Medication
Mar 24, 2022 · While Marfan syndrome has no cure, treatments can help delay or prevent problems, especially when started early. Your healthcare providers In addition to your primary …
Procedures
Although there is no cure for Marfan syndrome, doctors use treatments to relieve symptoms and prevent additional problems or complications. Treatment depends on the area of the body affected by the syndrome and may include: Medications to help manage pain and problems with your heart. Other treatments, such as braces.
See more
In general, you can expect some things you need to think about every day, such as medications and limitations on physical activity. Then, there are routine doctor appointments, which may be yearly or more frequent, as well as other evaluations to make sure that your Marfan features are not worsening. Sometimes, as features progress, your doctor will recommend surgery to …
What are the chances of getting Marfan syndrome?
in the early 1970s, it was suggested that reduction of the systolic ejection impulse (dp/dt, the rate of change of central arterial pressure with time) using β blocker treatment might reduce the risk of aortic dissection in marfan syndrome. 7 studies in turkeys prone to aortic dissection had shown improved survival following treatment with …
Do people with Marfan syndrome need medical assistance?
Mar 24, 2022 · People who have Marfan syndrome may be tall and thin and have long arms, legs, fingers, and toes, as well as flexible joints. The most serious problems happen when the condition affects the heart and blood vessels. Your healthcare provider may recommend medicines, surgery, or other treatments to manage or prevent complications.
How can you prevent Marfan syndrome?
May 30, 2017 · What is the treatment for Marfan syndrome? Individuals who have Marfan syndrome are treated by a multidisciplinary medical team that includes a geneticist, cardiologist, ophthalmologist, orthopedist and cardiothoracic surgeon. Eye …
What effects can Marfan syndrome have on persons life?
Marfan's syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder of connective tissue, which has both high penetrance and variable severity. The incidence of Marfan's syndrome is around 2–3 per 10 000 individuals. 4 In 25% of individuals there is no family history, which suggests that the condition has presented de novo.
See more

What are the main treatments for Marfan syndrome?
Treatment options include medication therapy or surgical intervention:Medical management of Marfan syndrome, such as beta blockers or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)Surgical interventions: Aortic root replacement. Valve sparing root replacement. Complex aortic surgery for dissections and aneurysms.
Can Marfan syndrome be fixed?
There is no cure for Marfan syndrome, but management of the associated symptoms can prolong and enhance the quality of a patient's life.
What treatments would a cardiologist recommend for Marfan syndrome?
The most common treatments for Marfan syndrome include:Medications to lower your blood pressure.Medications to make your heart beat slower and help avoid stressing the aorta (the large artery that carries oxygen-rich blood to your body)Treatments for complications that may affect your lungs, spine, or eyes.More items...
What are 4 symptoms of Marfan syndrome?
Marfan syndrome features may include:Tall and slender build.Disproportionately long arms, legs and fingers.A breastbone that protrudes outward or dips inward.A high, arched palate and crowded teeth.Heart murmurs.Extreme nearsightedness.An abnormally curved spine.Flat feet.May 19, 2021
What are 3 treatments for Marfan syndrome?
While there is no cure for Marfan syndrome, treatment focuses on preventing the various complications of the disease....Ascending aortic root aneurysm procedureAortic repair. ... Scoliosis treatment. ... Breastbone corrections. ... Eye surgeries.May 19, 2021
How long can you live with Marfan syndrome?
The mean life expectancy for untreated patients with Marfan syndrome is 32 years with aortic dissection, aortic rupture or cardiac failure due to mitral and aortic valve regurgitation as the predominant cause of death in > 90% of the cases.
What tests are done for Marfan syndrome?
A blood test can be used to help diagnose Marfan syndrome. This blood test is highly specialized and looks for changes in FBN1, the gene that is responsible for most cases of Marfan syndrome. Genetic counseling should accompany genetic testing because FBN1 testing is not always straightforward.
What treatments would a ophthalmologist recommend for Marfan syndrome?
