Medication
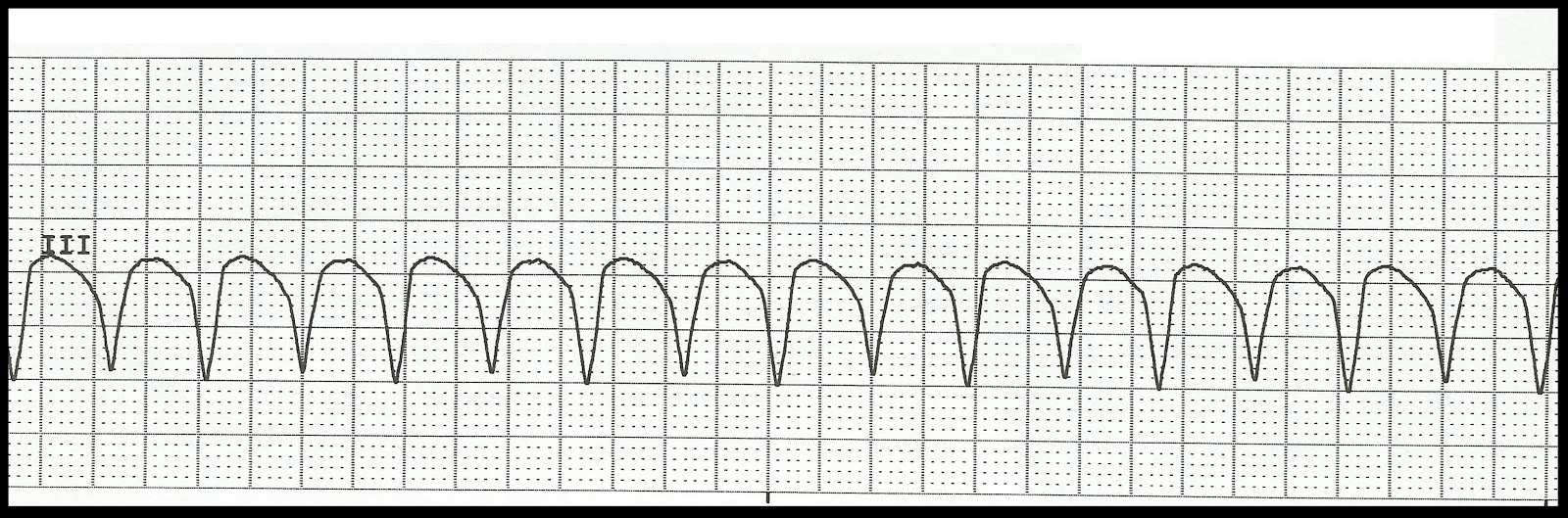
Ventricular tachycardia
- Overview. In ventricular tachycardia, an abnormal electrical impulse originating in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles) causes the heart to beat faster.
- Symptoms. Brief episodes of ventricular tachycardia may not cause any symptoms in some people. ...
- Causes. ...
- Risk factors. ...
- Complications. ...
- Prevention. ...
Procedures
- Perform high-quality CPR
- Establish an airway and provide oxygen to keep oxygen saturation > 94%
- Monitor the victim’s heart rhythm and blood pressure
Self-care
- Attempt vagal maneuvers.
- If unsuccessful, administer adenosine 6 mg IV bolus followed by a rapid normal saline flush.
- If unsuccessful, administer adenosine 12 mg IV bolus followed by a rapid normal saline flush.
Nutrition
What is the prognosis of ventricular tachycardia (VT)? , the prevalence of sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT) is low; therefore, it is considered a medical emergency as ppl often but not always become unconscious, cardiac arrest, as stated by AFIB Matters.
What is worse Vtach or Vfib?
How to fix Vtach?
How do you treat V tach with a pulse?
What is the prognosis of ventricular tachycardia (VT)?

What is the best treatment for ventricular tachycardia?
If you have ventricular tachycardia, you may be given medications called anti-arrhythmics by mouth or IV to slow the fast heart rate. Other heart medications, such as calcium channel blockers and beta blockers, may be prescribed with anti-arrhythmic drugs.
Which treatment is the most appropriate for monomorphic wide complex tachycardia in a stable patient?
The European resuscitation guidelines also recommend amiodarone for treatment of stable, monomorphic VT. In 2010, further modifications were made by the AHA, where sotalol was given a class IIb recommendation.
Which is the correct treatment for unstable regular monomorphic VT with a pulse?
