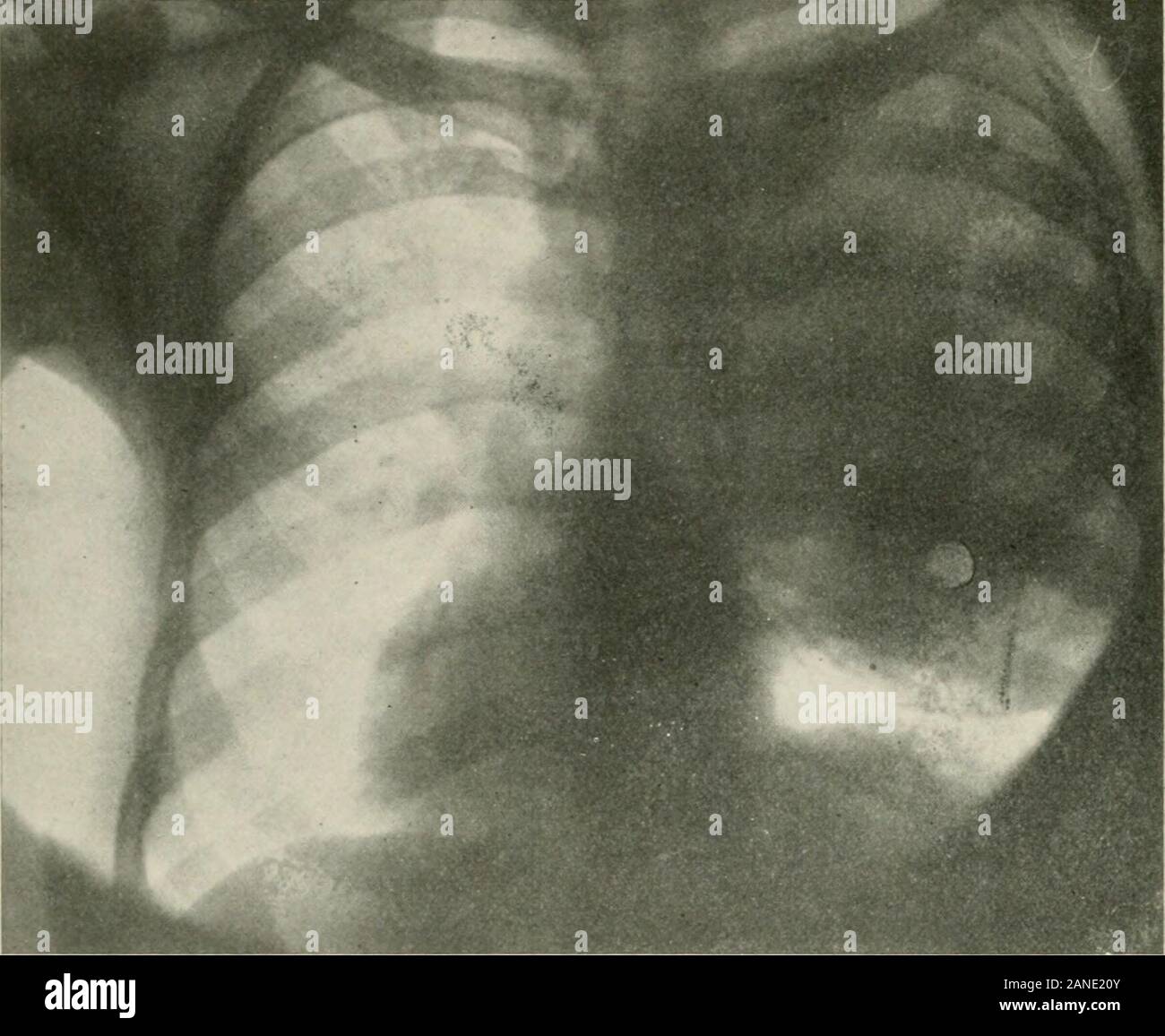
Treatment for pneumonia involves curing the infection and preventing complications. People who have community-acquired pneumonia usually can be treated at home with medication. Although most symptoms ease in a few days or weeks, the feeling of tiredness can persist for a month or more.
Full Answer
How to regain strength after pneumonia?
Most people can manage their symptoms such as fever and cough at home by following these steps:
- Control your fever with aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen), or acetaminophen. ...
- Drink plenty of fluids to help loosen secretions and bring up phlegm.
- Do not take cough medicines without first talking to your doctor. ...
Can pneumonia go away on its own?
Treatment for pneumonia depends on the type of pneumonia, how sick the patient is, the patient’s age, and if other underlying medical conditions are present. Mild cases of pneumonia will often go away on their own by managing symptoms and getting adequate rest.
What is the best cough medicine for pneumonia?
