Explore
Apr 01, 2022 · A condition called sinus bradycardia also causes the heart to beat slowly, resulting in faintness, lethargy and even fainting or death. The treatment for sinus bradycardia, which will vary depending on each patient's circumstances, could be an atropine injection, or the implantation of a pacemaker in
Can sinus bradycardia be cured?
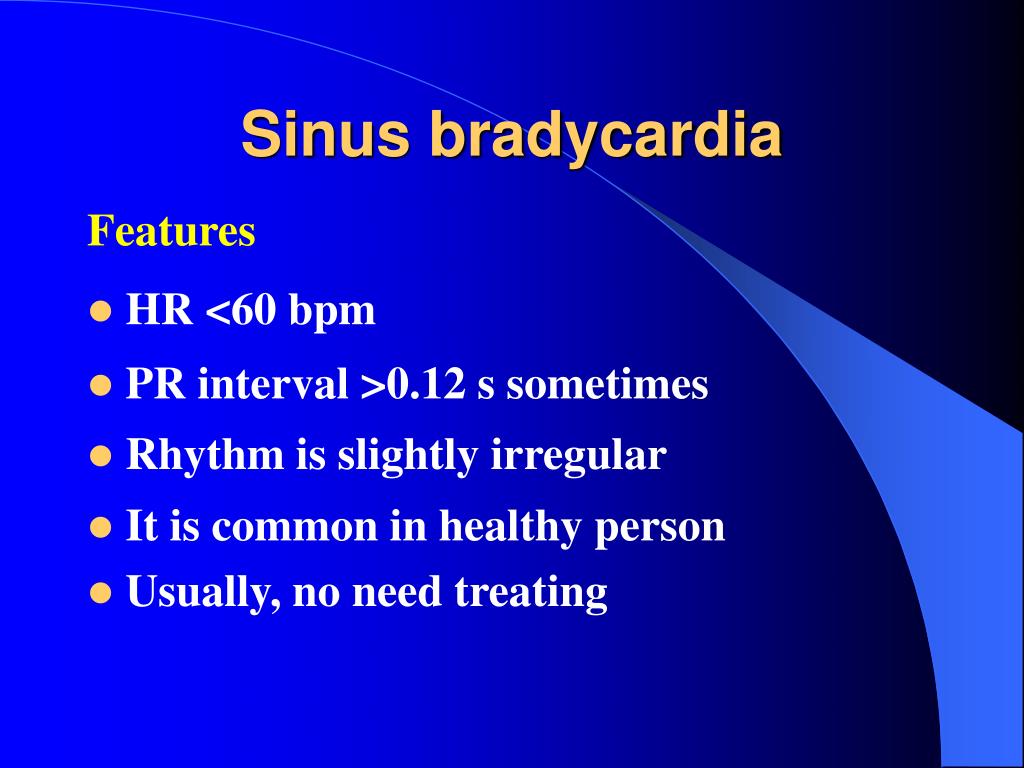
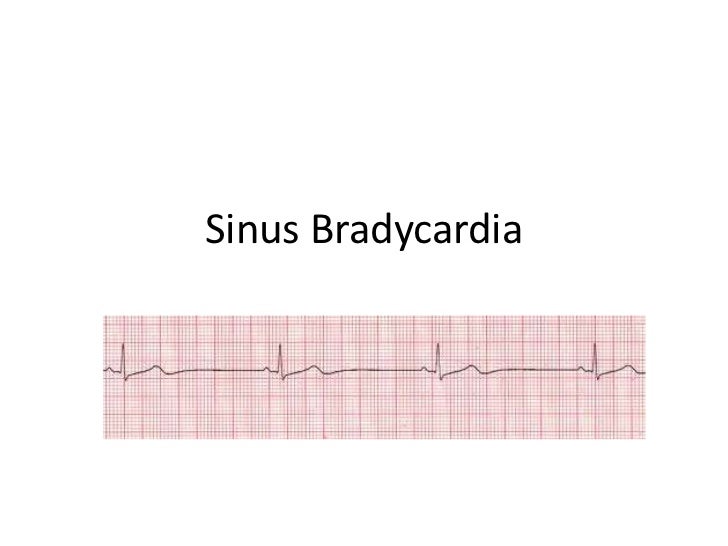
Sinus bradycardia is a type of slow heartbeat. A special group of cells begin the signal to start your heartbeat. These cells are in the sinoatrial (SA) node. Normally, the SA node fires at about 60 to 100 times per minute at rest. In sinus bradycardia, the node fires less than 60 times per minute.
