What does systemic treatment mean?
Other types of systemic therapy include: Hormone therapies Immunotherapies Targeted therapies
What does systemic therapy mean?
Jan 26, 2022 · Systemic therapy is a form of psychotherapy that focuses on how an individual's personal relationships, behavior patterns, and life choices …
What are some uses for systemic drugs?
Jan 04, 2022 · Systemic therapy is a therapeutic method that analyzes and treats clients from an individual and relational perspective. While some theories focus on behavior and others on emotion, systemic...
What are examples of systemic medicines?
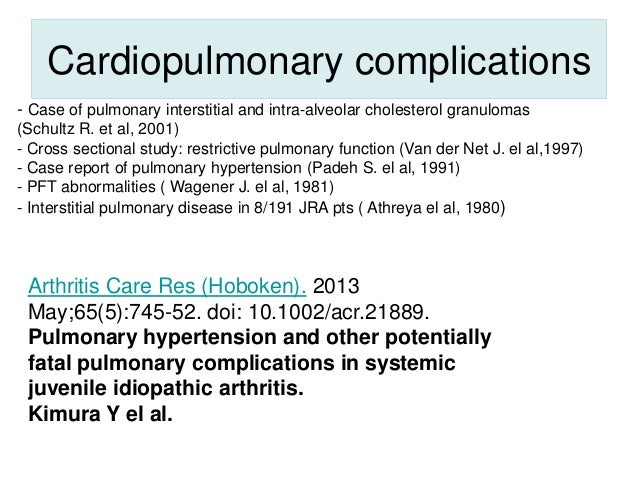
Definition. I. Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment and is the primary treatment for systemic malignancies (e.g., lymphomas, leukemias) and metastatic tumors. II. It is most effective against small tumors and least effective against large tumors, unless they are extremely sensitive (e.g., lymphoma, TVT). A.
What is meant by systemic treatment?
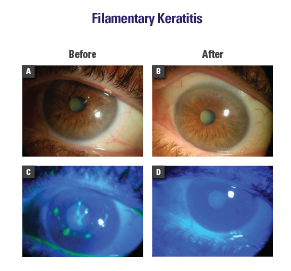
Systemic treatments are drug therapies that work throughout the whole of the body. They can be given as an injection, infusion, or oral medication. They include chemotherapy, hormonal treatment, targeted therapy or immunotherapy. The type of treatment we give will depend on the type of cancer.
What is the difference between local and systemic treatment?
Local therapy is what is done to the breast. Surgery and radiation therapy are examples of local therapy. Systemic therapy affects the whole body. In early, potentially curable breast cancer, systemic therapy reduces the likelihood that the tumor will come back in other parts of the body.
Why is it considered a systemic treatment?
Systemic therapy refers to any type of cancer treatment that targets the entire body. For example, chemotherapy – the most common form of systemic cancer treatment – circulates throughout the bloodstream to destroy cancerous cells in multiple locations.
What is the difference between systemic and chemotherapy?
When chemotherapy drugs travel through the bloodstream to reach cells throughout the body, it is known as systemic chemotherapy. When chemotherapy drugs are directed to a specific area of the body, it is called regional chemotherapy.
What is the difference between systemic and local infection?
An infection that is in the bloodstream is called a systemic infection. An infection that affects only one body part or organ is called a localized infection.Jan 16, 2021
What is systemic infection?
A systemic infection earns its name by being spread throughout the systems of the body. It can be compared to a local infection, in which the pathogen or symptoms are localized to one area. Such infections are sometimes known as local infections.Dec 27, 2020
What type of chemotherapy is systemic?
Systemic chemotherapy (chemo) uses anti-cancer drugs that are injected into a vein or given by mouth. These drugs travel through the bloodstream to all parts of the body.Jul 26, 2019
What is systemic therapy in pharmacy?
Systemic administration is a route of administration of medication, nutrition or other substance into the circulatory system so that the entire body is affected.
Is chemotherapy a systemic therapy?
Systemic therapies are drugs that spread throughout the body to treat cancer cells wherever they may be. They include chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, targeted drugs, and immunotherapy.
When is systemic chemotherapy used?
Systemic chemotherapy affects cancer cells located in the bladder as well as in different parts of the body, so it is most often used to treat patients with advanced bladder cancer.Oct 9, 2017
Is radiotherapy a systemic treatment?
Systemic therapy involves treatment that travels through your entire body rather than being aimed at one area. Systemic radiation therapy uses radioactive drugs (called radiopharmaceuticals or radionuclides) to treat certain types of cancer, including thyroid, bone, and prostate cancer.Dec 27, 2019
What is systemic therapy?
Systemic therapy is a therapeutic method that analyzes and treats clients from an individual and relational perspective. While some theories focus on behavior and others on emotion, systemic therapy emphasizes the importance of interactions. Systemic therapists strive to assess and treat a client's presenting problem within the context ...
What is a symmetrical relationship?
Symmetrical and Complementary Relationships 1 A symmetrical relationship occurs when both individuals within the relationship are equal in terms of their role. There is a sense of fairness regarding the distribution of power within the relationship. 2 A complementary relationship describes two individuals who assume roles that balance one another (e.g., pursuer/distancer).
