnesium and/or have an imbalance of calcium and phosphorus. Lack of water and water sources that are high in minerals are also contributing factors.
Why are goats prone to urinary calculi?
Goats used for show purposes are prone to Urinary Calculi because their owners tend to over-feed concentrates.
What is the condition that prevents both urination and breeding in male sheep?
Urinary Calculi, a urinary-tract condition in goats and sheep, prevents both urination and breeding in males. The twists and turns of the male urethra make passing solid particles difficult at best and impossible at worst. Urinary Calculi is a disease that can and does kill animals quickly.
What is the ratio of calcium to phosphorus in hay?
Proper calcium to phosphorus ratio in feed, hay and minerals is critical; this ratio should be 2 1/2 to 1. Although the disease is called Urinary Calculi, the real culprit is phosphorus -- specifically too much phosphorus in relation to the amount of calcium in the diet. Feeding too much concentrated feed and/or feeding concentrates ...
What are the symptoms of a urinary calculus?
Symptoms of Urinary Calculi include tail twitching in males, restlessness, anxiety and a "hunched-up" body posture as the animal strains to urinate.
What causes a goat to die from a concentrate?
Overfeeding or improper feeding of concentrates causes solid particles to develop in the urine; these solid particles block the flow of urine out of the goat's body, causing great pain, discomfort and oftentimes death. Besides concentrates, there are other factors affecting the calcium-to-phosphorus ratio in the goat's diet.
Can a burst bladder be fixed?
A burst bladder cannot be fixed and is fatal. The key to avoiding Urinary Calculi is feeding the animal a proper diet. Producers experiencing Urinary Calculi in their animals must change their feeding regimens. Carefully read feed labels for proper calcium-to-phosphorus ratios (2 1/2:1).
Can wethers get urethra calculi?
Young wethers (castrated males) are especially susceptible to Urinary Calculi. Castration stops both testosterone production and the growth of the urethra. Solid particles cannot pass through a urethra that has not been given the opportunity to grow to its normal diameter. The chance of contracting Urinary Calculi in male show animals can be ...
What is a urethral plug?
Urethral plugs are solid, soft masses composed of crystals, mucous protein and cellular debris. The mucous and cellular debris are thought to be a result of infection or chronic inflammation of the bladder lining. The male urethra in dogs and cats is much smaller in diameter than the females.
What are the crystals in dog bladder plugs?
Eighty-one percent of the plugs contained crystal formations called struvite. Struvite crystals are composed of magnesium, ammonia and phosphorus. In dogs, these crystals are most commonly associated with bladder infections.
Why don't plugs show up on X-rays?
Unlike stones, plugs may not show up on X-ray due to the lower concentration of crystals. A negative X-ray would not rule out urethral obstruction. It also highlights a red flag for Pugs with urination difficulties. Dr. Ken Tudor.
What is intravenous fluid therapy?
Intravenous fluid therapy is initiated to “flush” the kidneys and prevent further damage. This also promotes the production of large amounts of dilute urine to help dissolve plugs that were forced back into the bladder with urethral catheterization or plugs that may be forming in the bladder.
How long did a dog reobstructed a urinary tract?
Follow-up of the cases revealed that one dog reobstructed within nine weeks and was euthanized. Another obstructed four years later due to oxalate, not struvite stones.
What happens if you have backed up urine?
The backed-up urine increases pressure in the kidneys, causing potentially permanent dysfunction. Electrolyte (sodium, potassium) imbalances develop, endangering heart function and ammonia levels in the blood rise to toxic levels. Treatment requires relieving the obstruction and re-establishing urine flow through the urethra ...
Can a male cat have a urethral plug?
Cat owners are very familiar and concerned about urethral plugs in their male cats. This obstruction of urine flow from the bladder to the penis opening can be life threating if not treated. Although male dogs can become obstructed by stones, only recently has it been reported that they can also develop a plug in their urethra.
What is a scrotal urethrostomy?
