Treatment
- Medications. Hydroxyurea (Droxia, Hydrea, Siklos). ...
- Preventing infections. Children with sickle cell anemia might receive penicillin between the ages of about 2 months old until at least age 5.
- Surgical and other procedures. Blood transfusions. ...
What is the best treatment for sickle cell anemia?
Nov 18, 2019 · In summary, transplantation is the optimal treatment for sickle cell disease, being the only curative approach. However, clarification is needed on who is an optimal candidate, and donor sources must be expanded to balance the lesser availability of donors among minorities.
What are the medications used to treat sickle cell anaemia?
Treatments for sickle cell-related anaemia Anaemia often causes few symptoms and may not require specific treatment. But dietary supplements like folic acid , which helps stimulate the production of red blood cells, may sometimes be required to help improve anaemia if your child has a restricted diet, such as a vegetarian or vegan diet.
How to treat sickle cell anemia using home remedies?
May 20, 2020 · Different therapeutic approaches have been proposed to assess the impact in patients with SCD (Nasimuzzaman and Malik, 2019; Sundd et al., 2019; Telen et al., 2019). Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and statins have been studied for their anti-inflammatory effects on neutrophils and monocyte adhesion.
Is there a cure for sickle cell anemia?
Dec 03, 2019 · Several approved medications can help improve the symptoms of sickle cell disease. These include hydroxyurea and Endari (L-glutamine). Oxbryta (voxelotor), developed by Global Blood Therapeutics, is an approved therapy that targets the underlying cause of sickle cell disease, the abnormal hemoglobin.

Can sickle cell disease be cured?
There's no cure for most people with sickle cell anemia. Treatments can relieve pain and help prevent complications associated with the disease.Mar 9, 2022
What are the new treatments available for sickle cell anemia?
In July 2017, the FDA approved Endari (L-glutamine oral powder) to reduce acute complications of sickle cell disease, including the frequency of sudden, severe attacks of pain (called sickle cell crises). This product is for patients age 5 and older and was the first new treatment in nearly 20 years.Jun 18, 2018
Is there a cure for sickle cell anemia 2021?
13, 2021 (HealthDay News) -- A gene therapy that could provide a permanent cure for sickle cell disease continues to show success through a third wave of patients, researchers report.Dec 13, 2021
Which blood tonic is good for sickle cell?
It is more news that fluted pumpkin is a good blood tonic. Now scientists have shown the efficacy of fluted pumpkin also in reducing the incidence of sickle cell crisis in infants and adults.Aug 9, 2018
What happens if sickle cells get stuck in blood vessels?
A stroke can happen if sickle cells get stuck in a blood vessel and clog blood flow to the brain. About 10% of children with SCD will have a symptomatic stroke . Stroke can cause learning problems and lifelong disabilities.
When do you start to see symptoms of sickle cell disease?
People with sickle cell disease (SCD) start to have signs of the disease during the first year of life, usually around 5 months of age. Symptoms and complications of SCD are different for each person and can range from mild to severe. The reason that infants don’t show symptoms at birth is because baby or fetal hemoglobin protects ...
How to treat SCD?
There are simple steps that people with SCD can take to help prevent and reduce the number of pain crises, including the following: 1 Drink plenty of water. 2 Try not to get too hot or too cold. 3 Try to avoid places or situations that cause exposure to high altitudes (for example, flying, mountain climbing, or cities with a high altitude). 4 Try to avoid places or situations with exposure to low oxygen levels (for example, mountain climbing or exercising extremely hard, such as in military boot camp or when training for an athletic competition). 5 Adults with severe SCD can take a medicine called hydroxyurea to help reduce the number of pain crises.#N#People taking hydroxyurea are checked often by a doctor to prevent complications, including an increased risk of infections. 6 Research shows that babies and children with SCD can also benefit from hydroxyurea therapy.
Why do my hands and feet swell?
This swelling, often along with a fever, is caused by the sickle cells getting stuck in the blood vessels and blocking the flow of blood in and out of the hands and feet.
What is SCD treatment?
SCD is a disease that worsens over time. Treatments are available that can prevent complications and lengthen the lives of those who have this condition. These treatment options can be different for each person depending on the symptoms and severity.