Comprehensive ophthalmologic care is necessary to achieve the best possible vision in people with Marfan syndrome. Patients with subluxated lenses are treated with glasses or contact lenses whenever possible. If the visual acuity cannot be improved with these options, surgery may be necessary to optimize vision.
How do they test for Marfan syndrome?
If your doctor strongly suspects Marfan syndrome, a 29-gene genetic test is performed to look for mutations associated with Marfan syndrome and other genetic conditions that affect the body in a similar way. Genetic testing is done with an at-home saliva test kit or an in-office blood test.
Does Marfan cause pain?
Skeletal problems that develop as a result of Marfan syndrome can sometimes cause significant pain and discomfort. They may also affect your appearance, which some people find affects their confidence and self-esteem.
Are there prenatal tests for Marfan syndrome?
Prenatal testing is available when the FBN1 mutation in the family is known. o TGFBR1/2 Testing. If a mutation is not found in FBN1 and there is a strong clinical suspicion of Marfan syndrome, TGFBR1/2 genetic testing may be indicated.
When is Marfan syndrome usually diagnosed?
Prenatal testing for Marfan syndrome can be carried out approximately 10 to 12 weeks into the pregnancy using chorionic villus sampling (CVS). CVS involves taking a small sample of cells from the organ that links the mother's blood supply with her unborn baby's (the placenta) through the entrance of the womb.
Why is Marfan syndrome so difficult to diagnose?
Marfan syndrome can be challenging for doctors to diagnose because many connective tissue disorders have similar signs and symptoms. Even among members of the same family, the signs and symptoms of Marfan syndrome vary widely — both in their features and in their severity. Certain combinations of symptoms and family history must be present ...
What is the first test for Marfan syndrome?
Heart tests. If your doctor suspects Marfan syndrome, one of the first tests he or she may recommend is an echocardiogram. This test uses sound waves to capture real-time images of your heart in motion. It checks the condition of your heart valves and the size of your aorta.
What is Marfan test?
Genetic testing is often used to confirm the diagnosis of Marfan syndrome. If a Marfan mutation is found, family members can be tested to see if they are also affected. You may want to talk to a genetic counselor before starting a family, to see what your chances are of passing on Marfan syndrome to your future children.
What is the procedure for aortic root replacement?
In aortic root replacement, your surgeon removes a section of your aorta and your aortic valve, and replaces the section of the aorta with an artificial tube (graft). The aortic valve is replaced with a mechanical or biological valve, shown in the bottom right image.
Why do children with Marfan syndrome struggle in school?
For example, children with Marfan syndrome may struggle in school because of vision problems that can be corrected with glasses or contact lenses. For most young people, cosmetic concerns are at least as important as academic ones. Parents can help by anticipating these concerns and offering solutions, such as:
Why is Marfan syndrome so hard on young people?
But Marfan syndrome can be even harder on young people, especially because the often-inherent self-consciousness of childhood and adolescence may be exacerbated by the disease's effect on appearance, academic performance and motor skills.
How difficult is it to live with genetic disorders?
Coping and support. Living with a genetic disorder can be extremely difficult for both adults and children. Adults may wonder how the disease will affect their careers, their relationships and their sense of themselves. And they may worry about passing the defective gene to their children.
Why is it important to know the signs of Marfan syndrome?
Recognizing the signs of Marfan syndrome is important for prevention and treatment of serious and even life-threatening complications. People with Marfan syndrome are often tall and thin, with very long arms, legs, fingers, and toes.
What are the complications of Marfan syndrome?
Not everyone with Marfan syndrome has all of the complications. People with Marfan syndrome must be closely followed by their doctor to watch for the following complications: 1 Heart disease, including aortic aneurysms and problems with heart valves 2 Bone deformities such as scoliosis (a curved spine) or a breastbone that is sunken or sticks out 3 Eye conditions that can lead to blurred vision or loss of sight, such as a retinal detachment (where the retina—the part of the eye that senses light in the back of the eye—peels away from its supporting tissue) or dislocation of the lens (where the lens shifts out of place) 4 Teeth that are crooked or crowded together, which might require dental procedures 5 A collapsed lung, which makes breathing difficult
How rare is Marfan syndrome?
