
Medication
Sep 05, 2018 · Most healthy people recover from toxoplasmosis without treatment. Persons who are ill can be treated with a combination of drugs such as pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine, plus folinic acid. Pregnant women, newborns, and infants Pregnant women, newborns, and infants can be treated, although the parasite is not eliminated completely.
Nutrition
9 rows · Apr 01, 2019 · There are two time points for the introduction of specific anti-T. gondii treatment: 1) prenatal ...
How do you get rid of a Toxoplasma gondii infection?
External external icon. Freeze meat* for several days at sub-zero (0° F) temperatures before cooking to greatly reduce chance of infection. *Freezing does not reliably kill other parasites that may be found in meat (like certain species of Trichinella) or harmful bacteria.
Can Toxoplasma gondii be removed from the human body?
Treatment is required for: Acute infection Active lesions caused by T gondii (for example, in the skin or eye) Congenital infection Toxoplasmosis in patients with impaired immunity. The most effective treatment is sulfadiazine in combination with pyrimethamine. For patients allergic to sulfonamides, clindamycin is used.
Do Toxoplasma gondii really make people Love Cats?
Sep 28, 2015 · Toxoplasma-gondii remedy is a homeopathic dilution produced from the cysts of the parasite. In a blind, controlled, randomized study published in the European Journal of Integrative Medicine, researchers found that the homeopathic remedy reduced the number of bradyzoites and cysts in the brains of toxoplasma gondii-infected mice. Other homeopathic …
How many people are affected by toxoplasmosis?
This test looks for a parasite that can infect an unborn child. A pregnant woman can pick up this parasite by eating undercooked meat, drinking contaminated water, or handling cat feces.
What is the best treatment for toxoplasmosis?
Pyrimethamine, considered the most effective drug against toxoplasmosis, is a standard component of therapy. Pyrimethamine is a folic acid antagonist and can cause dose-related suppression of the bone marrow, which is mitigated by concurrent administration of folinic acid (leucovorin).
What antibiotics treat toxoplasmosis?
Sulfadiazine. This antibiotic is used with pyrimethamine to treat toxoplasmosis.Oct 13, 2020
Does Toxoplasma gondii go away?
For most people, toxoplasmosis will go away on its own, Dr. Edwards says. Eventually, after a few weeks or months, your immune system will fight off the disease. Those requiring treatment will be put on medication that can take weeks or even months to clear the infection, Edwards says.
Can toxoplasmosis be cured?
Many congenital toxoplasmosis cases can be cured with medications. Even children who had severe infections at birth may never show signs of severe long-term damage if they are diagnosed and treated early. Delays in diagnosis and treatment can contribute to a poor prognosis.May 10, 2021
Can cotrimoxazole treat toxoplasmosis?
Abstract. Cotrimoxazole (trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole [TMP-SMX]) is an alternative treatment for toxoplasmic encephalitis because it is inexpensive, well-tolerated, and as effective as pyrimethamine-sulfadiazine, which is the first-line drug regimen).
How do you know if you are infected with Toxoplasma gondii?
Symptoms of toxoplasmosisSwollen lymph glands, especially around the neck.Muscle aches and pains.Headache.Fever.Generally feeling unwell.Inflammation of the lungs.Inflammation of the heart muscle.Inflammation of the eye, for example, the retina (at the back of the eye).
Is there a vaccine for toxoplasmosis?
Congenital toxoplasmosis has a high impact on human disease worldwide, inducing serious consequences from fetus to adulthood. Despite this, there are currently no human vaccines available to prevent this infection.Feb 15, 2021
How do you get rid of parasites in the brain?
The infection is treated with albendazole or praziquantel (drugs used to treat parasitic worm infections, called antihelminthic drugs). However, if a person has many cysts, antihelminthic drugs may kill many organisms, causing the brain to swell significantly.
What happens if toxoplasmosis is not treated?
Untreated, these infections can lead to blindness. But if your immune system is weakened, especially as a result of HIV / AIDS , toxoplasmosis can lead to seizures and life-threatening illnesses such as encephalitis — a serious brain infection. In people with AIDS , untreated encephalitis from toxoplasmosis is fatal.Oct 13, 2020
How does Toxoplasma gondii affect the brain?