Can bradycardia go away on its own?
Dec 27, 2017 · Treatment of postinfectious bradycardia usually requires permanent pacing. In patients with hypothermia who have confirmed sinus bradycardia with a pulse, atropine and pacing are usually not...
How to treat bradycardia naturally?
If a patient is hemodynamically stable, treatment for sinus bradycardia is dependent on the respective cause of this cardiac rhythm and can vary from medication management to the placement of a permanent pacemaker (as examples). Sinus bradycardia can occur in both adult and pediatric patients.
Should I be worried about sinus bradycardia?
Oct 20, 2021 · Bradycardia (brad-e-KAHR-dee-uh) is a slower than normal heart rate. The hearts of adults at rest usually beat between 60 and 100 times a minute. If you have bradycardia, your heart beats fewer than 60 times a minute. Bradycardia can be a serious problem if the heart rate is very slow and the heart can't pump enough oxygen-rich blood to the body.
What drug is given for sinus bradycardia?
Atropine is the first line medication for the treatment of bradycardia. The administration of atropine typically causes an increase in heart rate. This increase in the heart rate occurs when atropine blocks the effects of the vagus nerve on the heart.
Does sinus bradycardia need treatment?
While sometimes sinus bradycardia may not need treatment, it can also be a sign of serious health conditions that need attention. Always seek emergency medical care if you experience chest pain that lasts longer than a few minutes, trouble breathing, or fainting.Sep 26, 2019
What is the most common cause of sinus bradycardia?
One of the most common pathologic causes of symptomatic sinus bradycardia is the sick sinus syndrome. The most common medications responsible include therapeutic and supratherapeutic doses of digitalis glycosides, beta-blockers, and calcium channel-blocking agents.Dec 27, 2017
What is the best treatment for bradycardia?
The standard treatment for a slow heart rate is to implant a pacemaker. For people with bradycardia, this small device can help restore a normal heartbeat.
Should I be worried about sinus bradycardia?
If you have bradycardia, your heart beats fewer than 60 times a minute. Bradycardia can be a serious problem if the heart rate is very slow and the heart can't pump enough oxygen-rich blood to the body. If this happens, you may feel dizzy, very tired or weak, and short of breath.Oct 20, 2021
Is a pacemaker the only treatment for bradycardia?
Surgery or other procedures. When other treatments aren't possible and bradycardia symptoms are severe, a device called a pacemaker is necessary to control the heart rhythm. Pacemakers work only when needed.Oct 20, 2021
Is exercise good for sinus bradycardia?
Get regular exercise. Try for 2½ hours a week. If you do not have other heart problems, you likely do not have limits on the type or level of activity that you can do. You may want to walk, swim, bike, or do other activities.
Can bradycardia be cured?
The good news is that bradycardia can be treated and even cured. Friedman explains that certain medications can slow down a person's heart rate, and stopping that treatment can in turn stop bradycardia. Even if the condition can't be reversed, doctors can still treat it with a pacemaker.Oct 13, 2015
How can I improve my low heart rate?
How to lower your resting heart rateGet moving. The most common cause of a high resting heart rate is a sedentary lifestyle, where you spend a lot of time not moving. ... Manage stress. ... Avoid caffeine and nicotine. ... Maintain a healthy weight. ... Stay hydrated. ... Sleep well. ... How long does it take to lower your heart rate?Feb 5, 2021
When does bradycardia require treatment?
Regardless of the patient's rhythm, if their heart rate is too slow and the patient has symptoms from that slow heart rate, the bradycardia should be treated to increase the heart rate and improve perfusion, following the steps of the bradycardia algorithm below.
