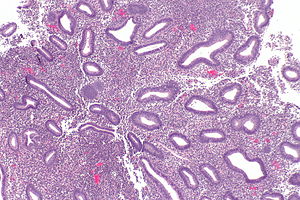
How do you fix benign proliferative endometrium?
What is a Proliferative Endometrium?
- Definition. A proliferative endometrium is a normal part of healthy uterine function when it occurs during the first half of the menstrual cycle.
- Disordered Proliferation. ...
- Associated Conditions. ...
- Common Symptoms. ...
- Diagnosis by Ultrasound. ...
- Endometrial Biopsy. ...
- Common Causes. ...
- Treatment Options. ...
- Surgical Treatment. ...
- Self-Help Measures. ...
What is the treatment for thickened endometrium?
What is the treatment for thickened endometrium? The most common treatment is progestin. This can be taken in several forms, including pill, shot, vaginal cream, or intrauterine device. Atypical types of endometrial hyperplasia, especially complex, increase your risk of getting cancer. If you have these types, you might consider a hysterectomy.
What does weakly proliferative endometrium?
Weakly proliferative endometrium suggests there has still been a little estrogen present to stimulate the endometrium, whether from your ovaries, adrenals, or from conversion in fat cells. The metaplasia doesn’t mean anything significant, and the glandular and stromal breakdown is often seen when there has been bleeding.
What does weak proliferative endometrium mean?
The term can refer to a form of simple endometrial hyperplasia — or the abnormal thickening of the endometrial lining — but it can indicate a more serious problem in some cases. Here is some information about the potential causes of disordered proliferative endometrium and what that might mean for your patients.

What does it mean to have disordered proliferative endometrium?
"Disordered proliferative endometrium" is a somewhat vague term that generally indicates the unusual growth of endometrial cells. The term can refer to a form of simple endometrial hyperplasia — or the abnormal thickening of the endometrial lining — but it can indicate a more serious problem in some cases.
Should I have a hysterectomy for endometrial hyperplasia?
How is endometrial hyperplasia managed or treated? If you're at increased risk of cancer due to atypical endometrial hyperplasia, your healthcare provider may recommend a hysterectomy to remove the uterus. After a hysterectomy, you won't be able to get pregnant.
What causes proliferate endometrium?
The normal endometrium increases in thickness during the proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle in response to estrogen. Following ovulation, the endometrium provides an attachment site for and a source of nourishment to an early embryo until the placenta develops.
What is the best treatment for endometrial hyperplasia?
In many cases, endometrial hyperplasia can be treated with progestin. Progestin is given orally, in a shot, in an intrauterine device (IUD), or as a vaginal cream. How much and how long you take it depends on your age and the type of hyperplasia. Treatment with progestin may cause vaginal bleeding like a period.
Is D&C better than endometrial biopsy?
In conclusion, as a gold standard method of endometrial sampling, higher accuracy with final pathology is expected from D&C than from aspiration biopsy. For an accurate diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia, D&C seems superior to aspiration biopsy.
What is the difference between a D&C and a hysteroscopy?
A D&C (dilatation and curettage) is a procedure where the opening of the uterus (called the cervix) is widened and the lining of the uterus is scraped away. look for growths ■ end an incomplete miscarriage. A hysteroscopy is a procedure that allows your doctor to see inside your uterus and make a diagnosis.
Is it normal to have proliferative endometrium?
Is this a diagnosable condition? Proliferative endometrium isn't a symptom or condition. The term describes healthy reproductive cell activity. It refers to the time during your menstrual cycle when a layer of endometrial cells is prepared for attachment of a fertilized egg.
Is proliferative endometrium cancerous?
Background: Proliferative endometrium has been reported in 15% of endometrial biopsies of women aged 50 years and older. Contrary to endometrial hyperplasia, proliferative endometrium has not been associated with the risk of endometrial cancer.
What happens if my endometrial biopsy is abnormal?
