Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Wastewater Treatment: How Do They Work?
- Primary Wastewater Treatment. Primary treatment of wastewater involves sedimentation of solid waste within the water. ...
- Secondary Wastewater Treatment. Secondary treatment of wastewater makes use of oxidation to further purify wastewater. ...
- Tertiary Wastewater Treatment. ...
What are the primary stages of sewage treatment?
Point Sources Of Water Pollution Algae And Bacteria Primary Sewage Treatment Involves Fecal Coliform Bacteria Ganges River Delta. TERMS IN THIS SET (51) The principal source of infectious waste material in water is A. industrial waste. B. surface runoff. C. human feces.
What does a primary sewage treatment involve?
Jun 27, 2017 · Primary treatment of wastewater involves sedimentation of solid waste within the water. This is done after filtering out larger contaminants within the water. Wastewater is passed through several tanks and filters that separate water from contaminants. The resulting “sludge” is then fed into a digester, in which further processing takes place.
What are the main steps in sewage treatment?
wastewater treatment - Primary treatment | Britannica Primary treatment Primary treatment removes material that will either float or readily settle out by gravity. It includes the physical processes of screening, comminution, grit removal, and sedimentation. Screens are made of long, closely spaced, narrow metal bars.
What is removed during primary wastewater treatment?
Apr 24, 2022 · 1) Primary treatment is the first step in wastewater treatment, and however, screening is always the primary stage of sewage treatment. The first step of this primary treatment is to use aeration tanks that let the liquid settle, and the liquid will then flow into more aeration tanks, where bacteria help remove dirt and debris particles from water. 2) Secondary …

What happens during the primary stage of sewage treatment?
In primary treatment, sewage is stored in a basin where solids (sludge) can settle to the bottom and oil and lighter substances can rise to the top. These layers are then removed and then the remaining liquid can be sent to secondary treatment. Sewage sludge is treated in a separate process called sludge digestion.Jan 3, 2021
What are the process involved in primary treatment?
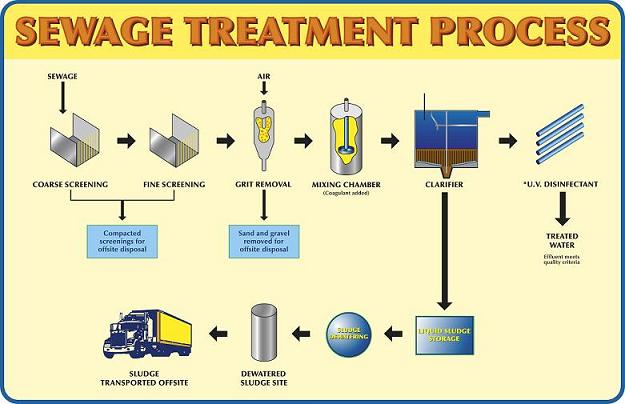
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 6: Filtration. ... Step 7: Disinfection. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake.
What processes are involved in sewage treatment?
The sewage treatment processTaking the wastewater away. ... Screening the wastewater. ... Carrying out primary treatment. ... Secondary treatment. ... Carrying out final treatment. ... Generating power. ... Returning water to the river and solids to land.
What is sewage explain primary and secondary sewage treatment?
Primary sewage treatment is a physical process that removes large impurities while secondary sewage treatment is a biological process that removes organic matter of sewage through the action of microbes.
What is primary and secondary wastewater treatment?
The main difference is the way each respective treatment is processed. Primary treatment works on sedimentation, where solids separate from the water through several different tanks. In contrast, secondary treatment uses aeration, biofiltration and the interaction of waste throughout its process.Nov 19, 2020
What are the 3 stages of sewage treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
What are the 4 stages required in the treatment of wastewater?
Four common ways to treat wastewater include physical water treatment, biological water treatment, chemical treatment, and sludge treatment. Let us learn about these processes in detail.Feb 8, 2018
What happens to sewage sludge after primary treatment?
Once treated, sludge can be recycled or disposed of using three main routes: recycling to agriculture (landspreading), incineration or landfilling.Oct 23, 2001
Screening – Primary treatment for waste water
The first process in Primary Treatment for Wastewater is screening. I will show you the screening process and different types of screens used in primary wastewater treatment.
Flow Equalisation – Primary treatment for waste water
Under uniform flow rates, clarifiers and mechanised secondary treatment are more efficient.
Sedimentation – Primary treatment for wastewater
The wastewater, then moves to sedimentation ponds, settling tanks, or clarifiers after the removal of settled grit. The sedimentation process removes the settleable solids by gravitational settling under quiescent conditions.