A research group from the University of Leeds has shown that infection by the brain parasite Toxoplasma gondii, found in 10-20 percent of the UK's population, directly affects the production of dopamine, a key chemical messenger in the brain.Nov 7, 2011
Does ivermectin treat toxoplasmosis?
(10). Our results indicated that ivermectin significantly inhibited replication of the tachyzoites of T. gondii RH strain. Therefore, the present study results may be useful for further studies in combination with other drugs and animal models to develop a better treatment model for toxoplasmosis in humans.
How long does it take to recover from toxoplasmosis?
In an otherwise healthy person who is not pregnant, treatment usually is not needed. If symptoms occur, they typically go away within a few weeks to months. For pregnant women or persons who have weakened immune systems, medications are available to treat toxoplasmosis.
How Do People Get Toxoplasmosis?
A Toxoplasma infection occurs by: 1. Eating undercooked, contaminated meat (especially pork, lamb, and venison). 2. Accidental ingestion of underco...
What Are The Signs and Symptoms of Toxoplasmosis?
Symptoms of the infection vary. 1. Most people who become infected with Toxoplasma gondii are not aware of it. 2. Some people who have toxoplasmosi...
Who Is at Risk For Developing Severe Toxoplasmosis?
People who are most likely to develop severe toxoplasmosis include: 1. Infants born to mothers who are newly infected with Toxoplasma gondii during...
What Should I Do If I Think I Am at Risk For Severe Toxoplasmosis?
If you are planning to become pregnant, your health care provider may test you for Toxoplasma gondii. If the test is positive it means you have alr...
What Should I Do If I Think I May Have Toxoplasmosis?
If you suspect that you may have toxoplasmosis, talk to your health care provider. Your provider may order one or more varieties of blood tests spe...
What Is The Treatment For Toxoplasmosis?
Once a diagnosis of toxoplasmosis is confirmed, you and your health care provider can discuss whether treatment is necessary. In an otherwise healt...
How Can I Prevent Toxoplasmosis?
There are several general sanitation and food safety steps you can take to reduce your chances of becoming infected with Toxoplasma gondii.Cook foo...
If I Am at Risk, Can I Keep My Cat?
Yes, you may keep your cat if you are a person at risk for a severe infection (e.g., you have a weakened immune system or are pregnant); however, t...
Once Infected With Toxoplasma Is My Cat Always Able to Spread The Infection to Me?
No, cats only spread Toxoplasma in their feces for a few weeks following infection with the parasite. Like humans, cats rarely have symptoms when i...
How do you know if you have toxoplasma gondii?
Some people who have toxoplasmosis may feel as if they have the “flu” with swollen lymph glands or muscle aches and pains that may last for a month or more.
How long does it take for toxoplasmosis to go away?
In an otherwise healthy person who is not pregnant, treatment usually is not needed. If symptoms occur, they typically go away within a few weeks to months. For pregnant women or persons who have weakened immune systems, medications are available to treat toxoplasmosis.
What is the cause of toxoplasmosis?
What is toxoplasmosis? Toxoplasmosis is an infection caused by a single-celled parasite called Toxoplasma gondii. While the parasite is found throughout the world, more than 40 million people in the United States may be infected with the Toxoplasma parasite.
What are the symptoms of ocular toxoplasmosis?
Signs and symptoms of ocular toxoplasmosis can include reduced vision, blurred vision, pain (often with bright light), redness of the eye, and sometimes tearing. Ophthalmologists sometimes prescribe medicine to treat active disease.
Can you keep a cat if you have a weakened immune system?
Yes, you may keep your cat if you are a person at risk for a severe infection (e.g., you have a weakened immune system or are pregnant); however, there are several safety precautions you should take to avoid being exposed to Toxoplasma gondii, including the following:
What does it mean if a test is positive?
If the test is positive it means you have already been infected sometime in your life. There usually is little need to worry about passing the infection to your baby. If the test is negative, take necessary precautions to avoid infection (See below).
What to do if your immune system is weakened?
If you have a weakened immune system, ask your doctor about having your blood tested for Toxoplasma. If your test is positive, your doctor can tell you if and when you need to take medicine to prevent the infection from reactivating. If your test is negative, it means you need to take precautions to avoid infection.
What is the cause of toxoplasmosis?
