Medication
The treatment options for thyroid cancer might include: Surgery for Thyroid Cancer Radioactive Iodine (Radioiodine) Therapy for Thyroid Cancer Thyroid Hormone Therapy External Beam Radiation Therapy for Thyroid Cancer Chemotherapy for Thyroid Cancer Targeted Drug Therapy for Thyroid Cancer
Procedures
Medullary thyroid cancer. Well-differentiated tumors ( papillary thyroid cancer and follicular thyroid cancer) can be treated and can usually be cured. Poorly differentiated and undifferentiated tumors ( anaplastic thyroid cancer) are less common. These tumors grow and spread quickly and have a poorer chance of recovery.
Self-care
Feb 18, 2022 · Thyroid cancer treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, radioactive iodine therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy, and observation. Get detailed information about the treatment options for newly diagnosed and recurrent thyroid cancer in this summary for clinicians.
Nutrition
There are lots of ways to treat thyroid cancer. The treatment you get will depend on the type and stage of the cancer. It also depends on your age, general …
See more
Mar 11, 2022 · In addition to surgery, radioactive iodine treatment, external beam radiation, alcohol ablation and chemotherapy are other treatment options based on the type and stage of the cancer. After initial treatment, neck imaging and thyroid tumor marker levels are checked regularly to monitor for recurrence and to decide if additional treatment is needed.
What is the life expectancy of someone with thyroid cancer?
Jan 21, 2020 · Learn about thyroid cancer diagnosis and treatment, including thyroid surgery, radioactive iodine and thyroid hormone therapy. COVID-19: Advice, updates and vaccine options Find out about COVID-19 , COVID-19 vaccines , and Mayo Clinic patient and visitor updates .
What are the long-term effects of thyroid cancer?
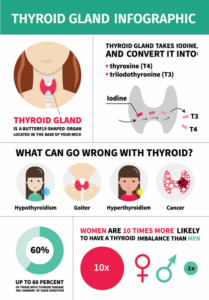
Cancer is a disease in which cells in the body grow out of control. When cancer starts in the thyroid gland, it is called thyroid cancer. Every year, about 12,000 men and 33,000 women get thyroid cancer, and about 900 men and 1,000 women die from the disease.
How dangerous is thyroid cancer?
1 day ago · Thyroid cancer is usually treatable, with a 10-year survival rate of 84 per cent, and in many cases can be cured completely. Symptoms a painless lump or …
How successful is radiation treatment for the thyroid?
See more

What is the main treatment for thyroid cancer?
Can thyroid cancer be treated successfully?
Can thyroid cancer be treated without surgery?
What are early warning signs of thyroid cancer?
- A lump in the neck, sometimes growing quickly.
- Swelling in the neck.
- Pain in the front of the neck, sometimes going up to the ears.
- Hoarseness or other voice changes that do not go away.
- Trouble swallowing.
- Trouble breathing.
- A constant cough that is not due to a cold.
Is thyroid cancer a death sentence?
How long is treatment for thyroid cancer?
What will happens if thyroid cancer is left untreated?
How long can you live with thyroid cancer?
What is the procedure to remove thyroid cancer?
Operations used to treat thyroid cancer include: Removing all or most of the thyroid (thyroidectomy). An operation to remove the thyroid gland might involve removing all of the thyroid tissue (total thyroidectomy) or most of the thyroid tissue (near-total thyroidectomy).
How to control thyroid cancer?
You can't control whether or not you develop thyroid cancer, but you can take steps to keep your body healthy during and after treatment. For instance, eat a healthy diet full of a variety of fruits and vegetables, get enough sleep each night so that you wake feeling rested, and try to incorporate physical activity into most days of your week.
What is radioactive iodine used for?
Radioactive iodine treatment is often used after thyroidectomy to destroy any remaining healthy thyroid tissue, as well as microscopic areas of thyroid cancer that weren't removed during surgery. Radioactive iodine treatment may also be used to treat thyroid cancer that recurs after treatment or that spreads to other areas of the body.
How to remove thyroid tissue?
Removing a sample of thyroid tissue. During a fine-needle aspiration biopsy, your doctor inserts a long, thin needle through your skin and into the thyroid nodule. Ultrasound imaging is typically used to precisely guide the needle into the nodule. Your doctor uses the needle to remove samples of suspicious thyroid tissue.