How to diagnose bradycardia?
To diagnose your condition, your doctor will review your symptoms and your medical and family medical history and do a physical examination. Your doctor will also order tests to measure your heart rate, establish a link between a slow heart rate and your symptoms, and identify conditions that might be causing bradycardia.
What causes bradycardia?
Change in medications. A number of medications, including some to treat other heart conditions, can cause bradycardia. Your doctor will check what medications you're taking and possibly recommend alternatives. Changing drugs or lowering dosages might correct problems with a slow heart rate.
What is an EKG?
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) An electrocardiogram, also called an ECG or EKG, is a primary tool for evaluating bradycardia. Using small sensors (electrodes) attached to your chest and arms, it records electrical signals as they travel through your heart. Because an ECG can't record bradycardia unless it happens during the test, ...
How does an event recorder work?
This device monitors your heart activity over a few weeks. You push a button to activate it when you feel symptoms so that it records your heart's activity during that time.
How long does a Holter monitor record heart rate?
Holter monitor. Carried in your pocket or worn on a belt or shoulder strap, this device records your heart's activity for 24 to 48 hours. Your doctor will likely ask you to keep a diary during the same 24 hours. You'll describe any symptoms you experience and record the time they occur. Event recorder.
What is a wireless pacemaker?
The pacemaker monitors your heart rate and generates electrical impulses as necessary to maintain an appropriate rate. A wireless pacemaker has been approved by the FDA. The leadless system holds promise for people who need pacing in only one ventricle, but more study is needed.
Where is the pacemaker implanted?
Pacemaker. This battery-operated device about the size of a cellphone is implanted under your collarbone. Wires from the device are threaded through veins and into your heart. Electrodes at the end of the wires are attached to heart tissues.
What is sinus bradycardia?
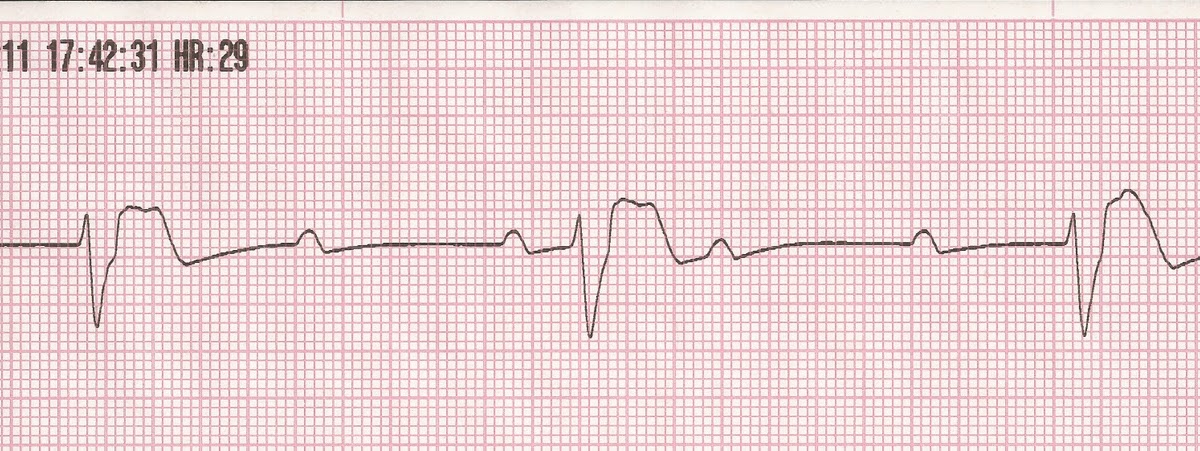
Continuing Education Activity. Sinus bradycardia is a cardiac rhythm with appropriate cardiac muscular depolarization initiating from the sinus node and a rate of fewer than 60 beats per minute (bpm). The diagnosis of this condition requires an ECG showing a normal sinus rhythm at a rate lower than 60 bpm.
What is the most important component of a patient's evaluation for sinus bradycardia?