Flocculation
Flocculation is a water treatment process to remove small suspended solids which don’t settle in the sedimentation tank. In this process solids form larger clusters, or flocs on the addition of a flocculent like aluminium sulphate.
Scum Removal
Lighter materials rise to the surface as sludge settles to the bottom of the sedimentation tanks. The constituents of ‘scum’ are grease, oils, plastics, and soap. Scum is skimmed off the surface of the wastewater by slow-moving rakes. Scum is thickened before being poured into the digesters with the sludge.
Most popular
Students like you are making the most of their study sessions with our most popular study sets.
Newly added
Check out our new Primary Sewage Treatment Involves study sets, and maximize your study time.
What is the third step in wastewater management?
This third and last step in the basic wastewater management system is mostly comprised of removing phosphates and nitrates from the water supply. Substances like activates carbon and sand are among the most commonly used materials that assist in this process.
What is the most effective method of secondary treatment of wastewater?
This method of secondary treatment of wastewater employs sand filters, contact filters, or trickling filters to ensure that additional sediment is removed from wastewater. Of the three filters, trickling filters are typically the most effective for small-batch wastewater treatment.
What is primary treatment of wastewater?
Primary treatment of wastewater involves sedimentation of solid waste within the water. This is done after filtering out larger contaminants within the water. Wastewater is passed through several tanks and filters that separate water from contaminants.
How long does it take for a wastewater solution to be aerated?
The resulting mixture is then aerated for up to 30 hours at a time to ensure results.
What is a trickling filter?
A trickling filter is simply a tank filled with a deep bed of stones. Settled sewage is sprayed continuously over the top of the stones and trickles to the bottom, where it is collected for further treatment. As the wastewater trickles down, bacteria gather and multiply on the stones. The steady flow of sewage over these growths allows the microbes to absorb the dissolved organics, thus lowering the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) of the sewage. Air circulating upward through the spaces among the stones provides sufficient oxygen for the metabolic processes.
How are screens cleaned?
In modern plants the screens are cleaned mechanically, and the material is promptly disposed of by burial on the plant grounds. A comminutor may be used to grind and shred debris that passes through the screens. The shredded material is removed later by sedimentation or flotation processes. activated sludge process.
How long does it take for a primary clarifier to settle?
These tanks, also called primary clarifiers, provide about two hours of detention time for gravity settling to take place. As the sewage flows through them slowly, the solids gradually sink to the bottom. The settled solids—known as raw or primary sludge —are moved along the tank bottom by mechanical scrapers.
How much of the secondary sludge must be treated?
The recycled microbes are well acclimated to the sewage environment and readily metabolize the organic materials in the primary effluent. The remaining 70 percent of the secondary sludge must be treated and disposed of in an acceptable manner ( see Sludge treatment and disposal ).
How long does activated sludge stay in the aerator tank?
Under such oxygenated conditions, microorganisms thrive, forming an active, healthy suspension of biological solids—mostly bacteria —called activated sludge. About six hours of detention is provided in the aeration tank. This gives the microbes enough time to absorb dissolved organics from the sewage, reducing the BOD.
What is the purpose of a secondary clarifier?
Air circulating upward through the spaces among the stones provides sufficient oxygen for the metabolic processes. Settling tanks, called secondary clarifiers, follow the trickling filters. These clarifiers remove microbes that are washed off the rocks by the flow of wastewater.
What is activated sludge?
activated sludge process. Primary and secondary treatment of sewage, using the activated sludge process. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Grit chambers are long narrow tanks that are designed to slow down the flow so that solids such as sand, coffee grounds, and eggshells will settle out of the water. Grit causes excessive wear and tear on pumps ...
Primary Wastewater Treatment
In the aspect of water resources pollution, primary treatment is a basic necessity for water resource conservation. The concept and function of primary sewage treatment plant (also called POT (Primary Oxygen Treatment)) will be introduced here briefly:
Secondary Wastewater Treatment
The secondary wastewater treatment is a process that separates the organic solids from the wastewater to form effluent, which is treated and safe to release, and solids that can be used as a fertilizer. It is achieved through the following ways:
Tertiary Wastewater Treatment
The tertiary phase includes chemical treatments to stabilize the water for discharge into waterways or reuse within the industry.
Conclusion
It is essential to select the right technology for a particular application based on the characteristics of the wastewater and the desired results.
Overview
Sewage Treatment Plants (STP) requires physical, biological and often chemical processes in order to eliminate contaminants. Its purpose is to produce sewage water that is environmentally friendly and suitable for disposal or reuse. By circulating air, a sewage treatment plant works to facilitate bacteria’s growth to break down sewage.