A scrotal urethrostomy allows urine to exit behind the os penis where the urethra is wider (Figures 2, 3). An opening is created that small stones may pass through. Patients with a scrotal urethrostomy may still get urinary obstruction by very large stones in the bladder or upper urethra.
Why is my dog's urethra blocked?
The urethra can also be blocked if the bone is fractured or if the dog develops a tumor of the penis. Scar tissue can also cause partial blockage. Signs and Symptoms: Clinical signs depend on the severity of the blockage. Dogs that have a partial obstruction may: urinate small amounts frequently.
How long does it take for a dog to die from a bladder obstruction?
The urinary bladder may rupture and spill urine into the dog’s abdomen with complete obstruction. Dogs with total urethral obstruction will die within days if the obstruction is not relieved.
What is the diagnosis of obstruction in dogs?
Diagnostics: Diagnosis of obstruction is usually based on an inability to advance a urethral catheter into the bladder. Your primary care veterinarian may feel the catheter pass over the calculi in dogs that are partially obstructed.
What causes a dog to have a urinary tract blockage?
Urinary tract calculi are the most common cause of urethral obstruction in dogs, anything that causes stone formation will increase the risk of urethral blockage (see urinary stones ). For example, Yorkshire Terriers and Schnauzers with liver shunts (see portosystemic shunts) and Dalmatian dogs are prone to forming urate calculi.
What is the name of the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body?
Only then did your veterinary surgeon earn the title of ACVS Diplomate. Language: English / Español. Overview: The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. In the male dog, it passes along the back side of the dog and between the rear legs.
How long does it take for a dog to drain urine from the bladder?
If your dog is very sick, surgery may be delayed, and a urinary catheter left in the urinary tract to drain urine from the bladder for a day or two, until medical conditions have improved and your pet is stable for general anesthesia and surgery.
What is a urethrostomy for dogs?
In dogs, a urethrostomy is indicated when bladder stones have traveled to the urethra and caused a partial or complete obstruction to the flow of urine. The breeds most commonly affected by this condition are Dalmatians and Lhasa Apsos.
What is the procedure to open the urethra?
A urethrostomy is a surgical procedure to create an opening in the urethra, the tube through which urine flows from the bladder and is voided. The surgery is performed to correct a urethral obstruction, which can be caused by protein plugs, stones, trauma, or scarring (stricture).
How long does it take for a urethrostomy to heal?
Patients that have had a urethrostomy must be kept calm and inactive during their recovery. Often times, they will bleed from the surgical site for up to 10 days post operatively. Keeping them calm may help in reducing the amount of bleeding.
What is the condition that makes cats prone to protein plugs?
It is most commonly performed on male cats that suffer from feline urologic syndrome, a condition that makes them prone to protein plugs, bladder “sand” or “sludge,” or bladder stones that enter the urethra and obstruct the flow of urine.
Can a dog have a urethrostomy?
In both cats and dogs, a urethrostomy would be performed in cases of severe penile trauma or scarring/stricture that does not allow for the normal passage of urine.
Can anesthesia cause scars in cats?
Other risks are hemorrhage, post-operative infection, and wound dehiscence (breakdown). Scar formation can occur in some cats, causing a stricture of the urethra, which requires additional surgery. Download PDF.
Is a urethra a life threatening condition?
A urethral obstruction is a serious, life-threatening condition ; therefore, urethtrostomies are often performed on an emergency basis. In male cats, a perineal urethrostomy, or PU, is performed, and in dogs a scrotal urethrostomy is performed.
What is the most effective diagnostic test for a urethra stone?
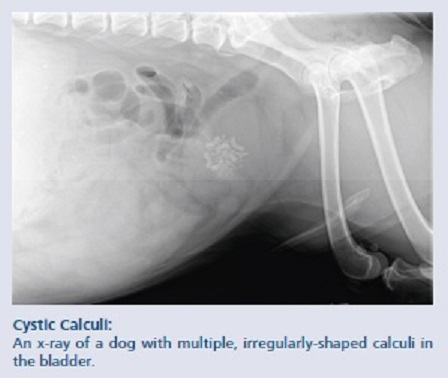
The most effective diagnostic test is a rectal exam (digital rectal exam in small ruminants). In an obstructed animal, the urethra is often pulsing. Imaging can be used to confirm or assess the number and location of stones. Most (but not all) stones are radio-opaque.