Biopsy results may show cell changes linked to hormone levels, or abnormal tissues, such as fibroids or polyps. These can lead to abnormal bleeding.
Can thickened endometrium be cured?
In most cases, endometrial hyperplasia is very treatable. Work with your doctor to create a treatment plan. If you have a severe type or if the condition is ongoing, you might need to see your doctor more often to monitor any changes.
How long do you take progesterone for endometrial hyperplasia?
Approximately 1% of patients who are on combined HRT develop benign EH. In such cases, the dose should be increased or they should be switched to 3 months of progestin-only therapy to encourage the regression of the hyperplastic endometrium.
Can endometrial hyperplasia resolve on its own?
Endometrial hyperplasia is a thickening of the womb lining (uterus). It usually causes abnormal vaginal bleeding. It may return to normal without any treatment in some cases. In others, hormone treatment or an operation may be needed.
How long does the endometrial lining last?
If it doesn’t, your body prepares to shed and discard your endometrial lining. This stage lasts for the second half of your cycle, usually another 14 to 18 days. On the first day of your period, this stage ends.
How often does the endometrium shed cells?
This process of shedding unused cells from your endometrium happens every 21 to 35 days, depending on the length of your cycle.
What happens if the lining of the uterus doesn't thicken?
If the lining doesn’t thicken quickly enough, an egg may have trouble implanting in your uterus to begin a pregnancy. Your doctor is the only one who can explain what this diagnosis means for you. Disordered proliferative endometrium is usually associated with these conditions: Endometrial hyperplasia.
What stage of menstruation is the secretory endometrium?
Secretory endometrium stage. Your ovaries release a mature egg, and the next phase of menstruation begins. The new endometrial cells mature and become ready for an egg to be implanted. For about a week, your uterus is waiting for a fertilized egg to arrive. If it doesn’t, your body prepares to shed and discard your endometrial lining.
What is the term for the time during the menstrual cycle when a layer of endometrial cells is
If this cell development is disordered in any way, it may be described as “disordered proliferative endometrium.”. Keep reading to learn more about ...
How long does a proliferative cycle last?
This causes your endometrium to thicken. Your ovaries also prepare an egg for release. This phase lasts for half your cycle, usually 14 to 18 days.
What to do if you have unusual pelvic symptoms?
If you’re experiencing any unusual symptoms, see your gynecologist. You can discuss your symptoms at your yearly pelvic exam, but you shouldn’t wait until then if your symptoms are new or unexpected. You should also talk with your gynecologist if you have questions about your Pap smear or other test results.
What causes irr in the womb?
Endometrium ?'s: If the production of estrogen in the ovary is irregular, the lining of the womb (endometrium) will grow and degenerate at different times, causing irr ... Read More
Is endometrium disorder pre-cancerous?
And it is definitely not a pre-cancerous diagnosis based on your biopsy. The strong family history, however, could be.
What is disordered proliferative endometrium?
Disordered proliferative endometrium is a descriptive diagnosis that needs to be considered together with your medical history, physical examination, and any other tests that were performed (b lood work, imaging tests, etc.).
How does the endometrium prepare for pregnancy?
During the menstrual cycle, the endometrium is preparing itself for the possible pregnancy by becoming thicker and richer in blood vessels. In the first part of the menstrual cycle, the endometrium is growing under the influence of estrogen (a hormone produced by the ovaries) ...
Which layer of the epithelium is lined by the endometrium?
The endometrium is composed of endometrial glands lined by one layer of columnar epithelium and surrounded by endometrial stroma. Myometrium – The myometrium is the middle layer and is made up of smooth muscle which allows the uterus to change size and contract.
Which part of the uterus is connected to the vagina?
The upper part of the uterus (fundus) is attached to the fallopian tubes while the lower part is connected to the vagina through the uterine cervix. Endometrium – The endometrium forms the inner lining of the uterus.
Can estrogen cause endometrial hyperplasia?
In some situations, however, the endometrium is exposed to a prolonged influence of estrogen. That results in increased growth and crowding of the endometrial glands and can lead to endometrial hyperplasia.
