- Medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve), can relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Therapy. A physical therapist can teach you exercises to maximize hip range of motion and hip and core strength and stability.
- Surgical and other procedures. If conservative treatments don't relieve your symptoms, your doctor might recommend arthroscopic surgery — in which a fiber-optic camera and surgical tools are inserted via small ...
What are the treatment options for hip pain?
With some conditions, it is possible to resolve the pain with rest, modifying one’s behavior, and a physical therapy and/or anti-inflammatory regimen. Such conservative treatments have been successful in reducing pain and swelling. How to manage hip pain. Anti-inflammatories. Physical therapy. Injections.
How is hip dysplasia treated?
May 14, 2020 · All treatments for hip osteoarthritis aim to manage pain and improve mobility, but the right option will depend on the individual. Initial treatment may simply be exercise and stretching. However ...
What is the best treatment for OA of the hip?
Feb 05, 2022 · Medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve), can relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Pain can also be controlled temporarily with an injection of corticosteroids into the joint.

What is a hip lesion?
What causes hip cam lesion?
Can hip impingement repair without surgery?
What is a hip cam lesion?
How do you fix a cam lesion?
Is walking good for hip impingement?
How do doctors treat hip impingement?
Your doctor may first recommended conservative treatment, such as rest, activity modification, anti-inflammatory medications and sometimes physical therapy. However, if your pain does not improve with these interventions, you may be a candidate for surgery.
What happens if hip impingement is left untreated?
Does MRI show hip impingement?
Does cam impingement need surgery?
Can you claim disability for hip dysplasia?
What is the recovery time for hip impingement surgery?
What is the best treatment for hip pain?
Minimally invasive surgery techniques including arthroscopy have revolutionized treatment. Non-surgical treatment should always be considered first when treating hip pain. With some conditions, it is possible to resolve the pain with rest, modifying one’s behavior, and a physical therapy and/or anti-inflammatory regimen.
How to remove inflamed hip joint?
By inserting heat-generating radio frequency probes inside the joint capsule, the inflamed tissue is then removed.
Where does hip pain come from?
An examination will help to determine what's causing the soreness, since hip pain can actually come from locations other than the hip, such as the spine, pelvis or leg . While waiting to see a physician, there are some modifications and exercises that may provide some relief.
Can a numbing drug cause pain in hips?
Following an injection of a numbing drug into the joint, immediate relief from pain will help confirm that the joint is the source of pain. If complete pain relief is achieved while the hip joint is numb, the joint is likely to be the source of pain. If not, further consideration of a possible cause is needed.
Can you walk without pain after hip replacement?
The vast majority of patients report significant improvement in pain and function and can walk without pain and limping. As opposed to a total hip replacement, there are fewer activity restrictions, and you may be able to resume sporting activities without pain and with better function than before your surgery. menu.
What is the purpose of anti-inflammatory drugs?
Anti-inflammatories, commonly known as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (usually abbreviated as NSAIDs or NAIDs) are used primarily to treat mild to moderate pain associated with inflammation. This inflammation may be the result of muscular tears, bursitis, tendonitis, arthritis, labral tears, or synovitis.
Why is physical therapy important?
The importance of physical therapy is to assist in gaining an understanding of the underlying causes of hip pain and then to collaborate with a team of physicians in order to design a comprehensive treatment approach.
How to treat hip osteoarthritis?
Initial treatment may simply be exercise and stretching. However, osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease, which means symptoms often worsen over time.
How to help hip arthritis?
discussing what is best for you with your healthcare provider. taking care of yourself regarding both diet and nutrition, restorative sleep, and appropriate exercise. Lifestyle factors that can contribute to hip arthritis include: dietary choices.
Does having a high BMI cause inflammation?
The additional weight puts extra strain on the joints. A higher BMI, including having obesity, may also contribute to inflammation .
Can you lose weight with obesity?
For people with overweight or obesity, medical experts strongly recommend losing weight. Your healthcare provider can help you decide if this option is suitable for you and, if so, the best way to approach weight loss.
Why is motivation important when exercising?