You need three things for a cough:
- Cough-triggering sensors
- A cough center in the brain
- Nerves and muscles actually needed to cough
What is the best home remedy for pneumonia?
Process 1:
- Boil water and stir in 5 drops of tea tree or eucalyptus oil.
- Pour the water into a bowl.
- Drape a towel over your head, lean over the bowl, and inhale the steam.
- Do this until Stopped getting oil fragrance.
- Now blow nose gently to clear the mucus which causes the problem.
- Repeat 3 times a day.
What is the best treatment for bronchopneumonia?
Recommended intravenous antibiotics for treatment of severe bronchopneumonia are: amoxicillin, co-amoxiclav, cefuroxime and cefotaxime or ceftriaxone. Use of these antibiotics can be rationalized if microbiological diagnostics is performed (7).
Which of the following priority for a patient diagnosed with pneumonia?
In the patient with pneumonia and early signs of respiratory distress, assess, and reassess periodically, the need for respiratory support (bilevel positive airway pressure, continuous positive airway pressure, intubation) (i.e., look for the need before decompensation occurs).
What priority nursing interventions should be implemented for the management of a patient with pneumonia?
Nursing interventions for pneumonia and care plan goals for patients with pneumonia include measures to assist in effective coughing, maintaining a patent airway, decreasing viscosity and tenaciousness of secretions, and assisting in suctioning.
What is the first line treatment for pneumonia?
Pneumonia should be treated with antibiotics. The antibiotic of choice for first line treatment is amoxicillin dispersible tablets. Most cases of pneumonia require oral antibiotics, which are often prescribed at a health centre.
What is the most common treatment for pneumonia?
Mild pneumonia can usually be treated at home with rest, antibiotics (if it's likely be caused by a bacterial infection) and by drinking plenty of fluids. More severe cases may need hospital treatment.
What is the medical management of pneumonia?
Treatment for pneumonia involves curing the infection and preventing complications. People who have community-acquired pneumonia usually can be treated at home with medication. Although most symptoms ease in a few days or weeks, the feeling of tiredness can persist for a month or more.
Which nursing diagnosis is the highest priority for a patient with pneumonia?
Although all of these nursing diagnoses are appropriate for the client with AIDS, impaired gas exchange is the priority nursing diagnosis for the client with P. carinii pneumonia. Airway, breathing, and circulation take top priority with any client.
What are important nursing care measures while treating a patient with pneumonia?
Nursing InterventionsAdminister oxygen as prescribed.Monitor respiratory status.Monitor for labored respirations, cyanosis, and cold and clammy skin.Encourage coughing and deep breathing and use of incentive spirometer.Position client in semi-Fowler position to facilitate breathing and lung expansion.More items...
What nursing interventions can be taken to prevent pneumonia?
Several fundamental therapeutic nursing interventions—adhering to infection prevention standards, elevating the head of the bed 30 to 45 degrees to prevent aspiration, ensuring good oral hygiene (cleaning teeth, gums, tongue, dentures), increasing patient mobility with ambulation to three times a day as appropriate, ...
What is the best antibiotic to treat pneumonia?
In otherwise uncomplicated pneumonia, azithromycin is the initial drug of choice, as it covers most of the potential etiologic agents, including Mycoplasma species.
How is Covid pneumonia treated?
Are There Treatments for COVID-19 Pneumonia? Pneumonia may need treatment in a hospital with oxygen, a ventilator to help you breathe, and intravenous (IV) fluids to prevent dehydration.
Is azithromycin used for pneumonia?
Azithromycin is used to treat certain bacterial infections, such as bronchitis; pneumonia; sexually transmitted diseases (STD); and infections of the ears, lungs, sinuses, skin, throat, and reproductive organs.
What is bronchopneumonia?
Bronchopneumonia is the most common type of pneumonia found in children. Among children under five years of age, it is the leading cause of death....
Is bronchopneumonia contagious?
Yes, bronchopneumonia is a contagious infection. The pathogens that can cause bronchopneumonia are usually breathed in by people. Normally, these a...
How long is bronchopneumonia contagious?
The exact length of time a person is contagious depends on the pathogen causing the infection. The average incubation period tends to be short, typ...
How do you diagnose bronchopneumonia?
Clinical findingsThe clinical presentation of bronchopneumonia varies widely. Factors such as the pathogen, age, and presence of comorbid condition...
How do you treat bronchopneumonia?
The causal pathogen of bronchopneumonia is oftentimes not known at diagnosis, therefore empiric treatment should be initiated with the most suspect...
What tests are done to confirm bronchopneumonia?
If the doctor suspects bronchopneumonia, they may order one or more of the following tests to confirm the diagnosis or determine the type and severity of the condition: Chest X-ray or CT scan. These imaging tests allow a doctor to see inside the lungs and check for signs of infection. Blood tests.
What is the cause of bronchopneumonia?
