Medication
Jul 22, 2021 · PID is usually treated with antibiotics to provide empiric, broad spectrum coverage of likely pathogens. Recommended regimens can be found in the 2021 STI Treatment Guidelines . Healthcare providers should emphasize to their patients that although their symptoms may go away before the infection is cured, they should finish taking all of the prescribed medicine.
Procedures
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Diagnostic Considerations. Acute PID is difficult to diagnose because of the considerable variation in symptoms and... Treatment. PID treatment regimens should provide empiric, broad-spectrum coverage of likely pathogens. Multiple... Intramuscular or Oral Treatment. ...
Self-care
If it's diagnosed at an early stage, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) can be treated easily and effectively with antibiotics. These can be prescribed by your GP or a doctor at a sexual health clinic. But left untreated, it can lead to more serious long-term complications. Find out more about the complications of PID. Antibiotics
What is the best antibiotic for PID?
Mar 14, 2022 · 1. Introduction. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is a spectrum of upper genital tract infections that includes endometritis, salpingitis, tuboovarian abscess, and/or pelvic peritonitis [].Typically, acute PID is caused by ascending spread of microorganisms from the vagina and/or endocervix to the endometrium, fallopian tubes, and/or adjacent structures [1–3].
What antibiotic treats PID?
Feb 10, 2019 · The antibiotics in general use in treatment of PID include: penicillins cephalosporins metronidazole (flagyl) clindamycin tetracyclines chloramphenicol aminoglycoside Patients with pelvic inflammatory disease can either be treated as outpatients or inpatients. The tetracyclines and metronidazole are used for outpatient treatment.
What medications are used for PID?
Sep 15, 2019 · Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the upper genital tract occurring predominantly in sexually active young women. Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae are common ...
What do antibiotics treat PID?
Your doctor or nurse will give you antibiotics to treat PID. Most of the time, at least two antibiotics are used that work against many different types of bacteria. You must take all of your antibiotics, even if your symptoms go away. This helps to make sure the infection is fully cured.

Can PID be fully treated?
Can PID be cured? Yes, if PID is diagnosed early, it can be treated. However, treatment won't undo any damage that has already happened to your reproductive system. The longer you wait to get treated, the more likely it is that you will have complications from PID.
What is the first line treatment for PID?
The CDC recommends the following for first-line treatment for outpatient therapy: Doxycycline (100 mg orally twice a day for 2 weeks) plus ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly (IM) for one dose or cefoxitin 2 g IM with probenecid (1g orally) for one dose or another parenteral third-generation cephalosporin.May 13, 2021
How long does it take for pelvic inflammatory disease to clear up?
To fully treat PID, you may need to take one or more antibiotics. Taking antibiotic medicine will help clear the infection in about 2 weeks.
What is the best treatment for PID at home?
Is there treatment for PID?Rest in bed. You might need to stay in bed for several days if you have a serious infection.Drink lots of water, and eat healthy foods.Don't douche or use tampons.If you're in pain, you can take aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil), acetaminophen (Tylenol), or naproxen (Aleve).
What are 3 causes of PID?
The main cause of PID is through a sexually transmitted infection (STI) such as chlamydia, gonorrhoea or mycoplasma genitalium. These bacteria usually only infect the cervix, where they can be easily treated with antibiotics.
Which antibiotics is best for PID?
Current recommendations. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 14 days, along with a second- or third-generation cephalosporin administered parenterally, for mild PID in ambulatory patients.
Is PID a serious infection?
Pelvic inflammatory disease is a serious infection that develops when certain STDs or other infections aren't treated. It can cause chronic pain and infertility.
Can azithromycin cure PID?
The clinical cure rates for patients who adhered to treatment protocol were 98.2 percent (56 out of 57) for azithromycin and 85.7 percent (42 out of 49) for doxycycline (P = . 02).Mar 15, 2008
What does PID pain feel like?
Pain in the lower abdomen is the most common symptom of pelvic inflammatory disease. 2 The pain can feel like dull pressure or a more intense cramping-type pain. In chronic PID, the pain might be mild but is present all the time.Jun 23, 2020
What happens if you leave PID untreated?
Untreated PID can cause scar tissue and pockets of infected fluid (abscesses) to develop in the reproductive tract, which can cause permanent damage. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the female reproductive organs.Apr 23, 2020
What are the symptoms of PID in a female?
Symptoms of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)pain around the pelvis or lower tummy.discomfort or pain during sex that's felt deep inside the pelvis.pain when peeing.bleeding between periods and after sex.heavy periods.painful periods.unusual vaginal discharge, especially if it's yellow, green or smelly.
