
Full Answer
Which blood test show if you have leukemia?
Mar 03, 2021 · 42 percent to 54 percent of total blood count for men. 37 percent to 47 percent for women. 32 percent to 44 percent for children. Hemoglobin is expressed in grams per deciliter (gm/dL). Normal ranges for hemoglobin are: 13.5 to 17.5 gm/dL for men. 12 to 15.5 gm/dL for women. 11 to 13 gm/dL for children.
Does a blood test always show leukemia?
Sep 15, 2021 · 5,000–10,000. If you have leukemia, your blood cells count will likely show higher than usual levels of white blood cells, which include …
Does low blood cell count mean you have leukemia?
Sep 15, 2021 · Leukemia is a type of blood cancer that begins in the bone marrow where many blood cells are made. If you have leukemia, you may not make enough of some kinds of blood cells. This cancer can also cause abnormal blood cells to form, crowding out other healthy blood cells in the bone marrow and spilling into the bloodstream.
Can you have leukemia with normal blood count?
Stages of Chronic Leukemia. The Rai system is used to stage chronic leukemia: Stage 0 – A patient has high levels of white blood cells, but no other physical symptoms. Stage 1 – A patient has high levels of white blood cells and enlarged lymph nodes. Stage 2 – A patient has high levels of white blood cells and is anemic.

What would your blood count be if you had leukemia?
Effects of Too Many White Blood Cells Typically a healthy person has a white blood cell count of about 4,000-11,000. Patients with acute or even chronic leukemia may come in with a white blood cell count up into the 100,000-400,000 range.Oct 4, 2018
When do you start treatment for leukemia?
Patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (chronic lymphoid leukemia, CLL) do not need drug therapy until they become symptomatic or display evidence of rapid progression of disease, as characterized by the following: Weight loss of more than 10% over 6 months. Extreme fatigue.Feb 8, 2022
Does your white blood count go up or down with leukemia?
If you have leukemia you will have lower than normal counts of red blood cells and platelets, and higher than normal counts of white blood cells.Nov 19, 2019
What is an alarming WBC count?
In general, for adults a count of more than 11,000 white blood cells (leukocytes) in a microliter of blood is considered a high white blood cell count.Jun 11, 2005
Can leukemia be cured if caught early?
Leukemia is the cancer of the blood-forming tissues that includes bone marrow and lymphatic system. Adults and children are equally affected by Leukemia, which is seen as production of abnormal white blood cells by the bone marrow.Mar 7, 2016
How does leukemia start?
In general, leukemia is thought to occur when some blood cells acquire changes (mutations) in their genetic material or DNA. A cell's DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do. Normally, the DNA tells the cell to grow at a set rate and to die at a set time.
What labs show leukemia?
Your doctor will conduct a complete blood count (CBC) to determine if you have leukemia. This test may reveal if you have leukemic cells. Abnormal levels of white blood cells and abnormally low red blood cell or platelet counts can also indicate leukemia.
Which white blood cells are high in leukemia?
According to the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society, the “normal” range of white blood cells per microliter of blood is: 5,000 to 10,000 for men. 4,500 to 11,000 for women....This included:55 percent increase in neutrophils.38 percent increase in monocytes.36 percent reduction in lymphocytes.no change to eosinophils and basophils.Jan 26, 2022
Does high WBC mean leukemia?
While having an elevated or abnormally high white blood cell count does not necessarily indicate leukemia, the source of the condition will need to be identified if it is found to exceed the levels and duration of a normal immune response to an infection.
Is a white blood count of 11.5 high?
Diagnosis of a high white blood cell count The normal range for your WBC is usually 4,500 to 11,000 cells per microliter. Your WBC is generally considered high if it is greater than 11,000 cells per microliter.
Is 12.4 WBC high?
The specific number for high white blood cell count varies from one lab testing facility to another, but a general rule of thumb is that a count of more than 10,500 leukocytes in a microliter of blood in adults is generally considered to be high, while 4,500-10,500 is considered within the normal range.Mar 15, 2013
Is 2.9 WBC too low?
The normal range is usually between 4,000 and 11,000 white blood cells per microlitre of blood. Anything below 4,000 is typically considered to be a low white blood cell count.
How does leukemia affect blood counts?
Leukemia mainly affects white blood cells called lymphocytes. These immune cells help your body fight off infections.
