Treatments for LRTIs in the hospital may include:
- Intravenous fluids
- Humidified oxygen
- Ventilation support, i.e., high flow oxygen, CPAP, BiPAP or mechanical ventilation, if severe respiratory insufficiency develops
How do you cure upper respiratory infection?
The following may help decrease your symptoms:
- Decongestants help reduce nasal congestion and help you breathe more easily. If you take decongestant pills, they may make you feel restless or cause problems with your sleep. ...
- Cough suppressants help reduce coughing. ...
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. ...
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. ...
What antibiotic is best for upper respiratory infection?
When Antibiotics Are Appropriate
- Sinusitis. A sinus infection, or sinusitis, is the inflammation of the mucous membranes of the sinuses due to a viral or bacterial infection.
- Bronchitis. Acute bronchitis is a lower respiratory tract infection. ...
- Other Upper Respiratory Tract Infections. There are a few other reasons you might be prescribed antibiotics for an upper respiratory infection.
How long do RSV symptoms last?
RSV infections are common in epidemics that last anywhere from late fall to early spring. An RSV infection and its symptoms, fever included, usually last anywhere from 7 to 14 days. However, if any complications occur, the virus can last even up to three weeks.
What can antibiotics help treat respiratory infections?
“Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections, such as pneumonia, and won't help viral illnesses like colds, flu and most sore throats,” says Emily Langer, a Mayo Clinic Health System Emergency Medicine physician assistant. Clinicians should not prescribe antibiotics for patients with bronchitis.

What is the best antibiotic for lower respiratory tract infection?
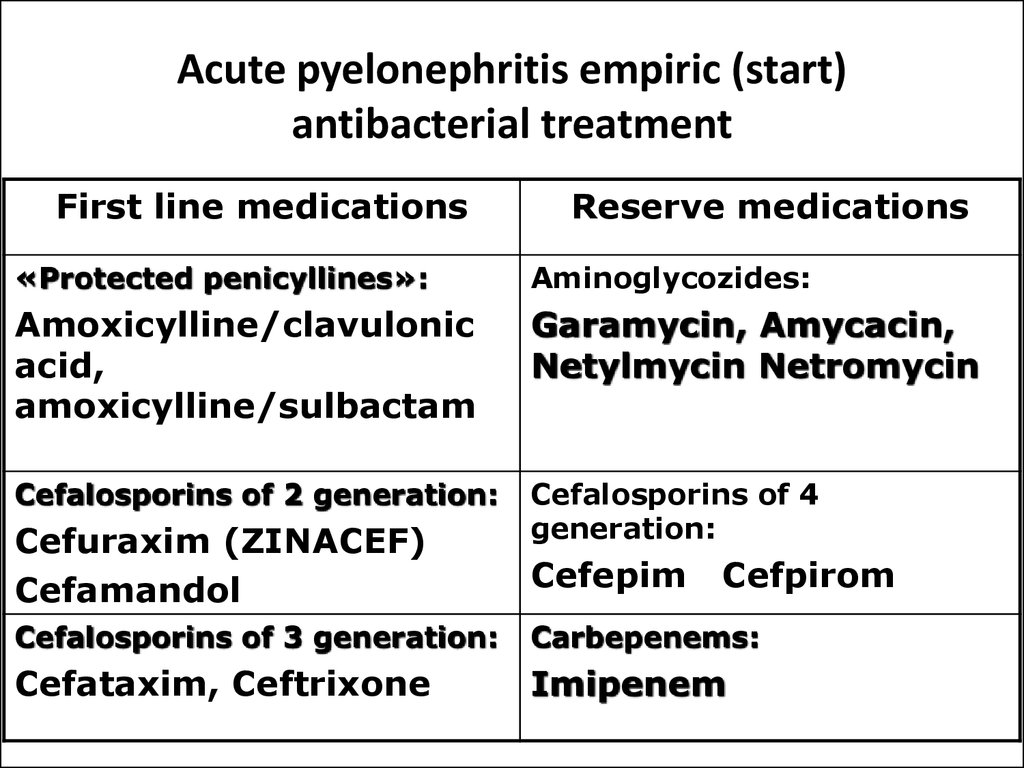
Which antibiotics should be used in patients with LRTI? Tetracycline and amoxicillin are first-choice antibiotics. In case of hypersensitivity, newer macrolides, such as azithromycin, roxithromycin or clarithromycin, are good alternatives in countries with low pneumococcal macrolide resistance.
