Monoclonal antibody therapy
Monoclonal antibody therapy is a form of immunotherapy that uses monoclonal antibodies (mAb) to bind monospecifically to certain cells or proteins. This may then stimulate the patient's immune system to attack those cells. Alternatively, in radioimmunotherapy a radioactive dose localiz…
Full Answer
What are the dangers of monoclonal antibodies?
Treatment with COVID-19 monoclonal antibodies is done through a one-time intravenous (IV) infusion. Another option for COVID-19 therapy is an antiviral called Remdesivir. Remdesivir is approved by the FDA and helps reduce the effects of COVID-19. Remdesivir is given by an intravenous (IV) infusion over three (3) consecutive days.
How effective is the monoclonal treatment?
B cells are a type of white blood cell. Other monoclonal antibodies bring T cells close to cancer cells, helping the immune cells kill the cancer cells. An example is blinatumomab (Blincyto®), which binds to both CD19, a protein found on the surface of leukemia cells, and CD3, a protein on the surface of T cells.
Can monoclonal antibodies kill you?
Monoclonal antibodies (also called moAbs or mAbs) are proteins made in laboratories that act like proteins called antibodies in our bodies. Antibodies are parts of your immune system. They seek out the antigens (foreign materials) and stick to them in order to destroy them. Laboratory-made monoclonal antibodies help stimulate your own immune ...
How often can you get monoclonal antibodies?
· Monoclonal antibody therapy is a way of treating COVID-19 for people who have tested positive, have had mild symptoms for seven days or less, and are at high risk for …
What is a monoclonal antibody?
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-produced molecules that act as substitute antibodies that can restore, enhance or mimic the immune system's attack on cells.
What is the difference between monoclonal antibodies and the COVID-19 vaccine?
COVID-19 vaccines help stimulate and prepare a person's immune system to respond if they are exposed to the virus. However, monoclonal antibodies boost the immune system only after a person is already sick, speeding up their immune response to prevent COVID-19 from getting worse.
How do monoclonal antibodies work against COVID-19?
Monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 may block the virus that causes COVID-19 from attaching to human cells, making it more difficult for the virus to reproduce and cause harm. Monoclonal antibodies may also neutralize a virus.
How many types of monoclonal antibody COVID-19 treatments are there in the US?
In the United States, there are three anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody treatments with FDA Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the treatment of COVID-19: bamlanivimab plus etesevimab, casirivimab plus imdevimab,, and sotrovimab.
Should you still get the COVID-19 vaccine if you were treated with monoclonal antibodies?
If you were treated for COVID-19 with monoclonal antibodies or convalescent plasma, there is no need to delay getting a COVID-19 vaccine.
Who is at higher risk of getting blood clots from the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine?
They are also more likely to occur in women who are pregnant or on oral contraceptives, or in people who have hereditary disorders that predispose them to blood clotting. As mentioned above, the clotting condition associated with the J&J vaccine is called thrombosis with thrombocytopenia (TTS).
How long do COVID-19 antibodies last?
At this time, it is unknown for how long antibodies persist following infection and if the presence of antibodies confers protective immunity.
Why antibody testing Is not currently recommended to assess immunity after COVID-19 vaccination?
Currently authorized SARS-CoV-2 antibody tests have not been evaluated to assess the level of protection provided by an immune response to COVID-19 vaccination. If antibody test results are interpreted incorrectly, there is a potential risk that people may take fewer precautions against SARS-CoV-2 exposure.
Can I get COVID-19 again after having the vaccine?
Getting COVID-19 after you've been vaccinated or recovered is still possible. But having some immunity -- whether from infection or vaccination -- really drops the odds of this happening to you.
How many types of COVID-19 vaccines are available in the US?
Three COVID-19 vaccines are authorized or approved for use in the United States to prevent COVID-19. Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna (COVID-19 mRNA vaccines) are preferred. You may get Johnson & Johnson's Janssen COVID-19 vaccine in some situations.