Can UTI cause PID?
Painful urination is most often a symptom of a bladder infection. If left untreated, a bladder infection can worsen and travel into your uterus or ovaries, causing pelvic inflammatory disease.Oct 13, 2015
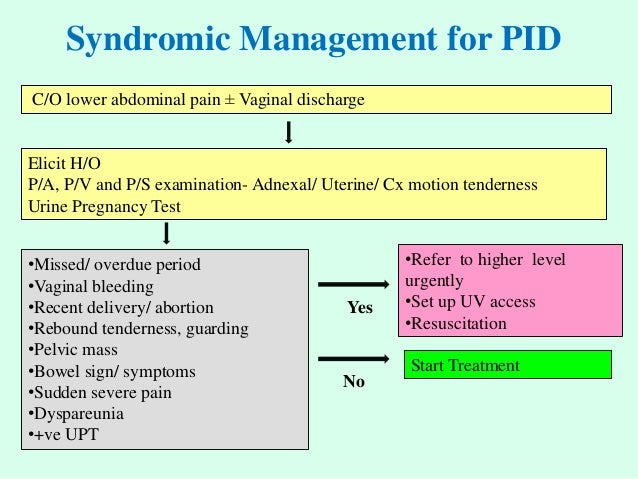
Diagnostic Considerations
Acute PID is difficult to diagnose because of the considerable variation in symptoms and signs associated with this condition. Women with PID often have subtle or nonspecific symptoms or are asymptomatic. Delay in diagnosis and treatment probably contributes to inflammatory sequelae in the upper genital tract.
Treatment
PID treatment regimens should provide empiric, broad-spectrum coverage of likely pathogens. Multiple parenteral and oral antimicrobial regimens have been effective in achieving clinical and microbiologic cure in randomized clinical trials with short-term follow-up ( 1171 – 1173 ).
Intramuscular or Oral Treatment
IM or oral therapy can be considered for women with mild-to-moderate acute PID because the clinical outcomes among women treated with these regimens are similar to those treated with IV therapy ( 1158 ). Women who do not respond to IM or oral therapy within 72 hours should be reevaluated to confirm the diagnosis and be administered therapy IV.
Other Management Considerations
To minimize disease transmission, women should be instructed to abstain from sexual intercourse until therapy is complete, symptoms have resolved, and sex partners have been treated (see Chlamydial Infections; Gonococcal Infections). All women who receive a diagnosis of PID should be tested for gonorrhea, chlamydia, HIV, and syphilis.
Follow-Up
Women should demonstrate clinical improvement (e.g., defervescence; reduction in direct or rebound abdominal tenderness; and reduction in uterine, adnexal, and cervical motion tenderness) <3 days after therapy initiation.
Management of Sex Partners
Persons who have had sexual contact with a partner with PID during the 60 days preceding symptom onset should be evaluated, tested, and presumptively treated for chlamydia and gonorrhea, regardless of the PID etiology or pathogens isolated.
Special Considerations
The risk for penicillin cross-reactivity is highest with first-generation cephalosporins but is negligible between the majority of second-generation (e.g., cefoxitin) and all third-generation (e.g., ceftriaxone) cephalosporins ( 619, 631, 653, 656) (see Management of Persons Who Have a History of Penicillin Allergy).
How to treat PID?
Treatment for PID most often includes: Antibiotics. Your doctor will prescribe a combination of antibiotics to start immediately. After receiving your lab test results, your doctor might adjust your prescription to better match what's causing the infection.
What causes a PID?
Get treatment. PID is most often caused by a sexually transmitted infection. Finding out that you have an STI can be traumatic for you or your partner. Nevertheless, you and your partner should both seek immediate treatment to lessen the severity of PID and to prevent reinfection.
What is pelvic exam?
In a pelvic exam, your physician inserts two gloved fingers inside your vagina. While simultaneously pressing down on your abdomen, he or she can examine your uterus, ovaries and other organs.
What is the test for gonorrhea?
The samples will be tested at a lab for signs of infection and organisms such as gonorrhea and chlamydia. Blood and urine tests. These tests may be used to test for pregnancy, HIV or other sexually transmitted infections, or to measure white blood cell counts or other markers of infection or inflammation. Ultrasound.
How to help with infertility?
Ask your doctor to explain the steps for infertility testing and treatment. Understanding the process may help reduce your anxiety. Seek support. Although sexual health, infertility and chronic pain can be deeply personal issues, reach out to your partner, close family members or friends, or a professional for support.
What to do if you have an abscess?