How often should sickle cell patients have their eyes checked?
People with sickle cell disease should have their eyes checked every year to look for damage to the retina. If possible, this should be done by an eye doctor who specializes in diseases of the retina.
What happens when sickle cells get trapped in the spleen?
It happens when a large number of sickle cells get trapped in the spleen and cause it to suddenly get large. Symptoms include sudden weakness, pale lips, fast breathing, extreme thirst, abdominal (belly) pain on the left side of body, and fast heartbeat.
What is the best treatment for sickle cell disease?
Stem cell or bone marrow transplants. Stem cell or bone marrow transplants are the only cure for sickle cell disease, but they're not done very often because of the significant risks involved. Stem cells are special cells produced by bone marrow, a spongy tissue found in the centre of some bones. They can turn into different types of blood cells.
What is the treatment for acute chest syndrome?
acute chest syndrome, a serious lung condition, usually requires emergency treatment with antibiotics, blood transfusions, oxygen and fluids given into a vein – hydroxycarbamide may be needed to prevent further episodes. People who need a lot of blood transfusions may also need to take medicine called chelation therapy.
How to treat a swollen ear?
The following things can help: 1 take over-the-counter painkillers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen (do not give aspirin to children under 16 unless a doctor has prescribed it) – if the pain is more severe, your GP may prescribe stronger painkillers 2 have plenty to drink 3 use a warm towel or a wrapped heated pad to gently massage the affected body part – many pharmacies sell heat pads that you can use for this purpose 4 distractions to take your mind off the pain – for example, children might like to read a story, watch a film or play their favourite computer game
How do stem cells work?
For a stem cell transplant , stem cells from a healthy donor are given through a drip into a vein. These cells then start to produce healthy red blood cells to replace the sickle cells. A stem cell transplant is an intensive treatment that carries a number of risks. The main risk is graft versus host disease, a life-threatening problem where ...
Does folic acid help with anemia?
But dietary supplements like folic acid, which helps stimulate the production of red blood cells, may sometimes be required to help improve anaemia if your child has a restricted diet, such as a vegetarian or vegan diet.
Can gallstones be treated with surgery?
a short course of hormonal medicine may be prescribed to trigger puberty in children with delayed puberty. gallstones may be treated with gallbladder removal surgery. bone and joint pain can be treated with painkillers, although more severe cases may require surgery.
Can a child have a stem cell transplant?
Stem cell transplants are generally only considered in children with sickle cell disease who have severe symptoms that have not responded to other treatments, when the long-term benefits of a transplant are thought to outweigh the possible risks.
What is the best medicine for sickle cell pain?
Because pain is a common and debilitating symptom of sickle cell disease, clinicians may recommend painkillers such as acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen and diclofenac. Opioids such as codeine or morphine may also be prescribed for more severe or chronic pain. Ketamine may be used to treat acute pain caused ...
What is sickle cell news?
Sickle Cell Disease News is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
What is the disease that affects the red blood cells?
Treatments. Sickle cell disease is an inherited condition that affects red blood cells, which transport oxygen throughout the body. The disease is caused by a mutation in the HBB gene, resulting in the production of an abnormal hemoglobin protein, called HbS. Hemoglobin is the protein that oxygen binds to inside red blood cells.
How does Adakveo work?
The therapy works by preventing hemoglobin from sticking together, which allows the red blood cells to maintain a more normal and flexible shape. Another approved treatment for sickle cell disease is Adakveo (crizanluzumab), developed by Novartis, which contains an antibody that blocks one of the proteins in the endothelial cells ...
What is Oxbryta approved for?
Oxbryta (voxelotor), developed by Global Blood Therapeutics, is an approved therapy that targets the underlying cause of sickle cell disease, the abnormal hemoglobin.
What is sickle cell disease?