What are the signs of a lower respiratory infection?
Symptoms of a more serious LRTI include: Fever. Severe cough. Rapid breathing or difficulty breathing....SymptomsCongestion or runny nose.Dry cough.Sore throat.Low-grade fever.Mild headache.
How long does it take for a lower respiratory infection to go away?
Recovery time for a lower respiratory tract infection varies from person to person. According to the American Lung Association, a healthy young adult can recover from a lower respiratory tract infection, such as pneumonia, in around 1 week. For older adults, it may take several weeks to make a full recovery.
Do you need antibiotics for lower respiratory infection?
The majority of antibiotics are prescribed in primary care, mainly for the treatment of acute respiratory tract infections [2, 3]. However, because of their limited effectiveness in only a limited number of infections, primary care guidelines recommend a restrictive use of antibiotics in respiratory infections [4].
What is the fastest way to get rid of a lower respiratory infection?
Treatment OptionsLifestyle. Ingest plenty of fluids, and get plenty of rest. Using a humidifier to breathe warm, moist air may provide relief. ... Medications. Since most LRTIs are viral, medications are generally not used in treatment. ... Other Treatments. In the case of serious LRTIs, treatment in a hospital may be necessary.
What is the most common cause of lower respiratory tract infection?
The number one cause of lower respiratory tract infections are viruses that invade the respiratory tract. Bacteria are the next most common cause. In bronchitis, the most common viruses are influenza (“the flu”) and the rhinovirus (which causes the common cold).
What are the respiratory symptoms of Covid?
Mild and Moderate Cases About 80% of people who have COVID-19 get mild to moderate symptoms. You may have a dry cough or a sore throat. Some people have pneumonia, a lung infection in which the alveoli are inflamed. Doctors can see signs of respiratory inflammation on a chest X-ray or CT scan.
Is Covid cough upper or lower respiratory?
Respiratory infections such as COVID-19 start in the upper respiratory tract and, in serious cases, can move into the lower respiratory tract. Respiratory infections are among the most common diseases that affect humans.
How is lower respiratory tract infection diagnosed?
DiagnosisPulse Oximetry: this test uses a small sensor that attaches to the finger or ear. ... Chest X-ray: creates an image of the lungs. ... Blood Test: a sample of blood is taken and inspected in a laboratory for the presence of viruses, bacteria, or other organisms.More items...
What is the best treatment for LRTI?
Since most LRTIs are viral, medications are generally not used in treatment. However, certain over-the-counter medicines may provide some relief from symptoms: 1 Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or aspirin can relieve pain and fever 2 Acetaminophen can also provide relief from pain and fever 3 Using a bronchodilator inhaler can help wheezing and shortness of breath 4 If an LRTI is bacterial, antibiotics may be prescribed, depending on how serious the infection is and your overall health. These treat the bacterial cause of the infection.
What is the best medicine for a fever?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or aspirin can relieve pain and fever. Acetaminophen can also provide relief from pain and fever. Using a bronchodilator inhaler can help wheezing and shortness of breath.
What is the best treatment for bacterial pneumonia?
The treatment of bacterial pneumonia is selected by considering the age of the patient, the severity of the illness and the presence of underlying disease. Amoxycillin and doxycycline are suitable for many of the lower respiratory tract infections seen in general practice. Introduction.
How long should you wait to treat Legionella?
Treatment for Legionella should be for at least 14 days. Prevention of respiratory tract infections.
Can bronchitis be treated as an acute exacerbation?
In these circumstances, the patient should be treated as for an acute exacerbation of chronic bronchi tis. Acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis.
Can sputum culture be used in isolation?
Although these organisms can cause infections, a positive sputum culture in isolation is not an indication for commencing therapy. The only benefit from culture is to identify the presence of a coloniser, and hence a potential cause of infection, which is resistant to one of the usual antibiotics used in the respiratory tract.
Do antibiotics help with pneumonia?
Pneumonia. Lower respiratory tract infection. Article. Authors. Summary. Antibiotics do not help the many lower respiratory infections which are caused by viruses. While acute bronchitis often does not require antibiotic therapy, antibiotics can be given to patients with acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis.
How to manage respiratory infection?
Respiratory infection are usually viral, in which case you will simply have to wait it out until your immune system fights off the virus. In the meantime, there are things you can do to manage your symptoms. These include getting lots of rest, drinking lots of water, sleeping on an extra pillow if you have a bad cough, ...
