What is the success rate of tPA in stroke?
Conclusions— IV-tPA treatment resulted in significantly better outcomes in patients with severely symptomatic stroke with major anterior circulation occlusions. The 35% good outcome rate was similar to rates found in endovascular therapy trials.
How long does tPA treatment take?
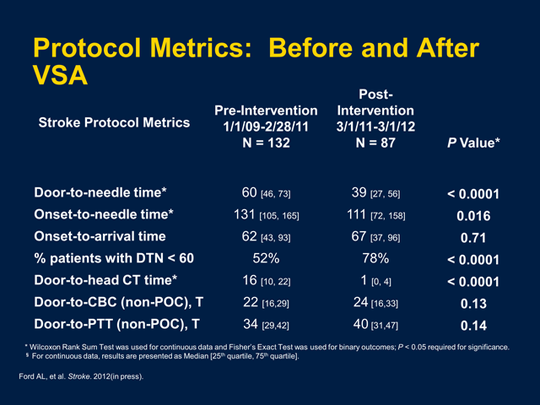
Ultrafast TPA administration A new study evaluated the change in DTNT and DTCT before and after implementation of a stroke protocol. After the protocol was implemented, DTNT of 59 minutes was unchanged, while DTCT decreased from 20.6 to 15.9 minutes.
What happens after tPA is given?
If bleeding into the brain happens after TPA is given, it may cause your stroke symptoms to be worse and may result in death. However, the death rate is the same with or without TPA and there is still a greater chance of recovery with TPA treatment. TPA may also cause bleeding in other areas of the body.
How long is tPA given for stroke?
Maarten Lansberg and his colleagues say that the time limit on use of the stroke drug tPA should be increased to 4.5 hours from the current recommendation of three hours. Once symptoms start, there's only a tiny window of time for stroke victims to get life-saving treatment.
How long do you stay in the hospital after tPA?
The mean length of time from tPA administration to bleed detection for those with sICH was 8.5 hours (Figure). The mean time from last known well to sICH was 10.5 hours. Only 4 patients experienced a sICH that occurred >12 hours after administration (1 at 13 hours and 3 between 23 and 25 hours).
What are the side effects of tPA?
What are the side effects of alteplase (TPA, Activase, Cathflo Activase)?Pulmonary embolism.Cholesterol embolism.Abnormal heartbeats.Allergic reactions.Re-embolization of deep DVT venous thrombi during treatment of acute massive pulmonary embolism.Angioedema.
What is the most critical time after a stroke?
The results strongly suggest that there is a critical time window for rehabilitation following a stroke. For this study, that window was 2-3 months after stroke onset. Larger clinical trials are needed to better pin down the timing and duration of this critical window.
Are there warning signs days before a stroke?
- Warning signs of an ischemic stroke may be evident as early as seven days before an attack and require urgent treatment to prevent serious damage to the brain, according to a study of stroke patients published in the March 8, 2005 issue of Neurology, the scientific journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
What are the signs of death after a stroke?
found a high prevalence of certain symptoms among dying stroke patients (n = 42), namely, dyspnea (81%) and pain (69%), mouth dryness (62%), and anxiety (26%)[12].
Can tPA reverse a stroke?
Restoring Blood Flow The most widely known and the only FDA-approved drug for treatment of ischemic stroke — intravenous tPA (tissue plasminogen activator) — can reverse stroke if given to carefully selected patients within a few hours of stroke onset.
Does tPA have long term effects?
TPA is very fast acting, and its effect does not last very long. If you receive TPA and do not experience any side effects or complications within the first few days, you do not need to be concerned about delayed or long-term side effects from TPA during your recovery or after you go home.
Who Cannot receive tPA?
Relative Exclusion Criteria Pregnancy. Seizure at the onset with postictal residual neurological impairments. Major surgery or serious trauma within prior 14 days. Recent GI or urinary tract hemorrhage (within previous 21 days)
How does TPA work?