Advantages and disaDVANTAGES of sewage treatment plant?
The main purpose of having a sewage treatment plant is to handle the wastewater as thoroughly as possible. While such plants can often cope with more waste than a septic tank, they will still require emptying from time to time. Sludge can also be developed over time in the system.
The Sewage Treatment Plant process comes into 2 main types
Anaerobic bacteria partially decompose sewage in a tank without oxygen. This leads to the removal of methane, hydrogen sulphide, carbon dioxide, etc., from organic matter. We commonly use them to treat sludge from wastewater since it offers a significant amount of volume and mass reduction in the raw material.
How does sewage treatment plant works?
The main objective of STP is to leave all solid particles back before the effluent discharges into the atmosphere. Conventional wastewater treatment includes mainly three phases. They are primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment
Bottom Line
Sewage water treatment is a combination of waste and water which contains organic or inorganic solids from various formations. Cleaning up wastewater is hence very important. In the most economical way, a sewage treatment plant (STP) removes hazardous pollutants and provides a healthy environment. We Jateen Trading Co.
What size screen is used in sewage treatment?
It removes plastics, rags, metals, fibrous objects etc. The size of the screen opening varies in sewage treatment plants (typical range: 0.2–6 mm). Some plants employ both coarse and fine screens. Comminutors and grinders are usually used to process the coarse solids and reduce their a size so.
What is the purpose of tertiary treatment?
The effluent from the secondary treatment undergoes chlorination before discharged. Hydrogen peroxides and UV can be used to kill any remaining microbe. Tertiary treatment is carried out if the effluent from the primary and secondary treatment failed to remove biologically degradable organic material.
What is the function of anaerobic digestion?
In anaerobic digestion, the anaerobic bacteria are grown and the organic waste is degraded to soluble substances and gases such as methane and carbon dioxide. Anaerobic sludge digester can convert the carbon dioxide and organic acids from the anaerobic fermentation of the sludge by the various anaerobic microorganism.
What is the BOD in water?
BOD can be defined as the measure of the biologically degradable organic matter in water. Primary treatment removes about 25-35% of the BOD off sewage. In secondary treatment, we reduce the BOD by digesting the organic material (dissolved) using aerobic bacteria.
What is sewage water?
Sewage water includes all the water from household activities including toilet water and water used washing clothes, utensils etc. The rainwater flowing into the street drains and the waste liquids from industries are also the part of sewage.
How does effluent enter a tank?
The effluent enters into the tank through an inlet and trickles over the bed layer by sprinklers. Microbial activities oxidize the organic matter in the effluent, resulting in the removal of fine solids, formation of sludge and effluent with less organic solids.
What is secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment. In this process, the biological waste from the human waste, soap, food waste, and detergent are substantially degraded. Most of the municipal sewage water treatment plants treat the sewage that is settled through the aerobic process.

Screening – Primary Treatment For Waste Water
Flow Equalisation – Primary Treatment For Waste Water
- Under uniform flow rates, clarifiers and mechanised secondary treatment are more efficient.
- Equalization basins store diurnal or wet-weather flow peaks temporarily and make the water flow rate uniform.
- Basins serve as a temporary holding area for the incoming wastewater during temporary plant shut down and maintenance.
- Under uniform flow rates, clarifiers and mechanised secondary treatment are more efficient.
- Equalization basins store diurnal or wet-weather flow peaks temporarily and make the water flow rate uniform.
- Basins serve as a temporary holding area for the incoming wastewater during temporary plant shut down and maintenance.
- It acts as a means of diluting and distributing hazardous or high-strength waste into batches.
Sedimentation – Primary Treatment For Wastewater
- The wastewater, then moves to sedimentation ponds, settling tanks, or clarifiers after the removal of settled grit. The sedimentation process removes the settleable solids by gravitational settling under quiescent conditions. On proper adjustment of water flow in the sedimentation tank, the suspended particles begin to fall to the bottom and form a...
Flocculation
- Flocculation is a water treatment process to remove small suspended solids which don’t settle in the sedimentation tank. In this process solids form larger clusters, or flocs on the addition of a flocculent like aluminium sulphate. The coagulant molecules have a positive charge. Hence, they can neutralize the negatively charged solid particles that are suspended in the water. Neutralizat…
Scum Removal
- Lighter materials rise to the surface as sludge settles to the bottom of the sedimentation tanks. The constituents of ‘scum’ are grease, oils, plastics, and soap. Scum is skimmed off the surface of the wastewater by slow-moving rakes. Scum is thickened before being poured into the digesters with the sludge. Primary treatment removes about 60% of the total suspended solids and nearly …