Marfan syndrome is rare, happening in about 1 in 5,000 people . 1 Marfan syndrome is caused by a mutation in a gene called FBN1. The mutation limits the body’s ability to make proteins needed to build connective tissue. 1, One in four people with Marfan syndrome develops the condition for unknown reasons.
How to treat an aortic aneurysm?
An aortic aneurysm may be treated with medicine or medicine plus surgery. Medicine is used to lower blood pressure to help prevent an aneurysm from rupturing and causing a dissection of the aorta. 2. Severe scoliosis and breastbone problems may require surgery. Eye conditions may also require surgery.
What causes blurred vision?
Eye conditions that can lead to blurred vision or loss of sight, such as a retinal detachment (where the retina—the part of the eye that senses light in the back of the eye—peels away from its supporting tissue) or dislocation of the lens (where the lens shifts out of place)
Does Marfan syndrome cause heart problems?
Not everyone with Marfan syndrome has all of the complications. People with Marfan syndrome must be closely followed by their doctor to watch for the following complications: Heart disease, including aortic aneurysms and problems with heart valves.
Can you have surgery for Marfan syndrome?
Sometimes, when symptoms progress, your doctor will recommend surgery. In some cases, you will have time to plan for an operation; in other cases, immediate surgery may be needed. Understanding how Marfan syndrome symptoms are treated will help you in your medical journey.
Can you live a full life with Marfan syndrome?
While Marfan syndrome is a condition that cannot be cured, you can live a long, full life with proper treatment and management. Everyone is different, depending on how severe or mild their features are. In general, you can expect some things you need to think about every day, such as medications and limitations on physical activity.
What is Marfan syndrome?
Marfan syndrome is a variable, autosomal dominant connective tissue disorder, affecting mainly the cardiovascular system, eyes, and skeleton. The incidence is approximately 1 in 9800, and around 26% of cases have no family history, the condition resulting from a new mutation.1Characteristic features include progressive aortic dilatation associated ...
What are the complications of Marfan syndrome?
Cardiovascular complications of Marfan syndrome include mitral valve prolapse and regurgitation, left ventricular dilatation and cardiac failure, and pulmonary artery dilatation, but aortic root dilatation is the most common cause of morbidity and mortality.
How many Marfan patients have fibrillin 1 mutations?
With current techniques, fibrillin 1 mutations can be detected in about 66% of Marfan patients, diagnosed by the Ghent nosology.4Most mutations are missense, suggesting that the phenotype is usually cause by a dominant negative effect of the mutant gene product on microfibrillar assembly.
What is the chromosome of fibrillin?
Fibrillin is a 350 kD glycoprotein, synthesised as a 375 kD precursor which is processed and secreted into the matrix. It is encoded by the fibrillin 1 gene which maps to chromosome 15q21.1. Mutation in another fibrillin gene (fibrillin 2, mapping to chromosome 5q23–31) causes Beals syndrome.
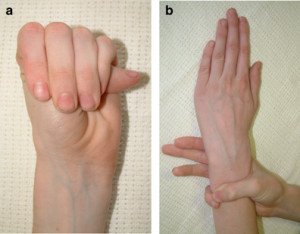
What is the Steinberg thumb sign?
In the skeletal system, arachnodactyly may be assessed (fig 22)) using the Steinberg thumb sign (the entire thumbnail projects beyond the ulnar border of the hand) and the Walker-Murdoch wrist sign (the thumb and fift h finger overlap around the wrist).
Is Lujan-Fryns a Marfan syndrome?
Lujan-Fryns syndrome is an unusual X- linked mental handicap disorder with marfanoid features, while in the autosomal dominant Shprintzen-Goldberg syndrome, craniosynostosis is also evident. Some Shprintzen-Goldberg cases have fibrillin 1 mutations, so this might be regarded as an unusual variant of Marfan syndrome.
Can arachnodactyly be seen on the thumb and fifth finger?