Are there different COVID-19 vaccine boosters?
The FDA has authorized three vaccine boosters — Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna and Janssen-Johnson & Johnson — and determined that it is safe to get a COVID-19 vaccine booster or additional dose that is a different brand than your initial dose or doses.
What antiviral drugs are available for treatment of COVID-19?
Remdesivir is the only drug that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of COVID-19. Ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid), molnupiravir, and certain anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have received Emergency Use Authorizations from the FDA for the treatment of COVID-19.
How do monoclonal antibodies work against cancer?
Monoclonal antibodies are immune system proteins that are created in the lab. Antibodies are produced naturally by your body and help the immune sy...
Which cancers are treated with monoclonal antibodies?
Many monoclonal antibodies have been approved to treat a wide variety of cancers. To learn about specific treatments for your cancer, see the PDQ®...
What are the side effects of monoclonal antibodies?
Monoclonal antibodies can cause side effects, which can differ from person to person. The ones you may have and how they make you feel will depend...
What is monoclonal antibody?
Monoclonal antibodies are immune system proteins that are created in the lab. Antibodies are produced naturally by your body and help the immune system recognize germs that cause disease, such as bacteria and viruses, and mark them for destruction.
Why are monoclonal antibodies used in immunotherapy?
Some monoclonal antibodies are also immunotherapy because they help turn the immune system against cancer. For example, some monoclonal antibodies mark cancer cells so that the immune system will better recognize and destroy them.
Can monoclonal antibodies cause side effects?
Monoclonal antibodies can cause side effects, which can differ from person to person. The ones you may have and how they make you feel will depend on many factors, such as how healthy you are before treatment, your type of cancer, how advanced it is, the type of monoclonal antibody you are receiving, and the dose.
Why do some antibodies mark cancer cells?
Some monoclonal antibodies mark cancer cells so that the immune system will better recognize and destroy them.
Can monoclonal antibodies cause cytokine release syndrome?
Cytokine release syndrome can sometimes occur with monoclonal antibodies, but it is often mild. Cytokines are immune substances that have many different functions in the body, and a sudden increase in their levels can cause:
Overview
Monoclonal antibodies (also called moAbs or mAbs) are proteins made in laboratories that act like proteins called antibodies in our bodies. Antibodies are parts of your immune system. They seek out the antigens (foreign materials) and stick to them in order to destroy them.
Procedure Details
In most cases, monoclonal antibodies are given mostly as intravenous (IV) solution injected right into your vein (sometimes referred to as an infusion). They’re often given in an infusion center where there are several people getting treatment at one time.
Recovery and Outlook
Infusion times can vary. As an example, though, monoclonal antibody treatment for COVID-19 under Emergency Use Authorization took about an hour for infusion and then another hour or so to watch for any reaction to the infusion.
When to Call the Doctor
If you’ve had a monoclonal antibody treatment, and you’re having an expected reaction, call your healthcare provider or go to an emergency room.
What is the purpose of monoclonal antibody therapy?
The goal of this therapy is to help prevent hospitalizations, reduce viral loads, and lessen symptom severity. The FDA has authorized the emergency use of monoclonal antibody therapy for the treatment of COVID-19 under an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for people 12 years of age or older.
Do you have antibodies to SARS?
However, if you haven’t received the COVID-19 vaccine or had a previous COVID-19 infection, your body will not have antibodies designed to recognize a new virus like SARS-CoV-2. “ Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-made proteins that mimic the body’s immune system to fight off COVID-19 infection ,” Spivak says. These antibodies are given to people directly through an intravenous (IV) infusion.
Is monoclonal antibody therapy effective?
Given that COVID-19 vaccination provides strong protection against severe disease and need for hospitalization, monoclonal antibody therapy is an option for high-risk patients with COVID-19 who are either not previously fully vaccinated, who are severely immunocompromised, or who remain at high risk for hospitalization or death, despite vaccination. Treatment is not effective for people who are already hospitalized or severely ill with COVID-19. Monoclonal antibodies should not be considered a replacement for vaccination.