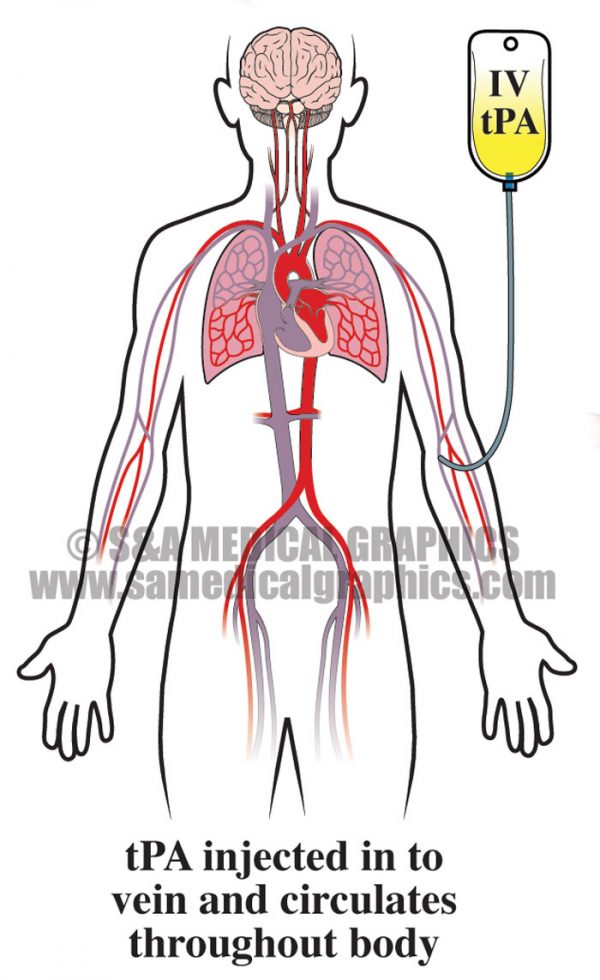
When TPA is injected into a vein, it quickly travels through the blood to reach the clogged blood vessel, where it works by trying to dissolve the blood clot and to restore blood flow to the brain.
How long does it take to use TPA?
Clinical guidelines for the early treatment of stroke published jointly by the American Heart Association and American Stroke Association strongly recommend the use of TPA for eligible patients within three hours of symptom onset. Some of the eligibility criteria involved in the decision to use TPA include ...
What is tissue plasminogen activator?
Tissue plasminogen activator is a powerful agent that dissolves blood clots. It is injected by intravenous administration (IV) for emergency stroke treatment. A stroke is caused by an interruption in blood flow either due to a blood clot ( ischemic stroke) or a bleed ( hemorrhagic stroke) in the brain. TPA is only used for strokes caused by blood ...
What is TPA in 2021?
Huma Sheikh, MD. on April 21, 2021. Tissue plasminogen activator, most commonly known as TPA, is a powerful blood thinner used for emergency stroke treatment. Approved 20 years ago for the treatment of stroke, it was initially viewed as both revolutionary and risky. Now, twenty years later, stroke treatment has advanced a lot, ...
Is TPA a blood thinner?
Because TPA is a powerful blood thinner, the main side effect is bleeding. Bleeding is a serious complication that can result in a hemorrhagic stroke, which is often more serious than an ischemic stroke.
Do patients ask for TPA?
Most of the time, patients do not ask for TPA. But emergency medical workers are trained to recognize a stroke and emergency rooms are equipped with the staff and provisions to administer TPA when it is necessary.
Is TPA safe after a stroke?
TPA is an important stroke treatment that can save your life. However, it can be dangerous and not everyone is a safe candidate for TPA. Also, if the narrow time interval has elapsed by the time you reach the hospital, you cannot receive intravenous TPA treatment because it is only beneficial if it is given within the first few hours after a stroke has started.
How long does it take for a stroke to be treated with tPA?
tPA is often used to treat ischemic strokes. It must be administered to the patient within three hours of the stroke’s onset, as approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). There are several benefits and risks of tPA as a stroke treatment, including the following:
How does a TPA work?
One such treatment, the tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), works to dissolve clots that block blood flow to the brain.
How to remove a tpa clot?
Physicians may decide to remove the clot directly, such as by inserting a catheter through a vein, threading it into the brain, and delivering tPA directly. Another option is to remove the clot with a stent, which could be beneficial for larger clots that tPA cannot dissolve on its own.
How to restore blood flow to the brain?
For ischemic strokes, physicians may recommend the following treatments to quickly restore blood flow to the brain: 1 Emergency IV medication, including tPA. tPA is usually given to stroke patients within the first three hours of a stroke. tPA may dissolve the clot causing the ischemic stroke, and help patients more fully recover. 2 Emergency endovascular procedures. Physicians may decide to remove the clot directly, such as by inserting a catheter through a vein, threading it into the brain, and delivering tPA directly. Another option is to remove the clot with a stent, which could be beneficial for larger clots that tPA cannot dissolve on its own.
Why is tPA controversial?
This treatment has become controversial because it can be helpful to some patients and quite harmful to others. Learn more about the benefits and risks of tPA as a stroke treatment and what you can do if you have been harmed from the improper implementation of this treatment.
What happens if you have a stroke in Baltimore?
If you suffered a stroke and your physician either did not administer the proper treatment or administered a treatment incorrectly, our Baltimore medical malpractice attorneys can determine whether you have a case. You may be entitled to significant compensation for medical bills, lost wages, and more.