Temporary abstinence. Avoid sexual intercourse until treatment is completed and symptoms have resolved. If you're pregnant, seriously ill, have a suspected abscess or haven't responded to oral medications, you might need hospitalization. You might receive intravenous antibiotics, followed by antibiotics you take by mouth.
What happens if an abscess ruptures?
However, if an abscess ruptures or threatens to rupture, your doctor might drain it. You might also need surgery if you don't respond to antibiotic treatment or have a questionable diagnosis, such as when one or more of the signs or symptoms of PID are absent.
How to treat pelvic inflammatory disease?
Treatment. If it's diagnosed at an early stage, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) can be treated easily and effectively with antibiotics. These can be prescribed by your GP or a doctor at a sexual health clinic.
How long does it take for a symtom to improve?
If your symptoms haven't started to improve within 3 days , you may be advised to attend hospital for further tests and treatment. If you have an intrauterine device (IUD) fitted, you may be advised to have it removed if your symptoms haven't improved within a few days, as it may be the cause of the infection.
How long before a sexual partner can you get a sex infection?
Any sexual partners you have been with in the 6 months before your symptoms started should be tested and treated to stop the infection recurring or being spread to others, even if no specific cause is identified.
What is PID in medicine?
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the upper genital tract (the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and the pelvic peritoneum). The infection usually spreads from the lower genital tract (vagina and cervix). It is an infection of the reproductive organs of women.
What antibiotics are used for PID?
The antibiotics in general use in treatment of PID include: penicillins. cephalosporins. metronidazole (flagyl) clindamycin. tetracyclines. chloramphenicol. aminoglycoside. Patients with pelvic inflammatory disease can either be treated as outpatients or inpatients.
How long does doxycycline last?
In summary, it is the usual practice to treat outpatients with doxycycline 100mg twice daily for 14 days in combination with metronidazole 400mg orally three times daily also for 14 days. Ofloxacin 400mg orally twice daily can be combined with clindamycin 450mg orally or metronidazole for 14 days.
What causes PID in women?
Several types of bacteria can cause PID, including the same bacteria that cause sexually transmitted infections-gonorrhea, mycoplasma and chlamydia. The bacteria first enters the vagina and cause an infection. With time, this infection can move into the pelvic organs- uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. In rare cases, the infection can be blood ...
Is clindamycin a macrolide?
Clindamycin is a member of the macrolide family and has good antibacterial activity. It is an effective drug for PID.. Tablets is taken as 300mg four times daily. Azithromycin (Zithromax) is another member of the macrolide family.
What are the risk factors for pelvic inflammatory disease?
Risk factors of pelvic inflammatory disease. The following factors increases your risk of developing PID: having an STI or a previously poorly treated STI from gonorrhoea, chlamydia, and mycoplasma. douching. multiple sexual partners.
Is quinolone good for chlamydia?
Quinolones as exemplified by ofloxacin and ciprofloxacin are good antibacterial activity against a wide range of infecting agents especially chlamydia. They are used in combination with other antibiotics. Ciprofloxacin tablets are taken as 500mg twice-daily. Ofloxacin is taken as 400mg daily.
What is PID in medical terms?
The diagnosis of PID is clinical, with imaging and more invasive studies reserved for cases of diagnostic uncertainty or concern for complications (e.g., tubo-ovarian abscess). 8, 13 Therefore, physicians should make the diagnosis and initiate treatment for PID if no other diagnosis is more likely in sexually active women younger than 25 years or in older women at risk for STIs who present with pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis and one or more of the clinical findings shown in Figure 1. 8
Why is PID underdiagnosed?
PID is often underdiagnosed because of the wide variation and severity of symptoms. 8 Patients may be asymptomatic. Many women with tubal factor infertility have histologic evidence of PID despite having no previous diagnosis. 11, 12 The cardinal symptom of PID is the abrupt onset of lower abdominal or pelvic pain in a sexually active woman. 8 Symptoms can be subtle with mild bilateral lower abdominal pain that worsens with coitus, abnormal uterine bleeding, increased urinary frequency, dysuria, or abnormal vaginal discharge. Fever may also occur, but it is not the dominant symptom. Right upper quadrant pain that is worse with movement and breathing is caused by inflammation and adhesions of the liver capsule, such as in perihepatitis (i.e., Fitz-Hugh–Curtis syndrome).
What is PID in a sex?
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) includes an array of infectious processes that damage the endometrium, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and pelvic peritoneum. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) cause most PID cases, but organisms associated with bacterial vaginosis (BV) have also been implicated.
How long does metronidazole last?
Mild to moderate disease can be treated in an outpatient setting with a single intramuscular injection of a recommended cephalosporin followed by oral doxycycline for 14 days. Additionally, metronidazole is recommended for 14 days in the setting of bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis, or recent uterine instrumentation.