Which monoclonal antibody is used for autoimmune diseases?
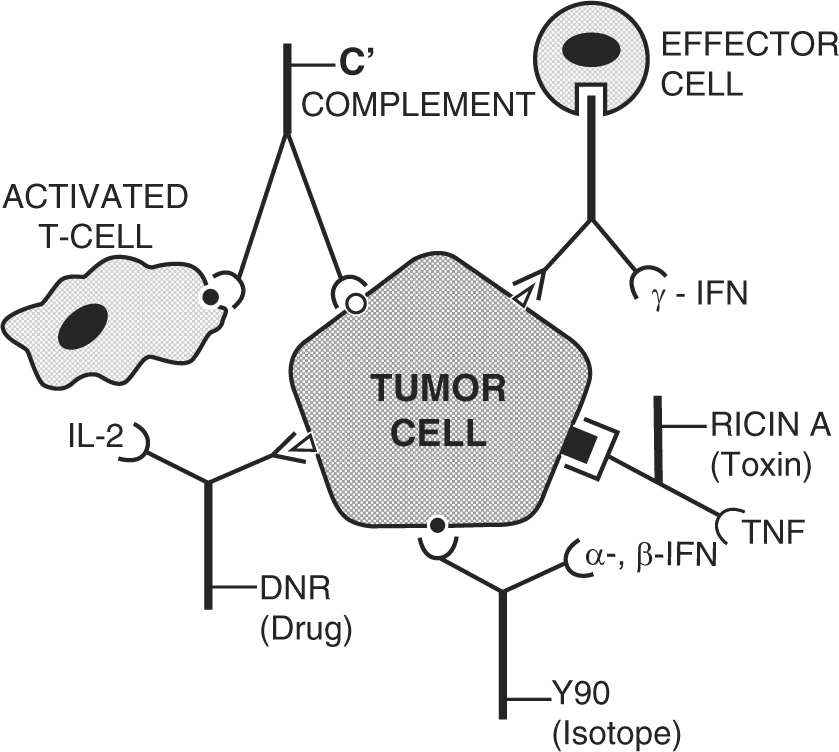
Monoclonal antibodies used for autoimmune diseases include infliximab and adalimumab, which are effective in rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis by their ability to bind to and inhibit TNF-α. Basiliximab and daclizumab inhibit IL-2 on activated T cells and thereby help preventing acute rejection of kidney transplants. Omalizumab inhibits human immunoglobulin E (IgE) and is useful in moderate-to-severe allergic asthma .
How can monoclonal antibodies be acquired?
Monoclonal antibodies can be acquired in the immune system via passive immunity or active immunity.
Is murine antibody a human antibody?
Murine antibodies in vitro are thereby transformed into fully human antibodies. The heavy and light chains of human IgG proteins are expressed in structural polymorphic (allotypic) forms. Human IgG allotype is one of the many factors that can contribute to immunogenicity.
What are the four major antibody types?
Four major antibody types that have been developed are murine, chimeric, humanised and human. Antibodies of each type are distinguished by suffixes on their name.
When was immunotherapy first used?
Immunotherapy developed in the 1970s following the discovery of the structure of antibodies and the development of hybridoma technology, which provided the first reliable source of monoclonal antibodies. These advances allowed for the specific targeting of tumors both in vitro and in vivo.
What does MAB stand for in cancer?