Toxoplasmosis is a worldwide infection caused by the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. T gondii infects up to one-third of the world's population. Prevalence of the infection varies with the age of the population studied and by geographic location. The likelihood of having antibodies to T gondii present in the blood (indicating past infection) ...
What is the best treatment for a congenital infection?
Congenital infection. Toxoplasmosis in patients with impaired immunity. The most effective treatment is sulfadiazine in combination with pyrimethamine. For patients allergic to sulfonamides, clindamycin is used.
Can chorioretinitis cause scarring?
Toxoplasmosis eye disease (chorioretinitis) can result from congenital or acquired (e.g. foodborne or zoonotic) T gondii infection. Eye infection leads to acute inflammation of the retina, which resolves leaving scarring. The eye disease can reactivate months or years later, each time causing more damage to the retina.
What are telangiectatic macules?
Lesions may be telangiectatic macules (small, flat, dilated blood vessels ), papules, or vesicles (small fluid-filled bumps). Rarely, patients present with erythroderma ( widespread reddening of the skin) and scleroderma (skin thickens and hardens); this condition may respond to local administration of corticosteroids.
How can humans get infected?
Humans can become infected via the following routes of transmission: Foodborne transmission is the most common — ingestion of the parasitic cysts in undercooked, contaminated meat (especially pork, lamb, and venison) or poor kitchen hygiene when handling raw contaminated meat.
Can T gondii cause chorioretinitis?
In healthy individuals, infection with T gondii goes unnoticed. Some people (around 10%) experience 'flu-like symptoms with enlarged lymph nodes, and in rare instances chorioretinitis ( inflammation in the eye) can occur. Very rarely, myocarditis, pneumonitis, or encephalitis (inflammation of the heart, lungs or brain respectively) may occur.
Is toxoplasmosis a life threatening disease?
In patients with impaired immunity ( for example, patients with AIDS) toxoplasmosis can be life-threatening. The illness is usually caused by reactivation of chronic infection. Encephalitis and pneumonitis is common in these patients.
How does Toxoplasma gondii work?
As compared to many other parasites, Toxoplasma gondii are capable of attaching and penetrating many different types of cells.
What is the life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii?
As is the case with a number of other parasites, the life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii is dependent on definitive and intermediate hosts. For Toxoplasma, specifically, felids (domestic and wild cats) serve as definitive hosts while a wide variety of domestic and wild animals ...
What is the best medication for a relapse?
Chronic maintenance therapy (used to prevent relapses) include: 1 Atovaquone 2 Atovaquone, and sulfadiazine 3 Clindamycin, pyrimethamine, and leucovorin 4 Atovaquone, pyrimethamine, and leucovorin
Is Toxoplasma gondii a parasite?
Because of the unusually wide spectrum of animals (warm-blooded animals) that serve as intermediate hosts, Toxoplasma gondii has been shown to be one of the most common parasites in animals and human beings across the world. Although only a single species in the genus (Toxoplasma) has been identified so far, the different strains ...
What are the similarities between sporozoites and tachyzoites?
Sporozoites. At the ultrastructure level, sporozoites of Toxoplasma gondii have many similarities to tachyzoites. Compared to tachyzoites, however, sporozoites contain a high abundance of granules in the micronemes, rhopties, and amylopectin. With regards to size, sporozoites are also similar to tachyzoites, measuring about 2um in width ...
Does Toxoplasma gondii reproduce sexually?
Sexual Reproduction. As compared to asexual reproduction, sexual reproduction of Toxoplasma gondii occurs within the definitive host. This cycle can be said to start when the host (wild or domestic cat) ingests oocysts/tissue infected with bradyzoite cysts.
Is toxoplasmosis asymptomatic?
For the most part, toxoplasmosis (the infection caused by Toxoplasma gondii) remains asymptomatic in healthy human beings. This is largely due to the fact that the body’s' immune system is able to control the parasite thus preventing the infection from getting out of control.
How to prevent toxoplasma?