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a common, severe disorder that includes congenital hemolytic anemias caused by inherited point mutations in the β-globin gene. 1 These mutations result in abnormal hemoglobin polymerization, which leads to a cascade of physiologic consequences, including erythrocyte rigidity, vaso-occlusion, chronic anemia, hemolysis, and vasculopathy. 1 This change in the behavior of hemoglobin has profound clinical consequences, including recurrent pain episodes (known as sickle cell—related pain crises or vaso-occlusive crises), hemolytic anemia, multiorgan dysfunction, and premature death. 1 Newborn screening, early immunization, and prophylactic penicillin treatment in infants and children, as well as comprehensive management for pain and disease complications, have improved outcomes in these patients; however, the average life expectancy of a patient with SCD remains only about 40 to 50 years. 2,3
What is a RBC transfusion?
Red blood cell (RBC) transfusion is common in patients with SCD for the management of acute complications, and regular or chronic transfusion regimens are used for stroke prevention in at-risk patients.
How many people are affected by SCD?
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is among the most common genetic diseases in the United States, affecting approximately 100,000 people. In the United States, SCD is characterized by a shortened life expectancy of only about 50 years in severe subtypes, significant quality-of-life impairments, and increased healthcare utilization and spending.
Is there a cure for SCD?
Early research also suggests that gene therapy may offer the potential for curative treatment.
What is the complication of SCD?
Venous thromboembolism (VTE), which includes both deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, is increasingly recognized as an important complication of SCD that occurs as a result of the hypercoagulable state that is elicited by the disease.
What is the purpose of hydrourea?
Hydroxyurea was approved by the FDA in 1998 to reduce the frequency of painful crises and to reduce the need for blood transfusions in adults with homozygous SCD who have recurrent moderate to severe painful crises. 13 Hydroxyurea is a ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase inhibitor that was first used in myeloproliferative disease 19 and its mechanism in SCD is multifactorial, but it primarily involves increasing production of fetal hemoglobin (HbF); the absence of the mutated β chain in HbF means that it is unaffected by the sickle mutation. 59 While the properties of HbF are somewhat different than those of normal adult hemoglobin, incorporation of HbF into normal adult RBCs is not associated with functional impairment. 60 Some patients with SCD who have naturally high levels of HbF have milder, although not asymptomatic, disease. 60