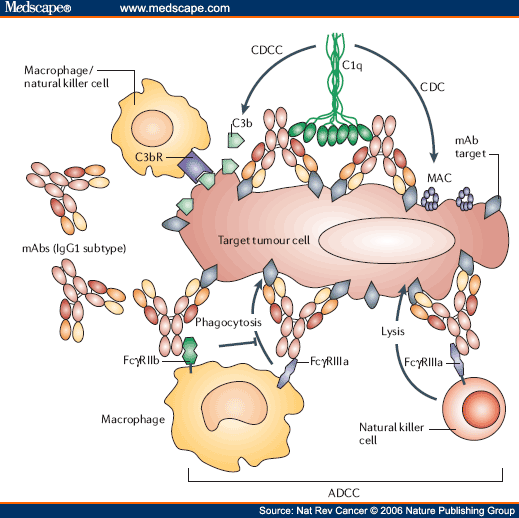
ADEPT: antibody directed enzyme prodrug therapy; ADCC: antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; CDC: complement-dependent cytotoxicity; MAb, monoclonal antibody; scFv, single-chain Fv fragment. Immunotherapy developed in the 1970s following the discovery of the structure of antibodies and the development ...
Can monoclonal antibodies target tumor cells?
Some such tumor antigens are inappropriate for the cell type or its environment. Monoclonal antibodies can target tumor cells or abnormal cells in the body that are recognized as body cells, but are debilitating to one's health.
How are monoclonal antibodies administered?
Monoclonal antibodies are administered through a vein (intravenously). How often you undergo monoclonal antibody treatment depends on your cancer and the drug you're receiving. Some monoclonal antibody drugs may be used in combination with other treatments, such as chemotherapy or hormone therapy.
Why is monoclonal antibody used in cancer treatment?
When a monoclonal antibody is combined with a small radioactive particle, it transports the radiation treatment directly to cancer cells and may minimize the effect of radiation on healthy cells.
Why do you need monoclonal antibodies for chemotherapy?
Similarly, some monoclonal antibodies are combined with a chemotherapy drug in order to deliver the treatment directly to the cancer cells while avoiding healthy cells.
What antibodies bind to cancer cells?
Monoclonal antibodies that bind to these immune system cells give the cancer-fighting cells an opportunity to work with less inhibition. Directly attacking cancer cells. Certain monoclonal antibodies may attack the cell more directly, even though they were designed for another purpose.
What is the best treatment for cancer?
Preventing blood vessel growth. In order for a cancerous tumor to grow and survive, it needs a blood supply. Some monoclonal antibody drugs block protein-cell interactions necessary for the development of new blood vessels. Blocking immune system inhibitors.
Why do immune cells depend on antibodies?
Some immune system cells depend on antibodies to locate the target of an attack. Cancer cells that are coated in monoclonal antibodies may be more easily detected and targeted for destruction. Triggering cell-membrane destruction.
What is the role of monoclonal antibodies in the immune system?
Monoclonal antibodies are designed to function in different ways. A particular drug may actually function by more than one means. The role of the drug in helping the immune system may include the following: Flagging cancer cells. Some immune system cells depend on antibodies to locate the target of an attack.
WHAT IS A MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY?
Your body naturally makes antibodies to fight infection. However, your body may not have antibodies designed to recognize a novel (or new) virus like SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
How Can I Get Monoclonal Antibodies?
To receive a mAb you should be referred for treatment by your healthcare professional and directed to available infusion locations. If you do not have a healthcare provider, call the Combat COVID Monoclonal Antibodies Call Center at 1-877-332-6585 to find out who to talk with about your symptoms and treatment.
WHAT IF I DO NOT QUALIFY FOR MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY TREATMENT?
Your healthcare professional may decide you do not qualify for mAb treatment. There could be several reasons for this. You may not meet all eligibility criteria or you may have an underlying health condition that disqualifies you for mAb treatment.
WHAT CAN I EXPECT FROM TREATMENT (INFUSION)?
The mAb treatment is usually offered at an infusion center because the treatment is given through an intravenous (IV) infusion or shots. Depending on the mAb treatment you receive, the whole process takes about 1-3 hours, depending on the treatment..
CAN MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY TREATMENT MAKE ME SICK?
Antibody treatments do not contain any live SARS-CoV-2, so there is no risk you will get COVID-19 from mAb treatment. However, the antibody treatment may have side effects:
What is monoclonal antibody therapy?