What is a thyroid lobectomy?
Removing a portion of the thyroid (thyroid lobectomy). During a thyroid lobectomy, the surgeon removes half of the thyroid. It might be recommended if you have a slow-growing thyroid cancer in one part of the thyroid and no suspicious nodules in other areas of the thyroid.
How to connect with thyroid cancer survivors?
Ask your doctor about support groups in your area. Or connect with thyroid cancer survivors online through the American Cancer Society Cancer Survivors Network or the Thyroid Cancer Survivors' Association.
What does a doctor do for thyroid nodules?
Physical exam. Your doctor will examine your neck to feel for physical changes in your thyroid, such as thyroid nodules. He or she may also ask about your risk factors, such as past exposure to radiation and a family history of thyroid tumors.
What is thyroid cancer?
Thyroid cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the thyroid gland.
How old is too old to get thyroid cancer?
Risk factors for thyroid cancer include the following: Being between 25 and 65 years old. Being female. Being exposed to radiation to the head and neck as an infant or child or being exposed to radioactive fallout. The cancer may occur as soon as 5 years after exposure. Having a history of goiter (enlarged thyroid).
What gene mutation is found in anaplastic thyroid cancer?
Patients with anaplastic thyroid cancer should have molecular testing for a mutation in the BRAF gene . Medullary thyroid cancer is a neuroendocrine tumor that develops in C cells of the thyroid. The C cells make a hormone ( calcitonin) that helps maintain a healthy level of calcium in the blood.
What is a lump in the thyroid?
Your doctor may find a lump ( nodule) in your thyroid during a routine medical exam. A thyroid nodule is an abnormal growth of thyroid cells in the thyroid. Nodules may be solid or fluid -filled.
What is the role of iodine in thyroid?
Thyroid hormones do the following: Control heart rate, body temperature, and how quickly food is changed into energy ( metabolism ). Control the amount of calcium in the blood.
How does chemo work?
When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle , the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body ( systemic chemotherapy ). When chemotherapy is placed directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, an organ, or a body cavity such as the abdomen, the drugs mainly affect cancer cells in those areas ( regional chemotherapy ).
Why do cancer tests have to be repeated?
Some tests will be repeated in order to see how well the treatment is working. Decisions about whether to continue, change, or stop treatment may be based on the results of these tests.
What is the treatment for thyroid lesions?
Surgery is the therapy of choice for all primary lesions. Surgical options include total thyroidectomy or lobectomy. The choice of procedure is influenced mainly by the age of the patient and the size of the nodule. Survival results with the two procedures are similar for early-stage disease, with differences in the rates of surgical complications and local recurrences. [ 2 - 8]
What is the most advanced stage of thyroid cancer?
Stage II is the most advanced stage possible in a patient younger than 55 years. Stage III papillary or follicular thyroid cancer is only possible in patients aged 55 years or older. The thyroid tumor demonstrates extension into surrounding soft tissues, larynx, trachea, esophagus, or recurrent laryngeal nerve.
How old is a stage 1 thyroid cancer patient?
Stage I papillary or follicular thyroid cancer is localized to the thyroid gland in patients aged 55 years or older. In those younger than 55 years, the cancer may have spread to nearby tissues and lymph nodes but not to other parts of the body. In as many as 50% of the cases, papillary thyroid cancer is multifocal.
How many people will die from thyroid cancer in 2021?
Estimated new cases and deaths from thyroid cancer in the United States in 2021: [ 2] New cases: 44,280. Deaths: 2,200. Thyroid cancer affects women more often than men and usually occurs in people aged 25 to 65 years. The incidence of this malignancy has been increasing over the last decade.
What are the two types of cells in the thyroid?
In thyroid cancer, cell type is an important determinant of prognosis and treatment. The thyroid has two cell types: follicular cells and parafollicular C cells. The management of thyroid cancer depends on the cell of origin and how well the integrity of the cell type is maintained.
What are the risks of radiation therapy?