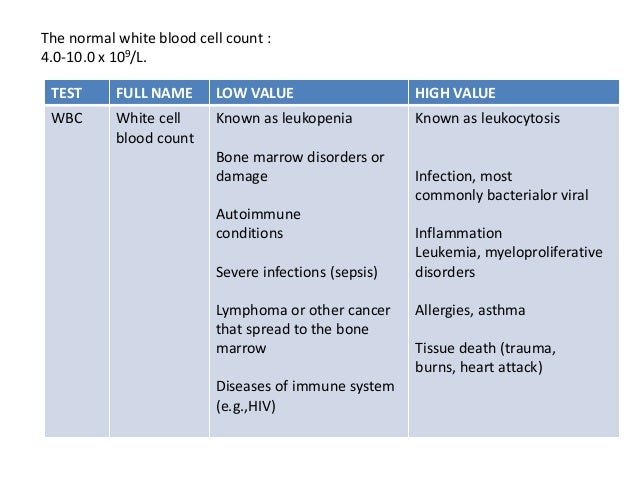
Understanding your blood count test results
Typical blood cell counts vary by age and gender. They can also temporarily change depending on whether you recently had a bad flu, infection, or even injury. The healthy blood cell ranges are shown in the table below:
What happens if my blood counts are out of range?
If you have higher than normal levels of white blood cells and low counts of red blood cells and platelets, the doctor will order additional tests atto get more information.
How are blood counts used to monitor leukemia during treatment?
Your doctor will let you know how often you’ll need to return for more blood tests. If you are diagnosed with leukemia, you may need regular physical exams and blood tests, so your doctor can watch for signs of disease progression or remission.
The bottom line
Leukemia is a type of blood and bone marrow cancer. You may not notice symptoms for a long time, if at all. This is why a complete blood count test can help show imbalances in your blood cells.
What tests can you do for leukemia?
If this happens, or if you have signs or symptoms that suggest leukemia, you may undergo the following diagnostic exams: Physical exam. Your doctor will look for physical signs of leukemia, such as pale skin from anemia, swelling of your lymph nodes, and enlargement of your liver and spleen. Blood tests. By looking at a sample of your blood, your ...
Why is leukemia confusing?
The term "leukemia" can be confusing because it refers to a group of cancers that aren't all that similar except for the fact that they affect the bone marrow and blood.
How to remove bone marrow from hip?
Bone marrow test. Your doctor may recommend a procedure to remove a sample of bone marrow from your hipbone. The bone marrow is removed using a long, thin needle. The sample is sent to a laboratory to look for leukemia cells.
What is the treatment for bone marrow transplant?
Radiation therapy may be used to prepare for a bone marrow transplant. Bone marrow transplant. A bone marrow transplant, also called a stem cell transplant, helps reestablish healthy stem cells by replacing unhealthy bone marrow with leukemia-free stem cells that will regenerate healthy bone marrow.
Where is bone marrow aspiration done?
In a bone marrow aspiration, a doctor or nurse uses a thin needle to remove a small amount of liquid bone marrow, usually from a spot in the back of your hipbone (pelvis). A bone marrow biopsy is often done at the same time. This second procedure removes a small piece of bone tissue and the enclosed marrow.
What does a blood test show?
A blood test may also show the presence of leukemia cells, though not all types of leukemia cause the leukemia cells to circulate in the blood.
How does immunotherapy work?
Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process. Engineering immune cells to fight leukemia.
How does identifying the stages of leukemia help physicians?
Identifying the stages of leukemia can provide important information about the progression of the condition that can help physicians determine the most appropriate treatments. Leukemia cells develop within the bone marrow and do not form masses or tumors, but instead affect the quantities of white blood cells, red blood cells ...
How are leukemia stages determined?
Therefore, while most types of cancer are staged based on the size and spread of a primary tumor, the stages of leukemia are determined differently based on blood cell counts and the accumulation of leukemia cells within organs, such as the liver and spleen.
What is stage 3 lymph node?
He or she may also have enlarged lymph nodes. Stage 3 – A patient has high levels of white blood cells and is anemic. He or she may also have enlarged lymph nodes and/or an enlarged liver or spleen. Stage 4 – A patient has high levels of white blood cells and low platelets.
What is the difference between a stage 1 and stage 2?
Stage 1 – A patient has high levels of white blood cells and enlarged lymph nodes. Stage 2 – A patient has high levels of white blood cells and is anemic. He or she may also have enlarged lymph nodes.
What is stage 0 leukemia?
Stage 0. In stage 0 chronic lymphocytic leukemia, there are too many lymphocytes in the blood, but there are no other signs or symptoms of leukemia . Stage 0 chronic lymphocytic leukemia is indolent (slow-growing).
Where does CLL spread?
In chronic lymphocytic leukemia ( CLL ), the leukemia cells may spread from the blood and bone marrow to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes, liver, and spleen. It is important to know whether the leukemia cells have spread in order to plan the best treatment.
What is the name of the cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (also called CLL) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow that usually gets worse slowly. CLL is one of the most common types of leukemia in adults.
What is the disease that causes swollen lymph nodes?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Leukemia may affect red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Signs and symptoms of chronic lymphocytic leukemia include swollen lymph nodes and feeling tired. Tests that examine the blood are used ...
What is PDQ cancer?
This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
What is BCL2 inhibitor therapy?