Why do Amy and Mark argue?
Amy and Mark are seeking couples therapy to help resolve their communication issues. The couple reports that they often argue over ''little things''. Amy describes Mark as ''self-centered'', and Mark feels that Amy is ''over-emotional''. The couple is receiving treatment from Jennifer, a systemic therapist.
What is homeostasis in a family?
Homeostasis refers to a family's norm. This term describes a family's sense of balance. Naturally, families want to maintain balance. The term self-correction explains how families have the ability to maintain their homeostasis or balance.
What is positive feedback?
Positive feedback occurs when a piece of information is introduced into the system and maintains homeostasis. Conversely, negative feedback occurs when a piece of information enters the system and disrupts homeostasis. Negative feedback loops are essential for creating first and second-order change.
What is a double bind?
When one person presents another person with a request but rejects their attempt to fulfill it, a double bind has been created. A wife says to her husband, ''You're never romantic''; therefore, the husband plans a romantic dinner. The wife tells him, ''You're only doing this because I told you to.'' The husband is in a double bind because his wife has presented him with no possible way of fulfilling her request.
What is the treatment for spirochetes?
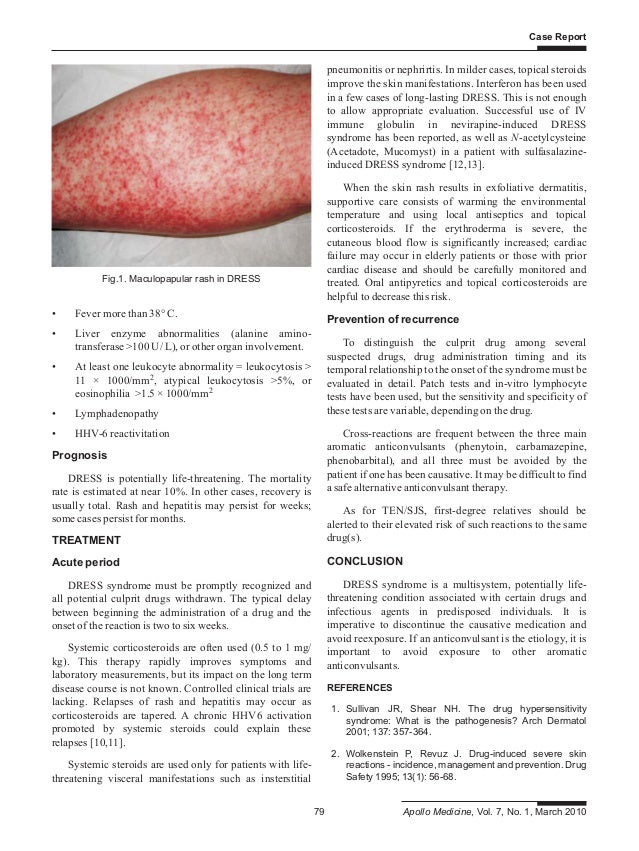
Systemic treatment can include antibiotics, exogenous progestagens, anti-inflammatories, tocolytic agents and medications that improve uterine perfusion.
What is TDDS in medicine?
TDDS are administration and controlled-release pathways for drugs used either for localized treatment of tissues underlying the skin or for systemic treatments. The purpose of using TDDS is to extend the permeation of therapeutic molecules through the skin, without destroying this natural and protective skin barrier.
Why is nasal route of administration important?
The nasal route of administration can be used for both local treatment and for systemic treatment, the local treatment is important in treating various nasal conditions such as rhinitis. The nasal route of administration can also be used to deliver drugs to the systemic circulation, because it has many advantages in comparison with other route of administrations, for example, it avoids the first-pass metabolism associated with the oral route of administration, which is important for drugs with low metabolic stability. In addition, the nasal route has rapid absorption and provides an easy way of administration (Gibson, 2016). Nasal formulations require a proper choice of excipients used, administration device, and avoidance of any incompatibilities in the formulation. Other important factors include the selection of proper preservative in the solutions and suspensions to prevent the microbial growth, e.g., benzalkonium chloride (BKC) is usually used as a preservative in nasal formulations. In cases where a poor penetration is observed, such as with proteins or peptides, a penetration enhancer may be used to increase the nasal absorption, examples of penetration enhancers are cyclodextrins and liposomes. It is also important to ensure the stability and compatibility of the substances used in the formulation (Davis and Illum, 2003; Bernstein, 2000 ).
What is griseofulvin used for?
Griseofulvin is one of the drugs of choice when systemic treatment is needed for dermatophyte infections caused by Microsporum spp. and Trichophyton spp. in dogs and cats. It is sometimes used in combination with topical therapy. Griseofulvin is not effective for the treatment of yeasts or bacteria. At least 4 weeks, and sometimes 3 months or more, are needed for successful therapy. Its use has been replaced by azole antifungal drugs in many cases (itraconazole, fluconazole, etc.). It also has a predilection to accumulate in inflammatory sites of the skin and may be effective for treating some noninfectious, inflammatory dermatoses other than dermatomycosis. Because of the frequent use of azole antifungals (e.g., fluconazole, itraconazole) the used of griseofulvin has declined.