Patients with a history of radiation therapy administered in infancy or childhood for benign conditions of the head and neck (such as enlarged thymus, tonsils, or adenoids; or acne) have an increased risk of cancer and other abnormalities of the thyroid gland.
What is the tissue of the thyroid gland?
Thyroid gland tissue envelops the upper trachea just below the thyroid and cricoid cartilages that make up the larynx. The gland has an isthmus and often asymmetric right and left lobes; usually four parathyroid glands lie posteriorly. When swallowing, the thyroid may be felt to rise with the larynx—most commonly in the presence of a disease process.
What is the best treatment for thyroid cancer?
Surgery is the most widely used method to get rid of thyroid cancer. If the entire thyroid gland is removed, It’s called a thyroidectomy. If part of your thyroid gland is removed, the procedure is called a lobectomy.
How do thyroid pills help cancer?
The pills also help stop leftover cancer cells from growing and returning. They do this by lowering the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH is made by your pituitary gland. It tells your thyroid gland to make thyroid hormones. But it also encourages growth of the cancer.
How long does radiation therapy last for thyroid cancer?
It is very carefully delivered to protect the rest of your body as much as possible. You’ll get radiation therapy over several weeks.
Where does iodine go in a thyroid scan?
The iodine goes to the thyroid tissue and the radiation destroys it. It may also be used for cancer that spreads to nearby lymph nodes, spreads to other parts of the body, or returns.The level of radiation in this treatment is far higher than what is used in a radioiodine scan.
Is there a side effect to chemotherapy?
Usually, there are fewer side effects than with chemotherapy. Deciding on Treatment. If you get a diagnosis of thyroid cancer, your doctor will help you figure out the best treatment. They’ll explain the benefits and tell you about the risks. Pagination.
Can you get chemo with pills?
You may get pills, shots, or intravenous (IV) chemo. It has side effects, but your doctor will help you to manage them. Targeted therapy is a newer treatment that targets only certain parts of cancer cells, to slow or stop growth. This is normally taken in pill form.
How is thyroid cancer treated?
Medullary thyroid cancer is generally treated with surgery. If the cancer is spreading, chemotherapy should be considered. If genetic mutation for the “RET” gene is detected, screening family members would be helpful for early diagnosis and treatment of the condition.
What are the different types of thyroid cancer?
There are three types of thyroid cancers: 1 Differentiated thyroid cancers (papillary, follicular and Hurthle cell). Papillary thyroid cancer (PTC), being 80 percent of all cases, is the most common type of thyroid cancer. It’s a slow-growing cancer, and except certain subtypes, the overall prognosis is excellent. PTC can spread to lymph nodes in the neck, but even in that case, it typically responds well to treatment. Follicular thyroid cancer constitutes about 10 percent of thyroid cancers and also has a favorable prognosis. However, the risk of spreading to the lungs and bones is higher than PTC. Hurthle cell cancer constitutes 3 percent of thyroid cancers. Although most patients do well, the prognosis can change based on the extent of disease at the time of diagnosis. 2 Medullary thyroid cancer. This form of thyroid cancer arises from parafollicular C cells of the thyroid gland and constitutes about 4 percent of thyroid cancers. This distinct form of thyroid cancer can be familial and associated with certain genetic endocrine syndromes. If diagnosed before the cancer spreads, treatment effectiveness is higher. 3 Anaplastic thyroid cancer. This is the most aggressive form of thyroid cancer and accounts for about 1 percent of thyroid cancers. It’s a rapid-growing form of cancer with poor response to treatment.
What percentage of thyroid cancer is follicular?
Follicular thyroid cancer constitutes about 10 percent of thyroid cancers and also has a favorable prognosis. However, the risk of spreading to the lungs and bones is higher than PTC. Hurthle cell cancer constitutes 3 percent of thyroid cancers. Although most patients do well, the prognosis can change based on the extent of disease at the time ...
What is the biopsy of thyroid nodules?
FNA is well-tolerated procedure and is generally done with guidance of ultrasound. Based on FNA results, about 80 percent of thyroid nodules are non-cancerous (benign), whereas less than 10 percent are cancerous (malignant) and the rest are generally indeterminate. Repeat biopsy or surgery can be considered for indeterminate results. Additional images like ultrasound, a CT scan, an MRI or a PET scan can be considered to see the extent of the disease once the diagnosis is made.