To help prevent toxoplasma infection, it is essential to thoroughly wash your hands after handling cat litter, soil, or raw meat. Avoid eating food possibly contaminated with cat feces. It is also extremely important to cook food at safe temperatures. Make sure to use a food thermometer to measure your cooked meat’s internal temperature. The following are some prevention guidelines against toxoplasmosis: 1 Cook whole cuts of meat at a minimum of 145 degrees Fahrenheit, and allow for three minutes of rest time before consumption. Ground meat should be cooked at 160 degrees Fahrenheit, and no rest time is required. 2 The cooking temperature exception is poultry, which should be cooked at least 165 degrees Fahrenheit. Three minutes of rest time is also required. 3 Chance of infection is significantly reduced from freezing meat for several days at sub-zero temperatures. 4 Wash or peel fruits and vegetables thoroughly before consumption. 5 After coming in contact with raw poultry, meat, seafood, or unwashed vegetables and fruit, always wash counters, utensils, dishes, and cutting boards. 6 Oysters, mussels, or clams should not be eaten raw, since they may be contaminated with Toxoplasma from seawater. 7 Always wear gloves when gardening or contacting soil or sand. Afterwards, hands should be washed with warm water and soap.
What are the symptoms of toxoplasmosis?
Most people with a strong immune system are often unaware they have contracted a toxoplasma infection; however, others may develop symptoms and signs that resemble the flu such as fatigue, fever, headache, body aches, and swollen lymph nodes.
What is Daraprim used for?
Daraprim (pyrimethamine) is the standard drug used to treat a life-threatening parasitic infection called toxoplasmosis. It has been on the market since 1953. In August of this year, Turing Pharmaceuticals acquired the drug. Shortly after, the price of the drug had skyrocketed from $13.50 a tablet to $750.00 per pill.
What is the best food for parasites?
Overall, the diet should contain high amounts of vegetables, some fruit, and adequate meat intake. Here are some natural remedies for parasites like toxoplasma: 1. Black walnut: Black walnut (Juglans nigra) is considered an effective herb against toxoplasmosis. It contains natural tannins that fight fungus, yeast, and parasites.
What is a parasite?
A parasite is also a person that exploits others. There are over 1,000 types of parasites that can live within the human body. On the other hand, someone with a parasitic nature can also be defined as an opportunist that takes advantage of others at the right time.
Can cats get Toxoplasma gondii?
The disease can occur from drinking unclean water, eating undercooked meat, cooking with contaminated boards and knives, and making contact with infected cat feces. Toxoplasma gondii is a common parasitic disease that can affect nearly all warm-blooded animals and humans—but cats are the primary living host.
What are the symptoms of AIDS?
Symptoms and signs related to a severe infection include poor coordination, confusion, headaches, seizures, or lung problems that resemble tuberculosis or a common infection in people with AIDS called pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia.
What is the best treatment for toxoplasmosis?
Treatment is recommended for people with serious health problems, such as people with HIV whose CD4 counts are under 200 cells/mm 3. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole is the drug of choice to prevent toxoplasmosis, but not for treating active disease.
What is the disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii?
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis usually cause no obvious symptoms in adults. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or months of mild, flu-like illness such as muscle aches and tender lymph nodes.
How is toxoplasmosis spread?
Toxoplasmosis is usually spread by eating poorly cooked food that contains cysts, exposure to infected cat feces, and from an infected mother to her baby during pregnancy . Rarely, the disease may be spread by blood transfusion. It is not otherwise spread between people.
Where are trophozoites found?
The toxoplasmic trophozoites causing acute toxoplasmosis are referred to as tachyzoites, and are typically found in various tissues and body fluids, but rarely in blood or cerebrospinal fluid. Swollen lymph nodes are commonly found in the neck or under the chin, followed by the armpits and the groin.
What is the condition of a baby with a positive antibody?
Congenital toxoplasmosis is a specific form of toxoplasmosis in which an unborn fetus is infected via the placenta. Congenital toxoplasmosis is associated with fetal death and miscarriage, and in infants, it is associated with neurologic deficits, neurocognitive deficits, and chorioretinitis. A positive antibody titer indicates previous exposure and immunity, and largely ensures the unborn fetus' safety. A simple blood draw at the first prenatal doctor visit can determine whether or not a woman has had previous exposure and therefore whether or not she is at risk. If a woman receives her first exposure to T. gondii while pregnant, the fetus is at particular risk.
Can you get T. gondii without knowing?