They can help you create a program that will suit you and minimize the chance of injury. Motivation is important when exercising for health. The American College of Rheumatology and the Arthritis Foundation (ACR/AF) recommend exercising with another person or a trainer and choosing an activity that you enjoy.
How to stretch your back and hips?
Start with your feet shoulder-width apart or sit in a chair. Slowly lean forward, keeping your upper body relaxed. You should feel the stretch in your hips and lower back.
How to stretch your knees?
Lie on your back. Pull your bent knee up toward your chest until you feel a stretch. If your body allows it, use your other leg to deepen the stretch.
What can a physical therapist do for hip pain?
A physical therapist can teach you exercises to maximize hip range of motion and hip and core strength and stability. Therapists can also teach you to avoid movements that put stress on your hip joint.
Why does my hip hurt?
Hip pain can be caused by problems within the joint or outside the joint. Your doctor might suggest injecting an anesthetic into the joint space. If this relieves your pain, it's likely that your problem is inside your hip joint.
What does a doctor do during a physical exam?
During the physical exam, your doctor will move your leg, and especially your hip joint, into various positions to check for pain and evaluate your hip's range of motion. He or she might also watch you walk.
Can labral tear be seen in isolation?
A hip labral tear rarely occurs in isolation. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for fractures and for structural abnormalities.
How long does it take to heal labrum?
Treatment depends on how severe your symptoms are. Some people recover with conservative treatments in a few weeks ; others need arthroscopic surgery to repair or remove the torn portion of the labrum.
What is the best medication for arthritis pain?
Medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve), can relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Pain can also be controlled temporarily with an injection of corticosteroids into the joint.
What is the best medicine for joint pain?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve), can relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Pain can also be controlled temporarily with an injection of corticosteroids into the joint.
Abstract
Impending and pathologic fractures about the hip due to metastatic tumors are debilitating to patients secondary to pain and loss of mobility. The results of internal fixation of impending or complete pathologic fracture about the hip in 29 patients undergoing 32 procedures were retrospectively reviewed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
There were 21 women and 8 men. Their ages ranged from 33 to 83 years, with an average age of 59.2 years.
CASE REPORTS
A 53-year-old man with renal cell carcinoma presented with dull constant ache in the left hip and with decreased activity tolerance. Radiographic examination showed a lytic lesion at risk for fracture in the left posterior acetabular wall (Fig 1A).
RESULTS
The operative time ranged from 80 to 270 minutes, with a mean of 169 minutes and a median of 180 minutes. Estimated intraoperative blood loss ranged from 200 to 4000 ml, with a mean of 960 ml and a median of 800 ml. Change in hemoglobin ranged from -6.0 to +1.9 g/dl (patient transfused), with a mean drop of 3.2 g/dl.
DISCUSSION
Numerous studies have reported internal fixation of pathologic fractures 6,8,10,11,13,14,19,21,22; however, no studies addressed a single device for management of pathologic lesions about the hip.
What is the orthopedic examination of hip?
The standard orthopedic examination of the hip joint is performed in any patient presenting with a suspected tumor. Examination is best expressed in degrees of motion as well as percentage comparison of the opposite side. Any maneuvers which elicit pain during the examination should be noted for further evaluation. In addition to a standard orthopedic joint evaluation, a full oncologic examination should be performed. This includes an assessment of any masses, evaluation for lymphadenopathy, and any skin changes which may be present in the region of the tumor. Masses should be investigated for the presence of any Tinel’s sign, mobility, tenderness, or pulsation. The presence of hepatosplenomegaly or other findings suggestive of disseminated disease are noted. As well, skin manifestations of any systemic disease or genetic syndrome (for example: café au lait spots suggestive of neurofibromatosis) are noted.
What is hip neoplasm?
The hip is a common location for many soft tissue and osseous neoplasms in addition to tumor simulators. It is the role of the orthopaedic surgeon to recognize and be aware of these lesions in order to treat them appropriately or refer these patients in a timely fashion. The spectrum of disease varies from latent benign to overly aggressive malignancies.
What are the characteristics of an osseous lesion?