Unstable polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is treated with unsynchronized shocks (defibrillation). Defibrillation is used because synchronization is not possible. These wide complex tachycardias tend to originate in the ventricles rather than like a normal rhythm which originates in the atria.
What is the first line treatment for ventricular tachycardia?
Anti-arrhythmic medications are the first-line therapy in emergency departments and CCUs, as discussed earlier. Amiodarone is most commonly used, along with lidocaine, and in some cases procainamide.
What is the difference between monomorphic and polymorphic ventricular tachycardia?
VT is considered sustained if it is continuous for at least 30 seconds. If the QRS complex has primarily a single morphology, the VT is monomorphic, whereas if the QRS complex varies, the VT is polymorphic.
Is amiodarone used for ventricular tachycardia?
Amiodarone is used to manage virtually all forms of supraventricular and ventricular tachycardia and has therefore become one of the most frequently used antiarrhythmic drugs in clinical practice.
Which is the correct treatment for unstable polymorphic VT?
Unstable polymorphic VT is treated with immediate defibrillation. The defibrillator may have difficulty recognizing the varying QRS complexes; therefore, synchronization of shocks may not occur.
Is monomorphic ventricular tachycardia stable or unstable?
Ventricular tachycardia is unstable any time a patient is in dysrhythmia and hemodynamic compromise. This is most often associated with mental status changes or a loss of consciousness.
Is polymorphic ventricular tachycardia shockable?
Ventricular tachycardia (v-tach) typically responds well to defibrillation. This rhythm usually appears on the monitor as a wide, regular, and very rapid rhythm. Ventricular tachycardia is a poorly perfusing rhythm; patients may present with or without a pulse.
What is the drug of choice for controlling ventricular tachycardia?
Abstract. For the emergency treatment of sustained, hemodynamically stable ventricular tachycardia, antiarrhythmic drugs are the therapy of choice. Mostly class I antiarrhythmic drugs, such as lidocaine or ajmaline, are preferred.
Do beta blockers prevent ventricular tachycardia?
Beta-blockers are the first-line treatment for long-term symptomatic rate control in patients with a range of cardiac arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia.
Does VT always require cardioversion?
Individuals suffering from pulseless VT or unstable VT are hemodynamically compromised and require immediate electric cardioversion to shock them out of the VT rhythm.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
What Is Ventricular Tachycardia?
- The goals of ventricular tachycardia treatment are: 1. Restore a normal heart rhythm 2. Control the fast heart rate when it occurs 3. Prevent future episodes of tachycardia The specific treatment you receive depends on what is causing the arrhythmia and the type or severity of your ventricular tachycardia. Ventricular tachycardia may go away on its...
What Makes RMVT Distinctive
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Symptoms
- If you have a plan in place to deal with an episode of a fast heartbeat, you may feel calmer and more in control when one occurs. Talk to your doctor about: 1. How to take your pulse and what a normal pulse rate is for you 2. When and how to use a variety of maneuvers or take additional medications if they are appropriate for you 3. When to call your doctor 4. When to seek emergen…
Treatment
- Whether you first see your family doctor or get emergency care, you'll likely be referred to a doctor trained in heart conditions (cardiologist) for one or more appointments for a complete evaluation. If possible, bring along a family member or friend who can give some moral support and help you keep track of new information. Because there may be a lot to discuss, it will be helpful to prepar…
What Is Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
Pathophysiology
- Three things make RMVT and other idiopathic ventricular tachycardias different from "typical" ventricular tachycardia: who gets is, what causes it, and how it is treated. Typical ventricular tachycardia is an arrhythmia that occurs in older people who have underlying heart disease. The diseased cardiac muscle creates a localized environment in which ventricular tachycardia occur…
Symptoms
- RMVT usually produces frequent, brief, non-sustained "bursts" of ventricular tachycardia, though it is also common for people with this condition to have occasional longer episodes. The most common symptoms caused by RMVT are palpitations and dizziness. More rarely, syncope(loss of consciousness) can also occur. Fortunately, the risk of cardiac arrest and sudden death with RM…
Laboratory Workup
- Fortunately, RMVT can often be controlled with a calcium blocker (verapamil) or with beta blockers(such as propranolol) — drugs that tend to produce relatively few side effects. If these drugs do not provide sufficient suppression of ventricular tachycardia, the use of more powerful antiarrhythmic drugscan be considered, although these drugs tend t...
Management
Preventive Measures
References