How does interstitial fluid pressure affect cancer?
Thus increased interstitial fluid pressure leads to decreased fluid flow into the tumor node and therefore less uptake of drugs into the tumor. Cancer cells are therefore exposed to a lower effective concentration of therapeutic agent than normal cells, lowering the therapeutic efficiency. Several studies indicate that high interstitial fluid pressure in the tumor is correlated with poor prognosis [ 18 ].
What are the properties of azoles?
The azoles have a similar mechanism of action and share other properties such as spectrum of activity, pharmacokinetics, tissue penetration, and adverse effect profiles. Proper understanding of these factors is most likely to result in successful treatment with minimal adverse effects. •.
Is the lung a drug delivery site?
The lung is an attractive drug delivery site with the capability of being used for specific, targeted, local therapy in addition to systemic treatment. Therapeutics given by other drug delivery routes often fail to adequately treat respiratory diseases and targeted therapy appears to be the ideal solution in many cases. The respiratory system has been successfully used to clinically deliver a number of therapeutics via various inhalers, nebulizers, and spray devices. However, it is a complex and diverse system, and continues to present a unique drug delivery challenge. Here, we present an overview of all aspects of the lung as a drug delivery site for nanotherapeutics, and current challenges and strategies to design an ideal lung-specific therapeutic will be explored. A number of respiratory diseases have a genetic basis and gene therapy approaches for these conditions are also discussed. Nanotechnology approaches to treating various pulmonary diseases are presented, and a number of new therapeutics being investigated in both early stage research and in the clinic, particularly gene-based inhalable therapeutics, are described.
What is systemic treatment?
In medicine systemic treatment refers to drugs or therapies that potentially affect the entire body. Local treatment addresses the disease or injury at a specific point. Cancer can be treated both ways.
What is palliative therapy?
palliative therapy / reduction in severity of symptoms. neoadjuvant therapy before surgery / induction therapy before radiation. adjuvant therapy after primary treatment. to extend the survival time of the patient.
How much of cancer is metastatic?
Either the body’s immune system or medical intervention prevents them from spreading broadly. Experts estimate 50% of discovered (diagnosed) cancers spread so far they are considered metastatic. Surgery and radiation are impractical for addressing distributed cancer.
Why do we use multidrug regimens?
More commonly, multidrug regimens incorporating drugs with different mechanisms of action and different toxicities are used to increase efficacy, reduce dose-related toxicity, and decrease the probability of drug resistance.
What is the objective of neoadjuvant therapy?
Another objective can be measuring response to neoadjuvant therapy and/or assessing the cancer when it is removed surgically , allowing for a more accurate prediction of the potential value of adjuvant therapy. Neoadjuvant therapy is increasingly used in breast, ovary, colorectal, lung, gastric, and other cancers.
What is the best treatment for prostate cancer?
Hormone Therapy. Hormone therapy uses agonists or antagonists to influence the course of cancer. It may be used alone or combined with other therapies. Hormone therapy is particularly useful in prostate cancer, which grows in response to androgens.
How long does tamoxifen last after breast cancer surgery?
The most common use of hormone therapy is in breast cancer. Tamoxifen and raloxifene are typically given for several years after breast cancer surgery (adjuvant therapy) and substantially reduce risk of cancer recurrence.
What is PD-1 used for?
PD-1 and PD-1L antibodies are now widely used to treat solid cancers but not blood and bone marrow cancers. Another example of active immune therapy is instilling bacille Calmette–Guérin (BCG) in the bladder of patients with bladder cancer.
Do cytotoxic drugs kill cancer cells?
Cytotoxic drugs damage DNA and kill many normal cells as well as cancer cells. Antimetabolites such as fluorouracil and methotrexate are cell cycle–specific and have no linear dose-response relationship. In contrast, other drugs (eg, DNA cross-linkers, also known as alkylating agents) have a linear dose-response relationship, killing more cancer cells at higher doses. At high doses, DNA cross-linkers damage the bone marrow.
What is monoclonal antibody?
They can also be directed toward lineage-specific antigens also present on normal cells. Some monoclonal antibodies are given directly; others are linked to a radionuclide or toxin. These linked antibodies are referred to as antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs).
Get Involved
If you are a clinician interested in collaborating with the Systemic Treatment Program, email the Drug Formulary Team.
Drug Formulary
Find Ontario cancer drug and regimen monographs, and symptom and side effect management information.
What is systemic treatment?
Systemics. Systemic treatments, aimed at those with varying degrees of psoriasis and psoriatic disease severity, are prescription drugs that work throughout the body. They are also used in those who are not responsive or are unable to tolerate topical treatments or phototherapy.
How are biologics given?
Biologic drugs, or biologics, are given by injection (shot) or intravenous (IV) infusion (a slow drip of medicine into your vein). A biologic is a protein-based drug derived from living cells cultured in a laboratory.