Characteristics that make an osseous lesion aggressive and concerning include an associated soft tissue mass, periosteal elevation, permeative appearance, large size and rapid growth. Plain film radiographs provide the first assessment of any patients presenting with a potential tumor about the hip.
What is the role of the hip?
It is the role of the orthopaedic surgeon to recognize and be aware of these lesions in order to treat them appropriately or refer these patients in a timely fashion.
What age can you get a bone tumor in your hip?
The age range is by no means absolute; however, certain neoplasms, such as Ewing’s sarcoma, are rarely seen beyond the age of 25. Most bone tumors have a predilection for males, with few exceptions.
What does a radiograph show?
Radiographs provide a rapid assessment of present or impending fracture.
What is fibro-osseous dysplastic?
Fibrous dysplasia is a benign intramedullary fibro-osseous dysplastic lesion first described by Lichtenstein in 1938 with an origin linked to an activating mutation in the gene that encodes the α-subunit of stimulatory G protein (G s α). This results in developmental failure in the remodeling of primitive bone to mature lamellar bone. The consequence is biomechanically inferior bone that is non–stress oriented and prone to fracture. The process can be monostotic or polyostotic, and the most extreme presentation is McCune-Albright syndrome, which consists of polyostotic disease with café au lait spots and hyperfunction of multiple endocrine glands. Monostotic disease is fairly common and is not hereditary. Most lesions are asymptomatic and are found incidentally. However, a fairly common clinical presentation consists of bone pain, deformity, and fatigue/pathologic fracture. Wide variability in radiographic features is seen on plain radiographs. The classic pattern is a “ground-glass” appearance. However, cortical thinning, expansile remodeling, endosteal scalloping, and mixed radiolucency and radiodensity are common. Other findings may include coxa vara, shepherd’s crook deformity, and protrusio acetabuli ( Fig. 49-1 ). A computed tomography (CT) scan is the best imaging modality, but magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is often helpful, especially in cases of cystic formation. A radionuclide bone scan will frequently be hot. Histopathology normally demonstrates a bland-spindle cell stroma with embedded trabeculae of woven (immature) bone with no osteoblastic rimming. This is often referred to as an “alphabet soup” appearance.
What is the best treatment for hip pain?
Injections may also be prescribed to relieve pain, but can also provide diagnostic information to differentiate from hip pain that might actually be caused by the spine or surrounding soft tissues. Conservative treatment options, such as physical therapy, are typically recommended. Surgical.
What is the hip joint?
The hip joint is the ball-and-socket joint where the ball-shaped top of the femur fits into the “socket” (acetabulum) of the pelvis. This joint is protected by a joint capsule, muscles, and ligaments to add to its stability.
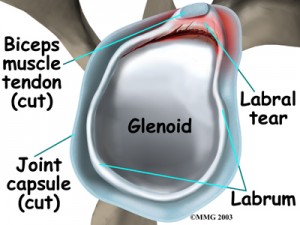
What is the labrum of the hip?
What Are Labral Tears? The rim of the socket of the hip joint is lined by a ring of cartilage called the labrum. The labrum provides additional support and cushioning at the rim of the joint, and facilitates adequate nutrition of the hip cartilage. It assists in normal motion of the hip.
What is labral tear?
What Are Labral Tears? The rim of the socket of the hip joint is lined by a ring of cartilage called the labrum. The labrum provides additional support and cushioning at the rim of the joint, and facilitates adequate nutrition of the hip cartilage. It assists in normal motion of the hip. When the labrum is damaged, the hip can catch, lock, ...
What is the rim of the hip called?
The rim of the socket of the hip joint is lined by a ring of cartilage called the labrum. The labrum provides additional support and cushioning at the rim of the joint, and facilitates adequate nutrition of the hip cartilage. It assists in normal motion of the hip. When the labrum is damaged, the hip can catch, lock, and cause pain.
What is the function of the labrum?
The labrum provides additional support and cushioning at the rim of the joint, and facilitates adequate nutrition of the hip cartilage. It assists in normal motion of the hip. When the labrum is damaged, the hip can catch, lock, and cause pain.