Is metronidazole used for trichomonas?
The CDC currently recommends that the addition of metronidazole be considered in all outpatient treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease and with coinfections of trichomonas and bacterial vaginosis or in the setting of recent uterine instrumentation.
What is the function of Chlamydia trachomatis?
Damage to the epithelium by infection (typically Chlamydia trachomatis or N. gonorrhoeae) allows organisms to ascend the upper genital tract from the cervix. A variety of microbes have been isolated in PID. 9 The role of Mycoplasma genitalium, Gardnerella vaginalis, and Ureaplasma urealyticum in PID is not clear.
Do women with PID have HIV?
Women with PID who also have HIV have similar symptoms and respond similarly to treatment as those without HIV; however, women with HIV are at increased risk of tubo-ovarian abscesses and have higher rates of mycoplasma and streptococcal infections. Therefore, they need to be followed closely for response to treatment. 30
What is a PID?
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection and inflammation of a woman's pelvic organs including the uterus (womb), Fallopian tubes (tubes), ovaries, and cervix. PID is very common and is estimated to affect around 1 million women every year in the US.
How old do you have to be to get a PID?
Are younger than 25 and have sex. PID is most common in women 15 to 24 years old. Have more than one sex partner or have a partner who has multiple sexual partners. Douche. Douching can push bacteria into the reproductive organs and cause PID.
How many women get PID every year?
PID is very common and is estimated to affect around 1 million women every year in the US. Pelvic inflammatory disease usually develops as the result of spread of a sexually-transmitted disease ( STD ).
What is pelvic inflammatory disease?
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an inflammatory and infectious disease, and is a complication of a sexually transmitted disease (STD) such as gonorrhea . Common symptoms of pelvic inflammatory disease are. Pelvic pain that radiates to the abdomen. An abnormal vaginal discharge.
What is the most common sexually transmitted disease in the U.S.?
Chlamydia is the most common sexually transmitted disease in the U.S. Signs and symptoms of chlamydia, a bacterial infection, include vaginal discharge, abdominal pain, burning with urination, blood in the urine, and feelings of urinary urgency and frequency. Untreated chlamydia can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), ...
What are the side effects of IUD?
Side effects of the IUD include spotting, infection, infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and heavy menstrual bleeding. Risks and complications of the IUD are miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, pelvic inflammatory disease, and increased menstrual bleeding.
Why do people wear condoms?
Condoms provide a way for men and women to prevent pregnancy. There are many methods of birth control; some types also protect against sexually transmitted diseases. Condoms are one type of birth control that in addition to preventing pregnancy also prevent the spread of STD's.
What is a PID?
Pelvic inflammatory disease, often abbreviated as PID, is a bacterial infection of the female reproductive organs - specifically the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries - leading to inflammation or swelling of those organs. If left untreated, PID can lead to an inability to get pregnant due to scar tissue formation, ...
How do you know if you have a PID?
Common symptoms of PID include: Fever and chills. Pain, which could also be described as fullness or pressure, in the area between the hipbones or lower abdomen (walking may make the pain worse) Discharge that is not a normal texture, color and/or odor coming from the vagina. Painful sex.
Why is it important to finish antibiotics?
It is very important that the antibiotics are finished by both partners so that the infection is treated completely. Failure to finish all antibiotics could result in the infection coming back. Pelvic inflammatory disease is an infection of the female reproductive organs.
Can you get pregnant with PID?
If left untreated, PID can lead to an inability to get pregnant due to scar tissue formation, ec topic pregnancy (a pregnancy that is found outside of the uterus) due to damage to the fallopian tubes, and/or long-term pelvic pain due to damage to the bowel and bladder. 3:33.
How to treat pelvic inflammatory disease?
Treatment. Once pelvic inflammatory disease is diagnosed, women are treated with antibiotics. Depending on the cause of PID, antibiotics may be given via shot or by mouth (or a combination of both). For mild cases of PID, this is all done on an outpatient basis.
Can a pelvic infection be sexually transmitted?
There are various types of bacteria that can cause pelvic inflammatory disease. These bacteria may be sexually transmitted, such as gonorrhea or chlamydia, or non-sexually transmitted. Any vaginal infection that goes untreated increases the risk of developing PID, since the infection can easily spread up through the cervix into ...
Can chlamydia cause bleeding?
Bleeding between periods. However, women with chlamydia infections may not have any symptoms. Women at higher risk, such as those who became sexually active before 20, who previously had PID, with multiple partners, or with partners with known chlamydia infection, should be tested routinely. Treatment.