Thumb and fifth finger can overlap around wrist. Both signs must be present to diagnose arachnodactyly according to the Ghent Marfan diagnostic criteria. In the ocular system, only lens dislocation is regarded as a major criterion, other less specific findings such as myopia being regarded as eye involvement.
What is Marfan syndrome?
Marfan syndrome is caused by mutations in the FBN1 gene. FBN1 mutations are associated with a broad continuum of physical features ranging from isolated features of Marfan syndrome to a severe and rapidly progressive form in newborns.
How often does Marfan syndrome occur?
It is an autosomal dominant condition occurring once in every 10,000 to 20,000 individuals .
What is the index case for Marfan syndrome?
To establish the diagnosis in a relative of a patient known to have Marfan Syndrome (index case ) requires the presence of a major criterion in the family history and one major criterion in an organ system with involvement of a second organ system.
What is FBN1 mutation?
FBN1 mutations are associated with a broad continuum of physical features ranging from isolated features of Marfan syndrome to a severe and rapidly progressive form in newborns. What is Marfan syndrome? Marfan syndrome is one of the most common inherited disorders of connective tissue.
What is the most common symptom of Marfan syndrome?
The most common symptom of Marfan syndrome is myopia (nearsightedness from the increased curve of the retina due to connective tissue changes in the globe of the eye). About 60 percent of individuals who have Marfan syndrome have lens displacement from the center of the pupil (ectopia lentis).
What is the risk of a dilated aorta?
They include dilated aorta just as it leaves the heart (at the level of the sinuses of Valsalva), mitral valve prolapse, tricuspid valve prolapse, enlargement of the proximal pulmonary artery, and a high risk for aortic tear and rupture (aortic dissection).
What is the chance of having a Marfan's syndrome?
In this family situation, the chance for future siblings (brothers and sisters of the child with Marfan syndrome) to be born with Marfan syndrome is less than 50 percent. But the risk is still greater than the general population risk of 1 in 10,000.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
What Is Marfan Syndrome?
- While there is no cure for Marfan syndrome, treatment focuses on preventing the various complications of the disease. To accomplish this, you'll need to be checked regularly for signs that the damage caused by the disease is progressing. In the past, people who had Marfan syndrome often died young. With regular monitoring and modern treatment, most...
What Causes Marfan Syndrome?
- You may need to avoid competitive sports and certain recreational activities if you're at increased risk of aortic dissection or rupture. Increases in blood pressure, common in activities such as weightlifting, place extra strain on the aorta. Less intense activities — such as brisk walking, bowling, doubles tennis or golf — are generally safer.
How Is Marfan Syndrome Diagnosed?
- Living with a genetic disorder can be extremely difficult for both adults and children. Adults may wonder how the disease will affect their careers, their relationships and their sense of themselves. And they may worry about passing the defective gene to their children. But Marfan syndrome can be even harder on young people, especially because the often-inherent self-consciousness of ch…
How Is Marfan Syndrome Treated?
- Marfan syndrome can affect many different parts of your body, so you may need to see a variety of medical specialists, such as: 1. A cardiologist, a doctor who specializes in heart and blood vessel disorders 2. An ophthalmologist, a doctor who specializes in eye disorders 3. An orthopedist, a doctor who specializes in structural problems of the skeleton 4. A geneticist, a do…
Additional Resources
- Marfan syndrome is a genetic condition that affects connective tissue, which provides support for the body and organs. Marfan syndrome can damage the blood vessels, heart, eyes, skin, lungs, and the bones of the hips, spine, feet, and rib cage. Some complications of Marfan syndrome can be treated or prevented, including heart disease, bone deformit...
References
- Marfan syndrome is rare, happening in about 1 in 5,000 people.1 Marfan syndrome is caused by a mutation in a gene called FBN1. The mutation limits the body’s ability to make proteins needed to build connective tissue.1, One in four people with Marfan syndrome develops the condition for unknown reasons.1 A person with Marfan syndrome has a 1 in 2 chance of passing it on to their …