What is pincer impingement?
In pincer impingement, the socket is either too deep or abnormally rotated. This results in the neck of the thigh bone impinging on the labrum and acetabular rim, often leading to labral tears and joint cartilage damage.
What are bone lesions?
Symptoms. Diagnosis. Outlook. Bone lesions are areas of bone that are changed or damaged. Causes of bone lesions include infections, fractures, or tumors. When cells within the bone start to divide uncontrollably, they are sometimes called bone tumors. Most bone lesions are benign, meaning they are not cancerous.
What is the diagnosis of bone lesion?
Diagnosis. A doctor will carry out a full physical assessment and several tests to diagnose the cause of a bone lesion. They might ask about general health, medications, and symptoms, as well as any family history of lesions or cancer.
What are the different types of bone cancer?
Malignant bone tumors are divided into two types: 1 Primary bone cancer, which is cancer that starts in the bone. 2 Secondary bone cancer, which is when cancer starts somewhere else and spreads to the bone.
Can bone cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Most bone lesions are benign, not life-threatening, and will not spread to other parts of the body. Some bone lesions, however, are malignant, which means they are cancerous. These bone lesions can sometimes metastasize, which is when the cancer cells spread to other parts of the body. Primary bone cancer, which is cancer that starts in the bone.
Is bone cancer a benign tumor?
Some bone lesions, however, are malignant, which means they are cancerous. These bone lesions can sometimes metastasize, which is when the cancer cells spread to other parts of the body. Malignant bone tumors are divided into two types:
What is the difference between primary and secondary bone cancer?
These bone lesions can sometimes metastasize, which is when the cancer cells spread to other parts of the body. Primary bone cancer, which is cancer that starts in the bone. Secondary bone cancer, which is when cancer starts somewhere else and spreads to the bone.
What is malignant bone cancer?
Malignant bone tumors are divided into two types: Primary bone cancer, which is cancer that starts in the bone. Secondary bone cancer, which is when cancer starts somewhere else and spreads to the bone.
Can hip dysplasia be corrected?
Sometimes surgery is needed to fit the joint together properly. If the dysplasia is more severe, the position of the hip socket can also be corrected. In a periacetabular (per-e-as-uh-TAB-yoo-lur) osteotomy, the socket is cut free from the pelvis and then repositioned so that it matches up better with the ball.
How to check for hip dysplasia?
During well-baby visits, doctors typically check for hip dysplasia by moving an infant's legs into a variety of positions that help indicate whether the hip joint fits together well. Mild cases of hip dysplasia can be difficult to diagnose and might not start causing problems until you're a young adult. If your doctor suspects hip dysplasia, he ...
How to make an appointment for a syringe?
Before your appointment, you might want to: 1 Write down any signs and symptoms you are experiencing, including any that may seem unrelated to the reason for which you scheduled the appointment. 2 Make a list of any medications, vitamins or supplements that you're taking. 3 Consider taking a family member or friend along. Sometimes it can be difficult to remember all the information provided during an appointment. Someone who accompanies you may remember something that you missed or forgot. 4 Request that a copy of previous medical records be forwarded to your current doctor, if you're changing doctors. 5 Write down questions to ask the doctor.
What is the term for a hip socket that doesn't fully cover the ball portion of the upper thigh
Periacetabular osteotomy. Hip dysplasia is the medical term for a hip socket that doesn't fully cover the ball portion of the upper thighbone. In periacetabular (per-e-as-uh-TAB-yoo-lur) osteotomy, the socket is cut free from the pelvis and then repositioned so that it matches up better with the ball.
What to do before a doctor appointment?
What you can do. Before your appointment, you might want to: Write down any signs and symptoms you are experiencing, including any that may seem unrelated to the reason for which you scheduled the appointment. Make a list of any medications, vitamins or supplements that you're taking.
What is a Pavlik harness?
Pavlik harness. Infants are usually treated with a soft brace, called a Pavlik harness, that holds the ball portion of the joint firmly in its socket for several months. This helps the socket mold to the shape of the ball. Spica cast.