What are the most common lower respiratory infections?
How do you treat a lower respiratory infection? Two of the most common lower respiratory infections are bronchitis and pneumonia. If you are feeling feverish, and if you have body aches, a cough with phlegm, congestion, tightness in the chest and a loss of appetite, you may have one of these conditions. The treatment of lower respiratory tract ...
What antibiotics are used for pneumonia?
Amoxicillin, doxycycline, erythromycin and roxithromycin are a few antibiotics that are commonly used to treat pneumonia. If you have a pre-existing health condition that weakens your immune system, such as HIV, or heart, lung, liver or kidney disease, or if you are undergoing chemotherapy, your doctor may prescribe precautionary antibiotics, ...
Can antibiotics cause respiratory infections?
Doctors are often hesitant to treat lower respiratory infections with antibiotics, since most of the time the infection is not caused by bacteria. In addition, if you use overuse antibiotics when treating minor infections, your body may develop resistance to the antibiotic, and the antibiotic will be less effective if you need to use it ...
What is the best treatment for bacterial infections?
For the initial oral chemotherapy of bacterial infections of the lower respiratory tract (chronic bronchitis, pneumonia) the effective and well tolerated cephalosporins, macrolides and amoxicillin plus beta-lactamase-inhibitor are recommended.
What antibiotics are used for Legionella?
If Legionella, Mycoplasma or Chlamydia spp., so-called 'atypical' pathogens, are involved, macrolide antibiotics are the therapy of first choice. Special attention should be given to the increase in resistance against cotrimoxazole (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole) and tetracyclines.
Does bronchitis require antibiotics?
Acute bronchitis is usually a viral infection which, unless there is a special disposition, does not require antibiotic therapy. For the initial oral chemotherapy of bacterial infections of the lower respiratory tract (chronic bronchitis, pneumonia) the effective and well tolerated cephalosporins, m ….
Is bronchitis a viral infection?
A guide to the treatment of lower respiratory tract infections. Acute bronchitis is usually a viral infection which, unless there is a special disposition, does not require antibiotic therapy.
How to prevent infections?
The best way to prevent infections is via vaccinations. Vaccination against pneumonia and influenza is commonly given to groups, such as the elderly or very young, who are most at risk.
What is the best way to check for pneumonia?
Pneumonia. An x-ray can be used to check for pneumonia and is likely to show shadowing on the lungs if the infection is present. Antibiotics are used to treat pneumonia and different approaches should be used according to the risk of the person and severity of the illness.
What is the most common cause of bronchitis?
Less than 10% are linked with bacteria. Bronchiolitis is most often caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in infants and babies.
What is the difference between CAP and hospital pneumonia?
There are three types of pneumonia: Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), which is contracted from coming into contact with the infection in daily life. Hospital-acquired pneumonia, which is contracted after a period of time in hospital.
How long does pneumonia last?
Pneumonia. Pneumonia is an infection of the lung, the most frequent cause of death due to infection in Europe and the USA. It causes symptoms for 3-4 weeks and is more common in very young children and elderly adults. There are three types of pneumonia:
What are the causes of infection?
Infections are caused by tiny organisms, known as bacteria or viruses. There are millions of organisms that surround us. Viruses are carried in tiny droplets and are passed between people when someone with the virus coughs or sneezes. People who are infected produce antibodies to fight the virus. Once they have fought off this strain, they will be able to fight it if infected again. However, over time, the virus can change into different forms, which means the body may not have the right antibodies to fight it again.
Can bronchitis cause lung problems?
The main symptom of acute bronchitis is a cough that cannot be explained by an existing long-term lung condition. Bronchiolitis causes babies and infants to have prolonged symptoms of wheeze and cough, lasting for weeks and months after the first symptoms.
Types of lower respiratory infections
The lower respiratory tract is made up of the windpipe, large airways of the lungs, small airways of the lungs, and air sacs of the lungs. The lower respiratory tract is important in delivering oxygen to the blood. During colder months, the lower respiratory tract can become infected with viruses and, sometimes, bacteria.
Causes of lower respiratory infections
The number one cause of lower respiratory tract infections are viruses that invade the respiratory tract. Bacteria are the next most common cause.
Symptoms of lower respiratory infections
Common symptoms of all lower respiratory tract infections are cough, fever, and shortness of breath. Depending on the type of illness, your age, and other medical problems, these symptoms can range from mild to severe.