The use of monoclonal antibodies to treat diseases is called immunotherapy therapy because each type of monoclonal antibody will target a specific targeted antigen in the body. Uses for monoclonal antibodies include: Cancer. Rheumatoid arthritis.
Why is monoclonal antibody therapy called immunotherapy?
The use of monoclonal antibodies to treat diseases is called immunotherapy therapy because each type of monoclonal antibody will target a specific targeted antigen in the body.
What are the conditions that require monoclonal antibodies?
Systemic lupus erythematosus. Crohn's disease. Ulcerative colitis. Psoriasis. Transplant rejection, and several more conditions. In these conditions the monoclonal antibody targets and interferes with the action of a chemical or receptor that is involved in the development of the condition that is being treated.
Is Regeneron a monoclonal antibody?
As of October 2020 , drug companies Regeneron and Eli Lilly were conducting clinical trials on two monoclonal antibody therapy cocktails for bridge treatment of the coronavirus disease COVID-19. Early results are promising, but there is far from enough data to show whether monoclonal antibody therapy is broadly useful against ...
What is the difference between monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies?
This causes the immune cells of the mice to produce the desired human antibody. The term monoclonal antibody means that the man-made antibody is synthesized from cloned immune cells, and the identical monoclonal antibody produced binds to one type of antigen. Polyclonal antibodies are synthesized from different immune cells and ...
How are man made antibodies produced?
Man-made antibodies are produced by introducing human genes that produce antibodies into mice or another suitable mammal. The mice then are vaccinated with the antigen that scientists want to produce antibodies against. This causes the immune cells of the mice to produce the desired human antibody.
Can antibodies be produced in the lab?
Antibodies are naturally produced by the immune system. However, scientists can produce antibodies in the lab that mimic the action of the immune system.
What is monoclonal antibody?
Again, monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-made antibodies that do what your body’s natural antibodies do: fight off infection. There are several antibody combinations or “cocktails,” but the one that’s most commonly used right now is a combination of two drugs called bamlanivimab and etesevimab.
How long does it take to get monoclonal antibodies?
Once you’ve been exposed to the virus, you should receive monoclonal antibodies within 10 days for them to have the most impact.
Is monoclonal antibody available?
Monoclonal antibody treatments are only available to certain patients.
Why does the body keep antibodies in reserve?
Once your body has experienced a particular infection, it keeps some antibodies in reserve so that if you’re exposed to the same infection again in the future, your body can start to fight it immediately.
What is an antibody?
In the simplest of terms, Dr. Bhimraj says, “Antibodies are basically proteins that your body makes to fight a specific infection.”
Can you get monoclonal antibodies through IV?
Monoclonal antibodies are only given intravenously (through an IV) or as a subcutaneous injection (as a shot). That means that in order to receive them, you need to be seen in a medical setting — which limits the overall availability of the treatment.
What is conjugated monoclonal antibody?
Conjugated monoclonal antibodies. Conjugated mAbs are combined with a chemotherapy drug or a radioactive particle. These mAbs are used as a homing device to take one of these substances directly to the cancer cells. The mAb circulates throughout the body until it can find and hook onto the target antigen.
Why are m onoclonal antibodies used to treat cancer?
NOTE: Some m onoclonal antibodies used to treat cancer are referred to as targeted therapy because they have a specific target on a cancer cell that they aim to find, attach to, and attack.
What is the treatment for a mAb?
Treatment with this type of antibody is sometimes known as radioimmunotherapy (RIT). The drug and radiation are delivered directly to the target cells because the mAb looks for the target, then the radiation affects the target and nearby cells to a certain extent.
What is a radiolabeled antibody?
Radiolabeled antibodies: Radiolabeled antibodies have small radioactive particles attached to them. Ibritumomab tiuxetan (Zevalin) is an example of a radiolabeled mAb. This is an antibody against the CD20 antigen, which is found on lymphocytes called B cells. The antibody delivers radioactivity directly to cancer cells.
How does mAb work?