BCL2 inhibitor therapy: This treatment blocks a protein called BCL2 which is found on some leukemia cells. This may kill leukemia cells and make them more sensitive to other anticancer drugs. Venetoclax is a type of BCL2 therapy used to treat symptomatic or progressive, recurrent, or refractory CLL.
How does chemo work?
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body ( systemic chemotherapy ). Combination chemotherapy is treatment using more than one anticancer drug.
Complete blood count
red blood cells (erythrocytes), which help move oxygen from the lungs to cells all around the body
White blood cell differential
A white blood cell differential is usually included with the CBC. For this test, the pathologist (a medical professional who studies diseases) smears a drop of blood on a slide. Then they examine it under a microscope.
Flow cytometry
In this test, the blood sample is treated with special antibodies and passed through a laser beam. These antibodies attach to cells with corresponding antigens. When that happens, they give off light that can be analyzed by a computer.
What is the normal hemoglobin level?
Normal is 25 to 35 picograms. Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) measures the concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells. Normal is 32% to 36%.
Why is my WBC low?
A low WBC count may be due to chemotherapy, a viral infection, a toxic reaction, or a process in the bone marrow that limits the body’s ability to make normal WBCs. A high WBC count may result from an infection or leukemia. A person is at an increased risk of infection if his/her WBC count drops below 1,000 cells per microliter.
What are the cells that help fight infection?
The white blood cells , or leukocytes, are part of the body's immune system. There are several types of white blood cells that help to prevent and fight infections. The platelets or thrombocytes are tiny particles that help the blood to clot or stop bleeding when there is an injury. If the platelets are low, a patient may bleed or bruise easily.
What is the stem cell in bone marrow?
All cells made in the bone marrow start out as a single kind of cell called a stem cell. Depending on what type of cell the body needs, a stem cell can become one of three major types of blood cells, a red cell, a white cell, or a cell that makes platelets.
What is the function of red blood cells?
Blood cells. Red blood cells, also called erythrocytes, contain hemoglobin that gives red blood cells their color and carries oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. If the number of red blood cells is low, a person may feel tired or short of breath. The white blood cells, or leukocytes, are part of the body's immune system.
What is the treatment for cancer?
Cancer chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used to damage or kill cancer cells. Some of the body's normal cells, including the blood cells, may also be damaged by these treatments. Some medicines can also slow down the making of blood cells.
Where are blood cells made?
Most types of blood cells are made in the bone marrow. The bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue found in the center of the large bones like the pelvic bones, the breast bone, and the long leg bones. All cells made in the bone marrow start out as a single kind of cell called a stem cell.
What is the WBC of a CLL patient?
Nine months after diagnosis, a fellow patient with CLL tells you that his WBC (white blood cell count) is 49,000 with an ALC (absolute lymphocyte count) of 42,000. He has clusters of 2 x 1 cm nodes in both axillae (armpits). Labs are otherwise OK. He feels well, just a bit tired and stressed. He asks what symptoms or lab results might indicate it is time to treat. You tell him:
What is CLL in hematology?
Hematology in general and CLL specifically are full of jargon and acronyms that can be both overwhelming and daunting . With time and experience, you’ll become familiar with the terminology and acronyms. We will try to explain each medical term the first time it appears in an article, but we will use the true terminology so that you gain comfort and familiarity with the medical terms that you will see in your lab reports and in medical articles. We have also provided a glossary and a list of abbreviations and acronyms for your reference.
What is the name of the disease where the body attacks its own platelets?
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA where the body attacks its own red cells) and/or Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP where the body attacks its own platelets) that is poorly responsive to steroids or other standard therapy.
How long can you sweat without infection?
Fevers >38°C for at least 2 weeks without evidence of infection. Drenching night sweats for more than a month without evidence of infection.
Is Watch and Wait better than Chlorambucil?
In fact this famous study published in 1998 compared “Watch And Wait” to early intervention with chlorambucil, an oral chemotherapy and at that time the standard of care, and found that the group on chlorambucil fared slightly worse. Admittedly, we have much better treatments today.
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Treatment for your leukemia depends on many factors. Your doctor determines your leukemia treatment options based on your age and overall health, the type of leukemia you have, and whether it has spread to other parts of your body, including the central nervous system. Common treatments used to fight leukemia include: 1. Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is the major form o…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- A diagnosis of leukemia may be devastating — especially for the family of a newly diagnosed child. With time you'll find ways to cope with the distress and uncertainty of cancer. Until then, you may find it helps to: 1. Learn enough about leukemia to make decisions about your care. Ask your doctor about your leukemia, including your treatment options and, if you like, your prognosis. As …
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Start by seeing your family doctor if you have signs or symptoms that worry you. If your doctor suspects you have leukemia, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in diseases of the blood and bone marrow (hematologist). Because appointments can be brief, and because there's often a lot of information to discuss, it's a good idea to be prepared. Here's some information to …