Diagnosing and treating lower respiratory tract infections
In most cases, lower respiratory tract infections can be diagnosed clinically. This means that a healthcare provider can make the diagnosis by asking about your symptoms and listening to your lungs. More testing or imaging is not always needed.
Lower respiratory infections vs. upper respiratory infections
The difference between lower respiratory tract infections and upper respiratory tract infections is the location of the infection and symptoms. The upper respiratory tract is made up of the nose, sinuses, throat, and voice box. Symptoms of upper respiratory tract infections include sneezing, runny nose, sore throat, and sinus pressure.
The bottom line
Lower respiratory illnesses are very common during the colder months and can affect all ages. Most of the time, they are caused by viruses and do not need specific medications. Pneumonia caused by bacteria is an exception — it requires antibiotics.
How to cure a respiratory infection?
1. Inhaling steam. This one is definitely the best home remedy for respiratory tract infections. All you need to do is boil one litre of water and add a piece of camphor to it. Now inhale this steam for 10 to 15 minutes. It will help in clearing blocked respiratory tracts by melting mucus membranes.
How to help a child with respiratory tract infection?
Add a lemon's juice to a glass of warm water with some honey and give them this drink twice or thrice a day. You could also give them two spoons of honey in a glass of milk for the same effect. Home remedies for respiratory tract infections : Give your kids some honey with milk . Photo Credit: iStock.
What is a viral infection in the respiratory tract?
HIGHLIGHTS. A viral infection in the respiratory tract is known as an RTI or respiratory tract infection. This one is a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract including the sinuses, tranchea, larynx and pharynx. Such infections spread easily to one another.
What is a viral infection?
A viral infection in the respiratory tract is known as an RTI or respiratory tract infection. This one is a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract including the sinuses, tranchea, larynx and pharynx. Such infections spread easily to one another. They include symptoms like wheezing, running nose, congestion, cough, ...
How to get rid of congestion in nasal cavity?
Boil a few eucalyptus leaves in some water and inhale its steam. You could also try sniffing some eucalyptus oil for clearing nasal congestion.
How to clear nasal passages?
It helps in thinning the mucus, thereby making it easier for you to expel it. All you need to do is take a glass of lukewarm water and add one teaspoon of salt to it. Now dissolve the salt in this and gargle with this every morning. You could also try preparing this solution, putting it into your nostrils and passing it through your nose every day to clear the nasal passages .
Is ginger good for respiratory problems?
You name the ailment and ginger is the solution. And for respiratory problems, it is one of the most effective home remedies. Antiviral, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties of ginger effectively fight the root cause of the respiratory tract infection. You can chew a few slices of ginger every day with some salt.

Treatment
- Antibiotics do not help the many lower respiratory infections which are caused by viruses. While acute bronchitis often does not require antibiotic therapy, antibiotics can be given to patients with acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis. The indications for treatment are increased dyspnoea, and an increase in the volume or purulence of the sput...
Research
- A meta-analysis2 also found a small, but statistically significant, improved outcome in the patients given antibiotics.
Diagnosis
- It is reasonable to start antibiotics when a patient fulfils the criteria mentioned above. In many infections, a culture provides useful information for choosing an antibiotic, but this can be misleading in patients with acute on chronic bronchitis. The respiratory tract of these patients is usually colonised with one or more of the recognised respiratory tract pathogens, Streptococcu…
Example
- For example, an acute illness characterised by fever, productive cough with blood-stained sputum, signs of lobar consolidation and a neutrophilia has been considered diagnostic for Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. A dry cough, low grade fever, extra pulmonary symptoms and diffuse infiltrates on chest X-ray were considered indicative of an infection due to Mycoplasma pneumo…
Clinical significance
- Presence of underlying disease The most common underlying condition of significance is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The airways are colonised with organisms such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis making infection with these organisms more likely. Similarly, patients with diabetes mellitus, alcoholism, renal disease, alter…
Prevention
- Prevention of respiratory tract infections Some respiratory tract infections can be prevented by the use of vaccination. Pneumococcal polyvalent vaccine is recommended for those at risk i.e. asplenia, the immuno compromised (in particular, patients with HIV, nephrotic syndrome, multiple myeloma, lymphoma, Hodgkin's disease and organ transplantation), patients with chronic illnes…