What is ruminant urolithiasis?
Ruminant urolithiasis. Urolithiasis podcast. Urolithiasis is a common problem in goats and feedlot cattle. It is not uncommon in pigs, camelids and horses. The type, number and location of stones varies by species. Pigs and camelids can also develop urethral polyps which present in very similar manner to stones but are much harder to treat ...
Why do goats have bladder marsupialization?
Bladder marsupialization was developed to manage recurrent urolithiasis in goats. The bladder is tacked to the body wall and cystostomy performed, similar to a rumenostomy. However, many goats die of ascending pyelonephritis within two years so it is not an ideal fix.
How long should you leave a uremic tube in?
antibiotic coverage is maintained while the tube is in place due to the risk of ascending infection. generally we leave the tube in for at least 8 days to create an adhesion to the body wall (this number is pulled out of thin air as far as I can tell) Uremic animals are not edible.
What is the stifle on a radiograph?
Ultrasound can be used to identify full bladders, urine leakage and occasionally urethral stones. The stifle is often right on top of the sigmoid flexure on radiographs so look carefully in that area. . Caprine urolithiasis.
What is the best medicine for goats?
Analgesics are needed, especially for goats. consider phenazopyridine (relieves bladder irritation), narcotics and NSAIDs. goats are pretty sensitive to pain and will tend to be in rough shape for a day or two post-operatively. Remove the tube once the goat can urinate on his own through the penis.
Where do stones lodge in goats?
All the other species present for partial or complete urinary obstruction. Stones will often lodge in the vermiform appendage of goats and in the sigmoid flexure of all ruminants (and generally in both). Animals may be seen straining to urinate or defecate.
WHAT IS PERINEAL URETHROSTOMY?
Perineal urethrostomy or PU is a surgical procedure that entails creating a permanent opening of the urethra (pipe that connects the urinary bladder to the outside) to prevent stones, crystals, mucous plugs to obstruct the urethra.
WHY DO CATS DEVELOP URINARY BLOCKAGE?
Urinary blockage is a very common condition in adult cats usually overweight / obese that are fed dry food. The cause of the obstruction of the urethra is multifactorial and associated with a syndrome named Feline Urologic Syndrome.
HOW DO I KNOW THAT MY CAT HAS URINARY BLOCKAGE?
Cats that experience urinary blockage strain to urinate and often urinate outside the litter box. Immediate medical attention should be considered if the patient is straining and no urine is produced. This condition is life threatening and cat that completely obstruct could die within days from kidney failure.
WHAT ARE THE TESTS NECESSARY TO DIAGNSOSE URINARY BLOCKAGE?
Cats that experience urinary blockage, should have blood work and urine test done to determine if their kidneys are failing. X rays of the belly are also necessary to determine the urinary bladder size, and presence of stones.
WHAT ARE THE TREATMENTS FOR URINARY BLOCKAGE?
The management of cats with urinary blockage can be addressed in two ways: medical and or surgery. The medical treatment entails placing a catheter into the urinary bladder to ensure urination and keep it in place for 2 to 3 days. Additionally, pain medication and special diet (wet) should be prescribed by the veterinarian.
WHAT IS THE AFTERCARE AFTER PU SURGERY?
After surgery, few things have to change in the household to ensure that the healing of the PU is going well. The litter box should have shredded paper instead of litter to prevent the clay contacting the incision, multiple water bowels should be available to increase water intake (add tuna juice) and the diet should be wet only and always.
WHAT THE COMPLICATIONS OF PU SURGERY?
The success of PU surgery is very good if performed correctly, however complications could always arise. The most common problems associated with PU surgery include scar tissue formation at the incision site that will lead to recurrence of the urinary blockage.