Takeaway. Bronchopneumonia is a type of pneumonia, a condition that causes inflammation of the lungs. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include coughing, breathing difficulties, and fever. Causes include bacterial, viral, or fungal chest infections.
What is the name of the disease that affects the lungs?
Takeaway. Bronchopneumonia is a type of pneumonia that affects the bronchi in the lungs. This condition commonly results from a bacterial infection, but viral and fungal infections can also cause it. Symptoms can vary but often include coughing, difficulty breathing, and fever.
What causes a bronchial ailment to fill with fluid?
Pneumonia causes an inflammation in the lungs that leads to these alveoli filling with fluid. This fluid impairs normal lung function, producing a range of respiratory problems. Bronchopneumonia is a form of pneumonia that affects both the alveoli in the lungs and the bronchi. Symptoms of bronchopneumonia can range from mild to severe.
What are the bronchial tubes?
Bronchopneumonia affects the alveoli and the bronchi. The bronchi are the large air passages that connect the windpipe to the lungs. These bronchi then split into many tiny air tubes known as bronchioles, which make up the lungs. At the end of the bronchioles are tiny air sacs called alveoli where the exchange of oxygen from ...
How old is too old to die from bronchopneumonia?
of death from infection in children aged under 5 years of age. The symptoms, causes, complications, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of bronchopneumonia are typically the same as that for pneumonia.
Can bronchopneumonia be severe?
The symptoms of bronchopneumonia vary, depending on the severity of the condition. Symptoms are more likely to be severe in people who have weaker immune systems, such as young children, older adults, or people who have certain conditions or are taking specific medications.
What test is used to determine if a person has bronchopneumonia?
It also allows the doctor to take a closer look at the airways. 6. Pulse Oximetry. Measuring the oxygen level in the bloodstream helps to diagnose the severity of the bronchopneumonia.
Why do people get bronchopneumonia?
Bronchopneumonia is caused by bacteria of various strains. Most cases are contracted within a hospital setting, since the immune system is at an all-time low due to other poor health conditions. The more common bacteria are:
What age can you get bronchial pneumonia?
There are several factors that can put you at high risk for contracting such a condition as bronchial pneumonia. 1. Age. Young children under the age of two years and adults over the age of 65 are susceptible to this form of pneumonia.
How does smoking affect bronchial pneumonia?
2. Lifestyle. Having bad habits such as tobacco use and excessive alcohol use can increase your chances for bronchial pneumonia as the immune system can be compromised with these activities. Following a poor nutrition diet can also lead to infection. 3.
Is bronchopneumonia a form of pneumonia?
Bronchopneumonia can also fall under the names of bronchial pneumonia and bronchogenic pneumonia. It affects the lungs as well as the bronchioles, which are the air pathways to the lungs. As a more severe form of pneumonia, bronchopneumonia demands immediate treatment.
Can pneumonia cause bronchioles to be inflamed?
The effects and symptoms of pneumonia can be scary enough, but add inflammation of the bronchioles, and your infection has jumped to the next level. Bronchopneumonia is seen when an upper respiratory tract infection spreads to the lower respiratory tract. Because this potentially life-threatening condition can cause an interruption in your ...
Is bronchial pneumonia contagious?
Yes and no. The bronchial pneumonia disease itself is not contagious, but the bacterial and viral microbes are. By coming into contact with these microorganisms, you may contract a disease but it will not be bronchopneumonia—not in this manner.
How long does bronchopneumonia treatment last?
Antibiotic therapy usually lasts between 5–7 days. Supportive therapy includes adequate hydration, rest, and home care.
What are the symptoms of bronchopneumonia?
Common symptoms include productive cough, purulent sputum, dyspnea, rigors, malaise, pleuritic pain and occasionally hemoptysis.
What is the most common type of pneumonia in children?
Bronchopneumonia is the most common type of pneumonia found in children. Among children under five years of age, it is the leading cause of death. In fact, bronchopneumonia accounts for 85% of all respiratory system diseases in children under two years of age. Incidence is also very high among older adults, especially people over 65 years of age.
What happens when you inhale pathogens?
After a person inhales these pathogen-containing droplets, they colonize the throat (nasopharynx or oropharynx), and then reach the lung alveoli through aspiration. Infection can result when the inoculum size is sufficient or the host immune system is impaired.
Where is bronchopneumonia found?
In pediatric patients, bronchopneumonia is characterized by scattered foci of consolidation (pus in many alveoli and adjacent air passages) that may be found in one or more lobes of one or both lungs.
Can you take antibiotics with a high severity score?
However, patients with a high-severity score (on either score) might require hospitalization in addition to treatment with IV antibiotics.
Can bronchopneumonia cause an abscess?