What is the role of adenosine in SCD?
Adenosine signaling contributes to the pathophysiology of SCD by stimulating the production of erythrocyte 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate, an intracellular signal that decreases oxygen binding to hemoglobin. 28.
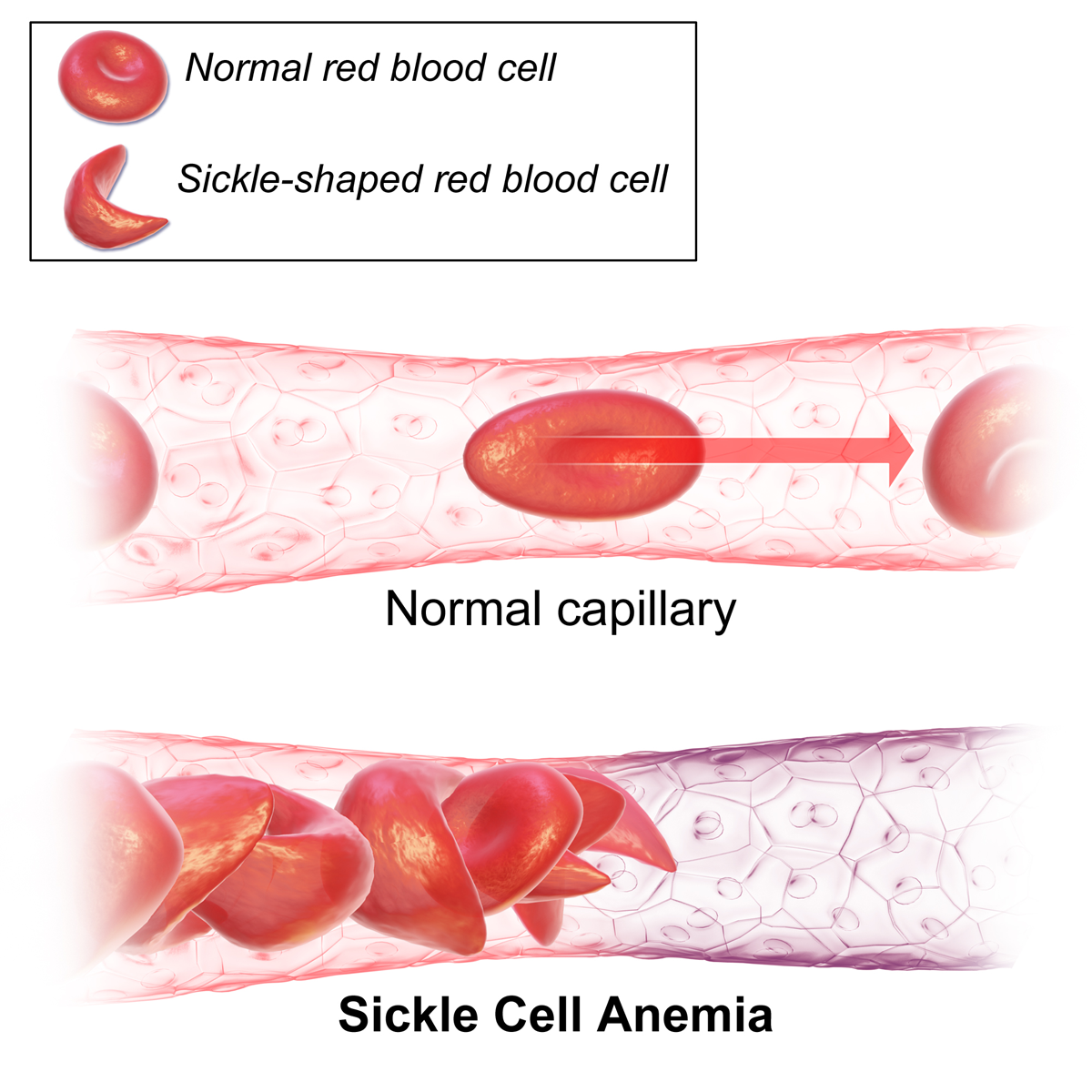
What does sickle cell anemia look like?
Overview. Normal red blood cells are rounded and disk-shaped. In sickle cell anemia, some red blood cells become deformed, so they look like sickles used to cut wheat. These unusually shaped cells give the disease its name. Sickle cell anemia is one of a group of disorders known as sickle cell disease.
How long do sickle cells last?
Red blood cells usually live for about 120 days before they need to be replaced. But sickle cells usually die in 10 to 20 days, leaving a shortage of red blood cells (anemia).
Why do my hands and feet swell?
Swelling of hands and feet. The swelling is caused by sickle-shaped red blood cells blocking blood flow to the hands and feet. Frequent infections. Sickle cells can damage your spleen, leaving you more vulnerable to infections.
Why are red blood cells important?
Red blood cells provide your body with the oxygen and nutrients needed for growth. A shortage of healthy red blood cells can slow growth in infants and children and delay puberty in teenagers. Vision problems. Tiny blood vessels that supply your eyes can become plugged with sickle cells.
What causes red blood cells to become sticky?
In sickle cell anemia, the abnormal hemoglobin causes red blood cells to become rigid, sticky and misshapen. Both mother and father must pass the defective form of the gene for a child to be affected. If only one parent passes the sickle cell gene to the child, that child will have the sickle cell trait.
How long does pain last in the body?
Pain can also occur in your bones. The pain varies in intensity and can last for a few hours to a few weeks. Some people have only a few pain crises a year.
Can anemia cause a stroke?
Sickle cell anemia can lead to a host of complications, including: Stroke. Sickle cells can block blood flow to an area of your brain. Signs of stroke include seizures, weakness or numbness of your arms and legs, sudden speech difficulties, and loss of consciousness.
How to prevent sickle cell crisis?
Drink more water to reduce the chances of sickle cell crises. Exercise regularly and reduce stress to reduce crises, too. Contact your doctor immediately if you think you have any type of infection. Early treatment of an infection may prevent a full-blown crisis.
When do sickle cell anemia symptoms appear?
Symptoms of sickle cell anemia usually show up at a young age. They may appear in babies as early as 4 months old, but generally occur around the 6-month mark. While there are multiple types of SCD, they all have similar symptoms, which vary in severity. These include:
Why is the spleen removed?