Evaluation. The most significant component of evaluation for a patient who presents with signs and symptoms of sinus bradycardia is history and physical exam. These should include vital signs (respiratory rate, blood pressure, temperature, and heart rate) and an electrocardiogram.
What is the SA in the heart?
The sinoatrial node (SA) is the default pacemaker and therefore a crucial component of the heart's conduction system. It is located subepicardial and is crescent in shape. In an average adult, a sinoatrial node is 13.5 millimeters in length and is innervated by the vagus and sympathetic nerves.
How long does it take to live with sinus bradycardia?
However, patients with sick sinus syndrome who have bradycardia tend to have a poor prognosis with 5-year survival rates between 45-70%. With the number of bariatric procedures increasing each year, it has been observed that many of these patients also develop sinus bradycardia.
Which artery supplies blood to the sinoatrial node?
The sinoatrial nodal artery supplies blood to the sinoatrial node, it branches off the right coronary artery in 60% of cases, whereas in 40% of cases it comes off the left circumflex coronary artery. [1][2] Sinus bradycardia is a cardiac rhythm with appropriate cardiac muscular depolarization initiating from the sinus node generating less ...
What is the maximum height of a P wave?
The p wave is upright in leads 1 and 2, P wave is biphasic in V1. The maximum height of a P wave is less than or equal to 2.5 mm in leads 2 and 3. The rate of the rhythm is between 60 bpm and 100 bpm. Etiology.
Is sinus bradycardia common in elderly patients?
In this disorder there is dysfunction of the SA node. The condition is most common in elderly patients with concomitant heart disease. Histopathology.
What is sinus bradycardia?
Sometimes, this sinus bradycardia is called physiologic sinus bradycardia. Many people with sinus bradycardia don’t know that they have it. Sinus bradycardia can be a sign of a problem with the heart or another medical condition. Sinus bradycardia can happen off and on in response to specific situations.
What are some examples of medical conditions that affect the SA node?
Heart attack (myocardial infarction) Obstructive sleep apnea. Medicines that affect the SA node and heart rate such as beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers. Hypothyroidism. Certain rare genetic conditions such as myotonic dystrophy.
What is the name of the cell that starts the heartbeat?
A special group of cells begin the signal to start your heartbeat. These cells are in the sinoatrial (SA) node. Normally, the SA node fires the signal at about 60 to 100 times per minute at rest. In sinus bradycardia, the node fires less than 60 times per minute. Bradycardia means a slow heartbeat.
What are some examples of problems with the SA node?
Advanced age. Problems with the SA node (sick sinus syndrome) Inflammatory heart conditions such as pericarditis or myocarditis. Heart conditions that exist at birth (congenital) Increased pressure inside the head. For example, in an injury to the brain. Heart attack (myocardial infarction) Obstructive sleep apnea.
What causes a slow heart rate?
This may include treating a cause such as an underactive thyroid. You may need to lower or stop medicines that may be causing the slow heart rate. These can include beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers. Some people may need a temporary or permanent pacemaker.
Is sinus bradycardia normal?
In some cases, sinus bradycardia is normal, but other times it can mean an underlying problem. Sinus bradycardia can be caused by some health conditions. But in some people, such as athletes and older adults, it’s normal. Most people with sinus bradycardia don’t have any symptoms.
Can sinus bradycardia happen in deep sleep?
Sinus bradycardia is more likely to happen during deep sleep . Sinus bradycardia can happen with or without any other heart rhythm problems. In some people, sinus bradycardia switches back and forth with a heart rhythm that is too fast. This fast heart rhythm is called tachycardia.
What is the care in the ED?
Care in the ED should first rapidly ensure the stability of the patient's condition. This is followed by an investigation into the underlying cause of the bradycardia. Patients in unstable condition may require immediate endotracheal intubation and transcutaneous or transvenous pacing.
Should patients have continuous cardiac monitoring and intravenous access?
Patients should have continuous cardiac monitoring and intravenous access. In hemodynamically stable patients, attention should be directed at the underlying cause of the bradycardia. In sick sinus syndrome, drug therapy approaches have been relatively disappointing.