When to give tpa?
Emergency IV medication, including tPA. tPA is usually given to stroke patients within the first three hours of a stroke. tPA may dissolve the clot causing the ischemic stroke, and help patients more fully recover. Emergency endovascular procedures.
What is the best medicine for a stroke?
If you get to the hospital within 3 hours of the first symptoms of an ischemic stroke, you may get a type of medicine called a thrombolytic (a “clot-busting” drug) to break up blood clots. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is a thrombolytic. tPA improves the chances of recovering from a stroke.
What do you need to do after a stroke?
After a stroke, you may need rehabilitation ( rehab) to help you recover. Before you are discharged from the hospital, social workers can help you find care services and caregiver support to continue your long-term recovery.
What is the best way to get to the hospital for a stroke?
Stroke Treatment. Calling 9-1-1 at the first symptom of stroke can help you get to the hospital in time for lifesaving stroke care. Your stroke treatment begins the moment emergency medical services (EMS) arrives to take you to the hospital. Once at the hospital, you may receive emergency care, treatment to prevent another stroke, ...
Why do people go to the hospital for stroke?
Stroke patients who are taken to the hospital in an ambulance may get diagnosed and treated more quickly than people who do not arrive in an ambulance. 1 This is because emergency treatment starts on the way to the hospital. The emergency workers may take you to a specialized stroke center to ensure that you receive the quickest possible diagnosis ...
What type of doctor treats strokes?
Brain scans will show what type of stroke you had. You may also work with a neurologist who treats brain disorders, a neurosurgeon that performs surgery on the brain, or a specialist in another area of medicine.
How many days after TIA can you get a stroke?
The risk of stroke within 90 days of a TIA may be as high as 17%, with the greatest risk during the first week. 6. That’s why it’s important to treat the underlying causes of stroke, including heart disease, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation (fast, irregular heartbeat), high cholesterol, and diabetes.
Do not drive to the hospital for a stroke?
Do not drive to the hospital or let someone else drive you. The key to stroke treatment and recovery is getting to the hospital quickly. Yet 1 in 3 stroke patients never calls 9-1-1. 1 Calling an ambulance means that medical staff can begin life-saving treatment on the way to the emergency room.
Why is tPA used in stroke?
The rationale behind the use of tPA in ischemic stroke is that by breaking down the clot, recanalization of the occluded blood vessel occurs. The restoration of blood vessel patency is meaningful, however, only if the brain tissue of the ischemic area is still viable.
What is a tPA?
Background. Ischemic stroke is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide and recombinant human tissue-type Plasminogen Activator (tPA) is the prominent among very few therapeutics used in its treatment.
How many people die from strokes in the world?
According to the World Health Organization, 15 million people suffer stroke worldwide each year. Of these, 5 million die and another 5 million are permanently disabled. 80% of stroke cases are of the ischemic type, in which a blood clot occludes a blood vessel supplying the brain [1].
Is tPA a plasminogen?
Combination and alternative therapies in stroke. tPA is not the sole plasminogen activator used as a thrombolytic therapeutically. Streptokinase, a bacterial enzyme derived from species of Streptococcus, is widely used for myocardial infarction thrombolysis.
Does LRP1 bind to TPA?
LRP1 also binds catalytically active tPA, but with lower affinity [10]. A neuronal-specific inhibitor of tPA, neuroserpin, is the primary modifier of tPA activity in the nervous system [11, 12]. Inhibited tPA-neuroserpin complexes are internalized by LRP1, similarly to tPA-PAI 1 complexes [13].
Does tPA activate MMP-9?
Thus, tPA functions both proteolytically to activate MMP-9 and non-proteolytically to induc e its expression . In agreement with the proposed mechanism, MMP inhibition reduces infarct size after focal cerebral ischemia and protects against intracerebral hemorrhage as a consequence of tPA thrombolysis [124, 125, 126].
How do doctors remove a clot from the brain?
In this procedure, doctors use a wire-cage device called a stent retriever. They thread a catheter through an artery in the groin up to the blocked artery in the brain. The stent opens and grabs the clot. Special suction tubes may also remove the clot.
How does Alteplase IV work?
Doctors administer Alteplase IV r-tPA through an IV in the arm, dissolving the clot and improving blood flow to the part of the brain being deprived. Many people don’t arrive at the hospital in time to receive the medication, which can save lives and reduce long-term effects of stroke.
What is Alteplase IV?
Medication Treatment with Alteplase IV r-tPA. Considered the gold standard, tissue plasminogen activator, r-tPA, (known as alteplase) is approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat ischemic stroke.