In severe cases, bronchopneumonia can lead to the formation of a lung abscess (pus-filled pocket in a focal area). In addition, the infection may spread to the pleural space, filling it with an exudate (pus-like fluid resulting from inflammation), this condition is also known as empyema.
How to prevent bronchopneumonia?
Speak to your doctor about ways by which you can prevent pneumonia. Wash your hands regularly to avoid germs.
What tests are done to check for bronchopneumonia?
If this condition is suspected, you would be asked to undergo the following tests: Chest X-ray or CT scan: Imaging tests allow the doctor to check for signs of infection inside the lungs.
What happens if you leave bronchopneumonia untreated?
If left untreated, bronchopneumonia can lead to the following complications: Respiratory failure: Occurs when the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs begins to fail. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: A severe form of respiratory failure that is life-threatening.
What happens when you have pneumonia?
When a person suffers from pneumonia, there is inflammation in the lungs that lead to the alveoli filling with fluid. Normal lung functionality is impaired due to this fluid. This leads to plenty of respiratory problems. Bronchopneumonia affects both the alveoli in the lungs as well as the bronchi.
How long does it take to recover from bronchopneumonia?
People who suffer from this condition but do not have any other health issues recover within 1 to 3 weeks. Mild forms of bronchopneumonia can be treated at home using a combination of rest and medication.
What is the symptom of bronchopneumonia?
Symptoms can be mild to severe and usually include breathing issues, fever and coughing. This illness can be caused due to bacterial, viral or fungal chest infections. People whose health is not compromised due ...
Do antibiotics work for bronchopneumonia?
Antibiotics do not work for viral infections. For viral bronchopneumonia, your doctor might prescribe an antiviral medicine. For people who have fungal bronchopneumonia, your doctor might prescribe antifungal medication.
What is the most common clinical manifestation of pneumonia in pediatrics?
Bronchopneumonia is the most common clinical manifestation of pneumonia in pediatric population. It is a leading infective cause of mortality in children under 5 years of age. In 2013, bronchopneumonia caused death in 935,000 of children under 5 years.
What is the most commonly prescribed medication in the aforementioned group?
The most commonly recommended medication in the aforementioned group was ampicillin in two forms (suspension and tablets).
What is the best medicine for pneumonia?
It may take time to identify the type of bacteria causing your pneumonia and to choose the best antibiotic to treat it. If your symptoms don't improve, your doctor may recommend a different antibiotic. Cough medicine.
What to do if pneumonia isn't clearing?
If your pneumonia isn't clearing as quickly as expected, your doctor may recommend a chest CT scan to obtain a more detailed image of your lungs. Pleural fluid culture. A fluid sample is taken by putting a needle between your ribs from the pleural area and analyzed to help determine the type of infection.
What is the test for pneumonia?
This measures the oxygen level in your blood. Pneumonia can prevent your lungs from moving enough oxygen into your bloodstream. Sputum test. A sample of fluid from your lungs (sputum) is taken after a deep cough and analyzed to help pinpoint the cause of the infection.
How to get rid of pneumonia?
Get plenty of rest. Don't go back to school or work until after your temperature returns to normal and you stop coughing up mucus. Even when you start to feel better, be careful not to overdo it. Because pneumonia can recur, it's better not to jump back into your routine until you are fully recovered.
What tests are done to determine if you have pneumonia?
If pneumonia is suspected, your doctor may recommend the following tests: Blood tests . Blood tests are used to confirm an infection and to try to identify the type of organism causing the infection. However, precise identification isn't always possible. Chest X-ray.
What kind of doctor do you see for lung cancer?
You may start by seeing a primary care doctor or an emergency care doctor, or you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in infectious diseases or in lung disease (pulmonologist).
How long does it take for a person to feel tired after pneumonia?
Although most symptoms ease in a few days or weeks, the feeling of tiredness can persist for a month or more. Specific treatments depend on the type and severity of your pneumonia, your age and your overall health. The options include: Antibiotics. These medicines are used to treat bacterial pneumonia.
What to do if you have pneumonia in the hospital?
If your pneumonia is so severe that you are treated in the hospital, you may be given intravenous fluids and antibiotics, as well as oxygen therapy, and possibly other breathing treatments.
How long does it take to recover from pneumonia?
Some people feel better and are able to return to their normal routines within a week. For other people, it can take a month or more. Most people continue to feel tired for about a month. Adequate rest is important to maintain progress toward full recovery and to avoid relapse.
What is the best medicine for cough and fever?
Most people can manage their symptoms such as fever and cough at home by following these steps: Control your fever with aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen), or acetaminophen. DO NOT give aspirin to children.
What to do if you are a smoker and have trouble staying smokefree?
This includes smoking, secondhand smoke and wood smoke. Talk to your doctor if you are a smoker and are having trouble staying smokefree while you recover. This would be a good time to think about quitting for good. Get lots of rest.