Can you use atropine for sinus bradycardia?
Occasionally, intravenous atropine and temporary pacing are required. Treatment of postinfectious bradycardia usually requires permanent pacing. In patients with hypothermia who have confirmed sinus bradycardia with a pulse, atropine and pacing are usually not recommended because of myocardial irritability.
Can you discontinue digitalis for sinus bradycardia?
In patients with sinus bradycardia secondary to therapeutic use of digitalis, beta-blockers, or calcium channel blockers, simple discontinuation of the drug, along with monitored observation, are often all that is necessary. Occasionally, intravenous atropine and temporary pacing are required.
Can bradycardia be followed up?
Outpatient follow-up care is dependent on the underlying cause of the bradycardia. Most patients should be able to follow up with their primary care provider or obtain a referral for a follow-up visit. Some patients may require specialized referral to a cardiologist.
Can sinus bradycardia be seen in hypothermia?
Rewarming and supportive measures are the mainstays of therapy. Sinus bradycardia may be seen in patients undergoing therapeutic hypothermia. [ 8] . These patients are likely to develop sinus bradycardia sometime during their course that will require close monitoring of perfusion status.
What Is Sinus Bradycardia?
Sinus bradycardia originates in the sinoatrial (SA) node of the heart (also known as the pacemaker) and occurs when an individual’s heart rate is 60 beats per minute or less and otherwise presents as a sinus rhythm on an electrocardiogram (ECG).
What Signs or Symptoms May Be Present?
Signs or symptoms the patient may experience with sinus bradycardia include:
What Causes Sinus Bradycardia?
There are numerous potential causes for the development of sinus bradycardia. Examples include:
Treatment of Sinus Bradycardia
Patients with sinus bradycardia may be asymptomatic. However, if the adult patient with sinus bradycardia is symptomatic, has a heart rate of less than 50 beats per minute, and the patient’s symptoms result from poor perfusion due to the decreased heart rate, this patient is presenting with unstable bradycardia.
Prepare for Your Certification Exam
The medical professional utilizing ACLS or PALS guidelines to care for patients must be able to identify cardiac rhythms in order to provide appropriate, safe, and effective care. An index of cardiac rhythms that the medical professional must be knowledgeable of is available as a resource.
How to prevent bradycardia?
The most effective way to prevent bradycardia is to reduce your risk of developing heart disease. If you already have heart disease, monitor it and follow your treatment plan to lower your risk of bradycardia.
What to do if you faint from bradycardia?
If you faint, have difficulty breathing or have chest pain lasting more than a few minutes, get emergency care or call 911 or your local emergency number. Seek emergency care for anyone with these symptoms.
What is the name of the cell that sends out electrical signals?
Normal heartbeat. In a normal heart rhythm, a tiny cluster of cells at the sinus node sends out an electrical signal. The signal then travels through the atria to the atrioventricular (AV) node and then passes into the ventricles, causing them to contract and pump out blood. Bradycardia. Open pop-up dialog box.
Why is my heart slow?
Bradycardia, shown on the right, is a slower heart rhythm that may occur because the sinus node in the heart may be discharging electrical impulses at a slower than normal rate. A heart with a normal heart rhythm is shown on the left. Bradycardia may also be due to other causes. Bradycardia can be caused by:
What causes a bamcardia?
Bradycardia can be caused by: Heart tissue damage related to aging. Damage to heart tissues from heart disease or heart attack. Heart disorder present at birth (congenital heart defect) Infection of heart tissue (myocarditis) A complication of heart surgery.
How many times does your heart beat a minute?
The hearts of adults at rest usually beat between 60 and 100 times a minute. If you have bradycardia (brad-e-KAHR-dee-uh), your heart beats fewer than 60 times a minute.
How to prevent heart disease?
Take the following steps: Exercise and eat a healthy diet. Live a heart-healthy lifestyle by exercising regularly and eating a healthy, low-fat, low-salt, low-sugar diet that's rich in fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Maintain a healthy weight.