The spleen may have to be removed due to complications of sickle cell disease in an operation known as a splenectomy. Some sickle cell patients will sustain enough damage to their spleen that it becomes shrunken and ceases to function at all. This is called autosplenectomy.
What is sickle cell disease?
Sickle cell anemia, or sickle cell disease (SCD), is a genetic disease of the red blood cells (RBCs). Normally, RBCs are shaped like discs, which gives them the flexibility to travel through even the smallest blood vessels. However, with this disease, the RBCs have an abnormal crescent shape resembling a sickle.
How long do sickle cells live?
This breaking apart of RBCs is called chronic hemolysis. RBCs generally live for about 120 days. Sickle cells live for a maximum of 10 to 20 days.
Why is sexual maturation delayed?
Sexual maturation may also be delayed. This happens because sickle cell RBCs can’t supply enough oxygen and nutrients.
What is the protein that carries oxygen?
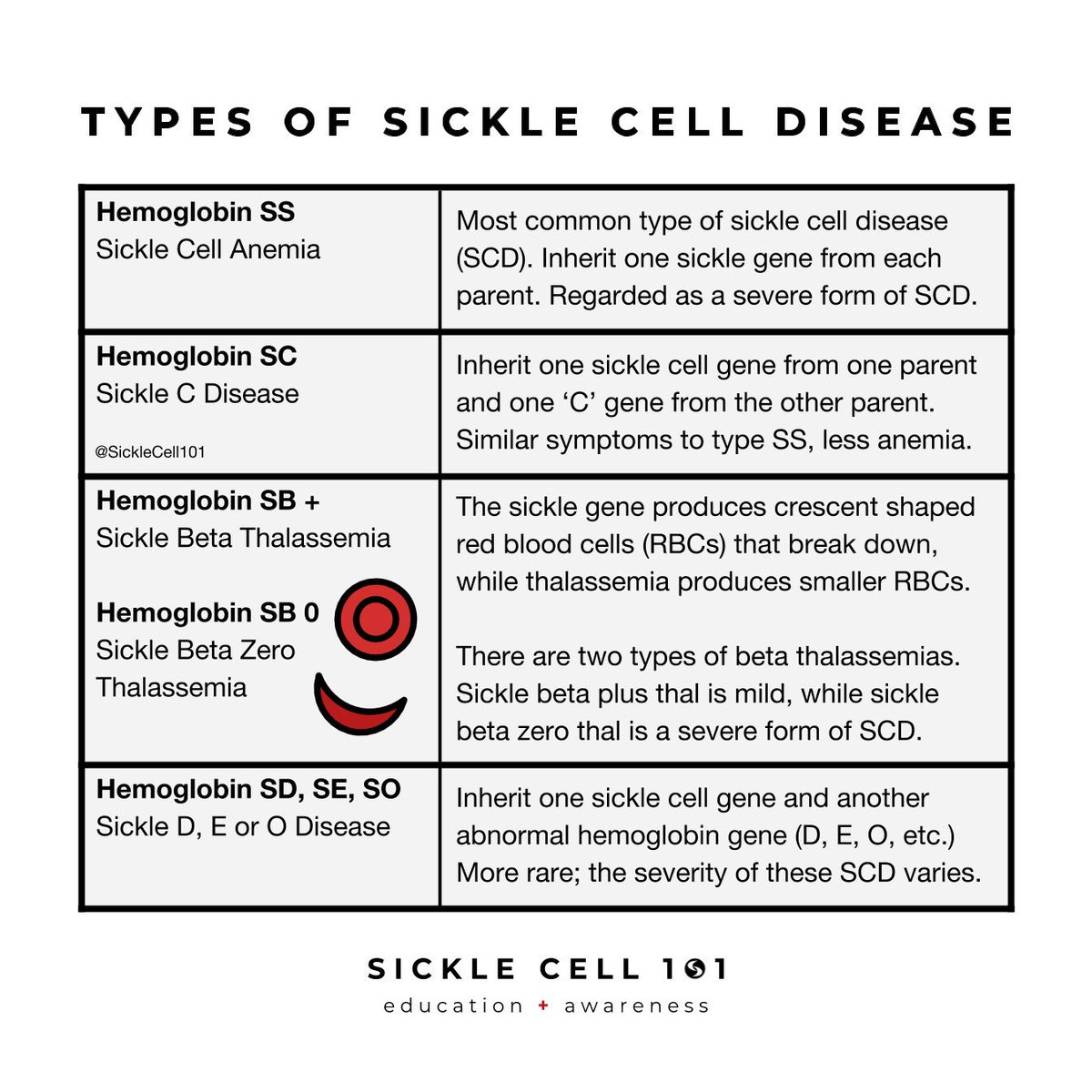
Hemoglobin is the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. It normally has two alpha chains and two beta chains. The four main types of sickle cell anemia are caused by different mutations in these genes.