Other naked mAbs work mainly by attaching to and blocking antigens on cancer cells (or other nearby cells) that help cancer cells grow or spread . For example, trastuzumab (Herceptin) is an antibody against the HER2 protein. Breast and stomach cancer cells sometimes have large amounts of this protein on their surface. When HER2 is activated, it helps these cells grow. Trastuzumab binds to these proteins and stops them from becoming active.
What is a naked mAb?
They work by themselves. These are the most common type of mAbs used to treat cancer. Most naked mAbs attach to antigens on cancer cells, but some work by binding to antigens on other, non-cancerous cells, or even free-floating proteins. Naked mAbs can work in different ways.
What are chimeric proteins?
Chimeric: These proteins are a combination of part mouse and part human and the names of the treatments end in -ximab. Humanized: These are made from small parts of mouse proteins attached to human proteins and the names of the treatments end in -zumab.

Overview
Monoclonal antibody therapy is a form of immunotherapy that uses monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to bind monospecifically to certain cells or proteins. The objective is that this treatment will stimulate the patient's immune system to attack those cells. Alternatively, in radioimmunotherapya radioactive dose localizes a target cell line, delivering lethal chemical doses. Antibodies have be…
Antibody structure and function
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies are large heterodimeric molecules, approximately 150 kDa and are composed of two kinds of polypeptide chain, called the heavy (~50kDa) and the light chain (~25kDa). The two types of light chains are kappa (κ) and lambda (λ). By cleavage with enzyme papain, the Fab (fragment-antigen binding) part can be separated from the Fc(fragment constant) part of the molecule. The Fab fragments contain the variable domains, which consist of three an…
History
Immunotherapy developed in the 1970s following the discovery of the structure of antibodies and the development of hybridoma technology, which provided the first reliable source of monoclonal antibodies. These advances allowed for the specific targeting of tumors both in vitro and in vivo. Initial research on malignant neoplasmsfound mAb therapy of limited and generally short-lived success wit…
Targeted conditions
Anti-cancer monoclonal antibodies can be targeted against malignant cells by several mechanisms. Ramucirumab is a recombinant human monoclonal antibody and is used in the treatment of advanced malignancies. In childhood lymphoma, phase I and II studies have found a positive effect of using antibody therapy.
Monoclonal antibodies used for autoimmune diseases include infliximab and adalimumab, which …
Therapy types
Radioimmunotherapy (RIT) involves the use of radioactively-conjugated murine antibodies against cellular antigens. Most research involves their application to lymphomas, as these are highly radio-sensitive malignancies. To limit radiation exposure, murine antibodies were chosen, as their high immunogenicity promotes rapid tumor clearance. Tositumomab is an example used for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
FDA-approved therapeutic antibodies
The first FDA-approved therapeutic monoclonal antibody was a murine IgG2a CD3 specific transplant rejection drug, OKT3 (also called muromonab), in 1986. This drug found use in solid organ transplant recipients who became steroid resistant. Hundreds of therapies are undergoing clinical trials. Most are concerned with immunological and oncological targets.
Tositumomab – Bexxar – 2003 – CD20
The first FDA-approved therapeutic monoclonal antibody was a murine IgG2a CD3 specific transplant rejection drug, OKT3 (also called muromonab), in 1986. This drug found use in solid organ transplant recipients who became steroid resistant. Hundreds of therapies are undergoing clinical trials. Most are concerned with immunological and oncological targets.
Tositumomab – Bexxar – 2003 – CD20
Economics
Since 2000, the therapeutic market for monoclonal antibodies has grown exponentially. In 2006, the “big 5” therapeutic antibodies on the market were bevacizumab, trastuzumab (both oncology), adalimumab, infliximab (both autoimmune and inflammatory disorders, ‘AIID’) and rituximab(oncology and AIID) accounted for 80% of revenues in 2006. In 2007, eight of the 20 best-selling biotechnology drugs in the U.S. are therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. This rapid growth in dem…
External links
• Cancer Management Handbook: Principles of Oncologic Pharmacotherapy (registration required)