What is the most aggressive form of thyroid cancer?
Anaplastic thyroid cancer. This is the most aggressive form of thyroid cancer and accounts for about 1 percent of thyroid cancers. It’s a rapid-growing form of cancer with poor response to treatment. Rarely, lymphoma, sarcoma and other tumors can be found in the thyroid as well.
Is thyroid nodule cancerous?
FNA is well-tolerated procedure and is generally done with guidance of ultrasound. Based on FNA results, about 80 percent of thyroid nodules are non-cancerous (benign), whereas less than 10 percent are cancerous (malignant) and the rest are generally indeterminate. Repeat biopsy or surgery can be considered for indeterminate results.
Can thyroid surgery remove lymph nodes?
With surgery, generally most all of thyroid gland — sometimes half the gland, if a small-sized lump is only on one side — and lymph nodes can be removed. Thyroid hormone replacement treatment would be needed to replace the thyroid function and keep the Thyroid Stimulation Hormone (TSH) at a certain level to prevent growth of remaining cells.
What type of cancer starts in the thyroid?
Other very rare types of cancer that start in the thyroid include thyroid lymphoma, which begins in the immune system cells of the thyroid, and thyroid sarcoma, which begins in the connective tissue cells of the thyroid.
How is thyroid cancer classified?
Thyroid cancer is classified into types based on the kinds of cells found in the tumor. Your type is determined when a sample of tissue from your cancer is examined under a microscope. The type of thyroid cancer is considered in determining your treatment and prognosis.
What age can you get thyroid cancer?
Papillary thyroid cancer can occur at any age, but most often it affects people ages 30 to 50.
What happens when thyroid cells are mutated?
Thyroid cancer occurs when cells in your thyroid undergo genetic changes (mutations). The mutations allow the cells to grow and multiply rapidly. The cells also lose the ability to die, as normal cells would. The accumulating abnormal thyroid cells form a tumor.
What is the medication that blocks the effects of radiation on the thyroid?
A medication that blocks the effects of radiation on the thyroid is sometimes provided to people living near nuclear power plants. The medication (potassium iodide) could be used in the unlikely event of a nuclear reactor accident. If you live within 10 miles of a nuclear power plant and are concerned about safety precautions, contact your state or local emergency management department for more information.
Where is the thyroid gland located?
Thyroid gland. Your thyroid gland is located at the base of your neck, just below the Adam's apple. Thyroid cancer typically doesn't cause any signs or symptoms early in the disease. As thyroid cancer grows, it may cause: A lump (nodule) that can be felt through the skin on your neck.
Where does thyroid cancer occur?
Thyroid cancer occurs in the cells of the thyroid. Thyroid cancer occurs in the cells of the thyroid — a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of your neck, just below your Adam's apple. Your thyroid produces hormones that regulate your heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature and weight. Thyroid cancer might not cause any symptoms ...
How many people die from thyroid cancer each year?
Cancer is a disease in which cells in the body grow out of control. When cancer starts in the thyroid gland, it is called thyroid cancer. Every year, about 12,000 men and 33,000 women get thyroid cancer, and about 900 men and 1,000 women die from the disease.
How do you know if you have thyroid cancer?
What Are the Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer? 1 A lump or swelling on the side of the neck is the most common symptom. 2 Having trouble breathing. 3 Having trouble swallowing. 4 Having a hoarse voice.
Why is the thyroid gland important?
The thyroid is important in many ways for keeping your body healthy. It sends out certain chemicals (hormones) that help control many activities in the body , such as breathing and pumping blood. The thyroid helps children’s bodies develop as they grow up, including getting taller and putting on muscle. It helps control weight and is also involved in other functions.
Why is thyroid important for children?
The thyroid helps children’s bodies develop as they grow up, including getting taller and putting on muscle. It helps control weight and is also involved in other functions.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Tests and procedures used to diagnose thyroid cancer include: 1. Physical exam.Your doctor will examine your neck to feel for physical changes in your thyroid, such as thyroid nodules. He or she may also ask about your risk factors, such as past exposure to radiation and a family history of thyroid tumors. 2. Blood tests.Blood tests help determine ...