What is sickle cell anemia?
Sickle cell anemia is a disease in which the body produces abnormally shaped red blood cells that have a crescent or sickle shape. These cells do not last as long as normal, round, red blood cells, which leads to anemia (low number of red blood cells). The sickle cells also get stuck in blood vessels, blocking blood flow. [1] Signs and symptoms of sickle cell disease usually begin in early childhood and may include anemia, repeated infections, and periodic episodes of pain (called crises). This condition is caused by mutations in the HBB gene and is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. [2] Treatment typically focuses on controlling symptoms and may include pain medicines during crises; hydroxyurea to reduce the number of pain episodes; antibiotics and vaccines to prevent bacterial infections; and blood transfusions. [1] On July 7, 2017, the FDA in the United States approved the use of Endari (prescription grade L-glutamine) to reduce the number of sickle cell crisis. Endari is the first FDA approved treatment that is also available for children with sickle cell disease five years of age and older. [3]
What is the FDA approved treatment for sickle cell disease?
On July 7, 2017, the FDA in the United States approved the use of Endari (prescription grade L-glutamine) to reduce the number of sickle cell crisis. Endari is the first FDA approved treatment that is also available for children with sickle cell disease five years of age and older. [3]
Who makes Hydroxyurea?
Hydroxyurea (Brand name: Siklos) - Manufactured by Addmedica Laboratories. FDA-approved indication: To reduce the frequency of painful crises and to reduce the need for blood transfusions in pediatric patients, 2 years of age and older, with sickle cell anemia with recurrent moderate to severe painful crisis.
What are the symptoms of sickle cell disease?
Signs and symptoms of sickle cell disease usually begin in early childhood and may include anemia, repeated infections, and periodic episodes of pain (called crises). This condition is caused by mutations in the HBB gene and is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern.
What is the HPO database?
People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. This information comes from a database called the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) . The HPO collects information on symptoms that have been described in medical resources.
What is the chance of having sickle cell anemia?
In regards to sickle cell anemia, a person who carries one copy of the mutated gene is said to be a carrier for the condition, or to have sickle cell trait. When two people who are carriers of an autosomal recessive condition have a child, there is a 25% (1 in 4) chance that the child will have the condition, a 50% ...
What do doctors look for in a diagnosis?
Healthcare professionals typically look at a person’s medical history, symptoms, physical exam, and laboratory test results in order to make a diagnosis.
Diagnosis
- A blood test can check for the form of hemoglobin that underlies sickle cell anemia. In the United States, this blood test is part of routine newborn screening. But older children and adults can be tested, too. In adults, a blood sample is drawn from a vein in the arm. In young children and babi…
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Taking the following steps to stay healthy might help you avoid complications of sickle cell anemia: 1. Take folic acid supplements daily and choose a healthy diet.Bone marrow needs folic acid and other vitamins to make new red blood cells. Ask your doctor about a folic acid supplement and other vitamins. Eat a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, as well as whole g…
Coping and Support
- If you or someone in your family has sickle cell anemia, you might consider the following to help you cope: 1. Finding someone to talk with.Living with a chronic illness is stressful. Consider consulting a mental health professional, such as a psychologist, counselor or social worker, to help you cope. 2. Join a support group.Ask your health care provider about support groups for fa…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Sickle cell anemia is usually diagnosed through genetic screening done when a baby is born. Those test results will likely be given to your family doctor or pediatrician. He or she will likely refer you to a doctor who specializes in blood disorders (hematologist) or a pediatric hematologist. Here's information to help you get ready for your appointment.