What is a disordered proliferative endometrium?
Follow Us: Disordered proliferative endometrium is a result of an anovulatory cycle that lacks ovulation and leads to high levels of estrogen from low progesterone levels. The University of Virginia School of Medicine describes anovulation as the absence of ovulation during the reproductive years, not including pregnancy, ...
What happens when endometrial glands are proliferative?
When endometrial glands are proliferative, a histology report shows changes in the shape and structure, which are subtle. One of these mild changes is cystic dilation. When the stroma is broken down, pieces of isolated glands do not secrete, notes the University of Virginia School of Medicine. ADVERTISEMENT.
Why does bleeding occur when estrogen levels are low?
However, in some cases when there is no drop in estrogen levels, bleeding can still occur because the necessary blood flow to the proliferative endometrium is not steady. In a histological test, doctors can determine that there is estrogen stimulation but no progesterone production.
What is the purpose of the endometrium?
The main purpose of the endometrium is to provide an attachment site and a source of nourishment to an early embryo.
Which genes are involved in the early endometrial proliferative phase?
This research discusses evidence of a higher expression of the genes related to proliferation, inflammation and immune response — including the genes TGFB2 and ligand 18 — during the early endometrial proliferative phase. Changes in genes associated with implantation, as well as with cell growth, appear to occur during the mid-proliferative phase.
What happens if the ovaries don't produce progesterone?
If conception doesn't occur, hormone levels drop, and the endometrium begins to shed. While this cycle is common knowledge to gynecologists, the causes of disordered proliferative endometrium are less clear. Researchers are uncovering various potential influences ...
What is the term for a thickening of the endometrium?
Endometrial hyperplasia, a thickening of the endometrium that, according to The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, typically occurs during perimenopause, after menopause or in response to high doses of estrogen or medications that act like estrogen.
Can obesity cause endometrial hyperplasia?
Obesity is also a risk factor for endometrial hyperplasia. Uterine polyps, which can occur in women of all ages but are most common after menopause. Endometrial cancer. Symptoms include heavy bleeding, painful periods, bleeding between periods or after menopause (proliferative endometrium after menopause), irregular menstrual cycles ...
What is the best treatment for endometrial hyperplasia?
The most common surgical treatment, especially for endometrial hyperplasia, is a hysterectomy. Although this solves the problem by removing the uterus altogether, this major surgery renders the woman infertile. For this reason, hysterectomies are generally a final option when there is a high risk of malignancy.
What is the endometrium?
The endometrium is the lining of the uterus. Every month, this lining builds and thickens in preparation for a potential pregnancy, providing the ideal environment for the implantation of a fertilized egg. If pregnancy does not occur, the endometrium is shed during the woman's monthly period. The term proliferative endometrium refers to ...
What happens to the endometrium during pregnancy?
If pregnancy does not occur, the endometrium is shed during the woman's monthly period. The term proliferative endometrium refers to the state of the endometrial layer while it grows. Advertisement.
Why is my endometrium thin?
A disordered proliferative endometrium usually has a hormonal cause, such as excess estrogen for overproliferation or lower levels of estrogen during menopause, which can cause the endometrium to become too thin.
Why does the endometrium become thicker?
The endometrium becomes thicker leading up to ovulation to provide a suitable environment for a fertilized egg to grow inside the uterus. A proliferative endometrium in itself is not worrisome. However, sometimes problems can develop during the proliferative phase of endometrial growth. lukpedclub / Getty Images.
How to diagnose endometrial growth?
Diagnosis by Ultrasound. The doctor will ask the patient for a description of her symptoms. If they suspect disordered endometrial growth, the physician may order an ultrasound to get a detailed view of the lining of the uterus.
What causes uterine polyps?
The most common is endometrial hyperplasia, where too much estrogen and too little progesterone in the system causes the cells to overgrow or causes polyps to grow in the uterine cavity. After menopause, some women develop an atrophic endometrium, where the endometrial tissue becomes too thin.