Due to the absence of obvious symptoms, hosts easily become infected with T. gondii and develop toxoplasmosis without knowing it. Although mild, flu-like symptoms occasionally occur during the first few weeks following exposure, infection with T. gondii produces no readily observable symptoms in healthy human adults. In most immunocompetent people, the infection enters a latent phase, during which only bradyzoites ( in tissue cysts) are present; these tissue cysts and even lesions can occur in the retinas, alveolar lining of the lungs (where an acute infection may mimic a Pneumocystis jirovecii infection), heart, skeletal muscle, and the central nervous system (CNS), including the brain. Cysts form in the CNS ( brain tissue) upon infection with T. gondii and persist for the lifetime of the host. Most infants who are infected while in the womb have no symptoms at birth, but may develop symptoms later in life.
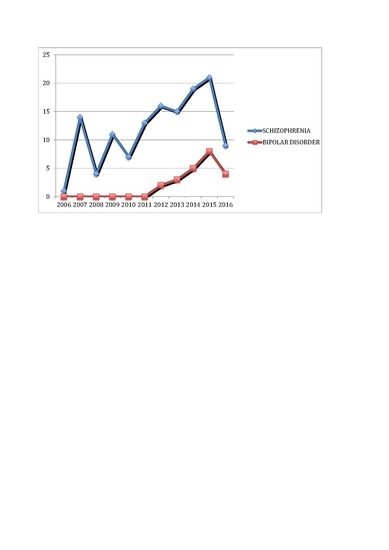
Does T. gondii cause schizophrenia?
Some evidence links T. gondii to schizophrenia. Two 2012 meta-analyses found that the rates of antibodies to T. gondii in people with schizophrenia were 2.7 times higher than in controls. T. gondii antibody positivity was therefore considered an intermediate risk factor in relation to other known risk factors. Cautions noted include that the antibody tests do not detect toxoplasmosis directly, most people with schizophrenia do not have antibodies for toxoplasmosis, and publication bias might exist. While the majority of these studies tested people already diagnosed with schizophrenia for T. gondii antibodies, associations between T. gondii and schizophrenia have been found prior to the onset of schizophrenia symptoms. Sex differences in the age of schizophrenia onset may be explained in part by a second peak of T. gondii infection incidence during ages 25–30 in females only. Although a mechanism supporting the association between schizophrenia and T. gondii infection is unclear, studies have investigated a molecular basis of this correlation. Antipsychotic drugs used in schizophrenia appear to inhibit the replication of T. gondii tachyzoites in cell culture. Supposing a causal link exists between T. gondii and schizophrenia, studies have yet to determine why only some individuals with latent toxoplasmosis develop schizophrenia; some plausible explanations include differing genetic susceptibility, parasite strain differences, and differences in the route of the acquired T. gondii infection.

Definition
Classification of The Genus Toxoplasma
Life Cycle and Characteristics
Sexual Reproduction
Specialist to consult
Asexual Reproduction
Attachment and Invasion
- · Order - Eucoccidiorida- consists of spore-forming parasites of the class Conoidasida · Family - Sarcocystidae- is a family of Apicomplexa that has been associated with many diseases in human beings · Genus - Toxoplasma · Species - Toxoplasma gondii
Characteristics and Adaptations
- As is the case with a number of other parasites, the life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii is dependent on definitive and intermediate hosts. For Toxoplasma, specifically, felids (domestic and wild cats) serve as definitive hosts while a wide variety of domestic and wild animals (including birds) serve as intermediate hosts. Because of the unusually wide spectrum of animals (warm-blooded anim…
Tachyzoites
- As compared to asexual reproduction, sexual reproduction of Toxoplasma gondii occurs within the definitive host. This cycle can be said to start when the host (wild or domestic cat) ingests oocysts/tissue infected with bradyzoite cysts. Once they are ingested, the cyst wall is dissolved by proteolytic enzymes in the stomach and small intestine to release bradyzoites. The free bradyzo…
Bradyzoites
- Whereas sexual reproduction cycle only involves the definitive host (wild/domestic host), asexual reproduction requires both the definitive and intermediate hosts. To describe this type of reproduction, we can assume that it starts with the release of the oocysts into the environment. Typically, the oocysts released into the environment along with fecal matter (by the definitive ho…
Sporozoites
- Before penetrating the cell, the parasite first has to attach to the surface of the host cell. In order to do this, the parasite relies on receptor-ligand interactions to overcome the repulsive force caused by the net negative charge of both the parasite and host cell membrane. As compared to many other parasites, Toxoplasma gondii are capable of attaching and penetrating many differe…