What is the best way to remove a clot?
Mechanical Treatment to Remove the Clot. An endovascular procedure or a mechanical thrombectomy is a strongly recommended option to remove a clot in eligible patients with a large vessel occlusion, or LVO. In this procedure, doctors use a wire-cage device called a stent retriever.
Administration
- IV: Activase:ST-elevation MI or acute ischemic stroke: Administer bolus dose (prepared by one of three methods) over 1 minute followed by an infusion.Infusion: Remaining dose for STEMI or AIS may be administered as follows: Any quantity of drug not to be administered to the patient must be removed from vial(s) prior to administration of remaining dose.50 mg vial: Either PVC bag or …
- The protocol required that no anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents be given for 24 hours after treatment and that blood pressure be maintained within prespecified values. The medical monitor reviewed each patient's compliance with the protocol throughout the trial.
Treatment
- Recommended criteria for treatment: Based on the 2015 American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (AHA/ASA) focused update of the 2013 guidelines for the early management of patients with AIS, endovascular therapy with stent retrievers is recommended over intra-arterial fibrinolysis. Initial treatment with intra-arterial fibrinolysis is beneficial for selected patients with …
Adverse Reactions
- >10%: Cardiovascular: Intracranial hemorrhage (CVA: Within 90 days: 15%, within 36 hours: 6%; AMI: <1%)1% to 10%:Cerebrovascular accident (new ischemic stroke in CVA: 6%)Dermatologic: Ecchymosis (AMI: 1%)Gastrointestinal: Gastrointestinal hemorrhage (AMI: 5%)Genitourinary: Genitourinary tract hemorrhage (AMI: 4%)Frequency not defined:Hematologic & oncologic: Arteri…
Benefits
- This study found a benefit of intravenous t-PA therapy for patients with ischemic stroke when treatment was initiated within three hours of the onset of symptoms. As compared with patients given placebo, patients treated with t-PA were at least 30 percent more likely to have minimal or no disability at three months, as measured by the outcome scales (absolute increase in favorabl…
Results
- >50% present in plasma cleared ~5 minutes after infusion terminated, ~80% cleared within 10 minutes; fibrinolytic activity persists for up to 1 hour after infusion terminated (Semba 2000)
- For each primary hypothesis, MantelHaenszel tests were used to compare the proportion of patients with improvement in the NIHSS 24 hours after the onset of stroke. There was no adjustment for multiple comparisons, since the three hypotheses were prespecified. Patients who for some reason were not assessed with the NIHSS at 24 hours were considered to have had no …
Research
- Data from an early study in patients with undifferentiated out of hospital cardiac arrest suggest that the use of alteplase as a bolus may improve rates of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) and survival to hospital admission in these patients [Bottiger 2001]. However, a similar randomized, controlled study reported no difference in these endpoints [Abu-Laban 2002]. Sever…
- Two previous small, randomized studies of intravenous t-PA for stroke found no conclusive evidence of efficacy.24,25 In a recently completed large, placebo-controlled European trial in which 1.1 mg of t-PA per kilogram was given intravenously within six hours of hemispheric ischemia, the investigators reported no benefit in the population analyzed according to the inten…
Diagnosis
- STEMI (ACCF/AHA [OGara 2013]): Ischemic symptoms within 12 hours of treatment or evidence of ongoing ischemia 12 to 24 hours after symptom onset with a large area of myocardium at risk or hemodynamic instability.
- Intracranial hemorrhage, serious systemic bleeding, death, and new stroke were the primary adverse events monitored. To detect intracranial hemorrhage, CT scans were required at 24 hours and 7 to 10 days after the onset of stroke and when any clinical finding suggested hemorrhage. A hemorrhage was considered symptomatic if it was not seen on a previous CT scan and there ha…
Pharmacology
- Initiates local fibrinolysis by binding to fibrin in a thrombus (clot) and converts entrapped plasminogen to plasmin...
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to alteplase or any component of the formulationTreatment of STEMI or PE: Active internal bleeding; history of recent stroke; recent (within 3 months [ACCF/AHA: Within 2 months]) intracranial or intraspinal surgery or serious head trauma; presence of intracranial conditions that may increase the risk of bleeding (eg, intracranial neoplasm, arteriovenous malfo…
Monitoring Parameters
- Acute ischemic stroke (AIS): Baseline: Neurologic examination, head CT (without contrast), blood pressure, CBC, aPTT, PT/INR, glucose. During and after initiation: In addition to monitoring for bleeding complications, the 2013 AHA/ASA guidelines for the early management of AIS recommends the following: Perform neurological assessments every 15 minutes during infusio…