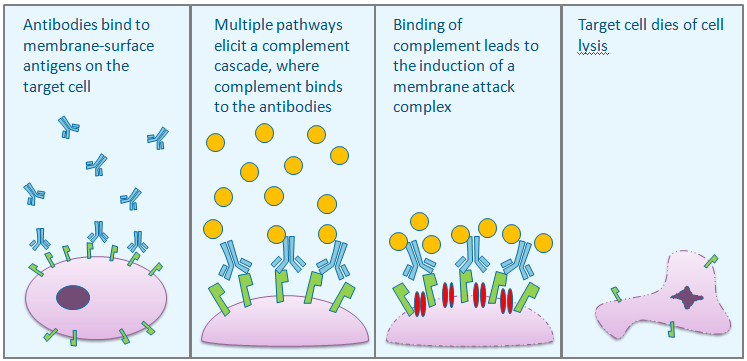
When an antibody binds to a toxin it becomes an antitoxin. The binding generally disables the toxin's chemical action. When an antibody binds to a virus particle's outer coat or the cell wall of a bacterium it can stop the virus or bacterium's movement through cell walls.
Are there side effects of monoclonal antibody treatment?
Treatment with COVID-19 monoclonal antibodies is done through a one-time intravenous (IV) infusion. Another option for COVID-19 therapy is an antiviral called Remdesivir. Remdesivir is approved by the FDA and helps reduce the effects of COVID-19. Remdesivir is given by an intravenous (IV) infusion over three (3) consecutive days.
How long does the antibody infusion take?
Jul 05, 2021 · It was not until 1975 when the generation of mAbs for use in humans was established by Drs Kohler and Milstein.[1][2] The concept of mAbs as therapeutic options is modeled after the immune system, particularly the humoral immunity (i.e., antibodies) generated by the immune system in response to foreign antigen exposure.[3] Modern-day medicine has …
What to expect from monoclonal antibody treatment?
Jan 06, 2022 · Given that COVID-19 vaccination provides strong protection against severe disease and need for hospitalization, monoclonal antibody therapy is an option for certain high-risk patients with COVID-19. THE FDA expanded EUA of two monoclonal antibody treatments to include patients as young as newborns. Criteria for younger pediatric patients includes a …
What are monoclonal antibodies and how do they work?
Sep 02, 2021 · Aruchamy said the treatment has lab-created antibodies in it that specifically target the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. The treatments help the patient by supplying concentrated doses of one or two...

How do monoclonal antibodies work against COVID-19?
Monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 may block the virus that causes COVID-19 from attaching to human cells, making it more difficult for the virus to reproduce and cause harm. Monoclonal antibodies may also neutralize a virus.Mar 31, 2022
Are antibodies beneficial during the COVID-19 pandemic?
When reinfections or breakthrough infections happen, having antibodies plays an important role in helping prevent severe illness, hospitalization, and death. For many diseases, including COVID-19, antibodies are expected to decrease or “wane” over time.Nov 10, 2021
Who could benefit from monoclonal antibody therapy to prevent COVID-19?
See full answerVaccines are the best way to protect against COVID-19. But some people with weakened immune systems do not produce enough antibodies after vaccination, and others are severely allergic to the vaccine. The FDA recently authorized Evusheld, a pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) monoclonal antibody therapy developed by AstraZeneca, which should help prevent COVID-19 in these populations.To be eligible for Evusheld, individuals must be 12 years or older and have a moderately to severely weakened immune system, or have a history of severe adverse reactions to the COVID-19 vaccine or its components. In addition, the therapy cannot be given to someone with a current SARS-CoV-2 infection, or who has been recently exposed to someone who is infected. Evusheld is given as two consecutive shots, and evidence suggests it can help prevent symptomatic infection for at least six months.Apr 1, 2022
How long do COVID-19 antibodies last?
At this time, it is unknown for how long antibodies persist following infection and if the presence of antibodies confers protective immunity.Jan 31, 2022
Do I need the COVID-19 vaccine if I still have antibodies?
Yes, the COVID-19 vaccines are recommended, even if you had COVID-19.Nov 23, 2021
Can you get COVID-19 if you already had it and have antibodies?
It is important to remember that some people with antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 may become infected after vaccination (vaccine breakthrough infection) or after recovering from a past infection (reinfected).Nov 10, 2021
Is there a monoclonal antibody therapy for post Covid-19 exposure?
FDA authorizes bamlanivimab and etesevimab monoclonal antibody therapy for post-exposure prophylaxis (prevention) for COVID-19 | FDA.Sep 16, 2021
Who might benefit from dexamethasone if they have Covid-19?
Dexamethasone is a corticosteroid used in a wide range of conditions for its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant effects.It was tested in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in the United Kingdom’s national clinical trial RECOVERY and was found to have benefits for critically ill patients.Oct 16, 2020
Who are some groups at higher risk for serious illness from Covid-19?
Some people may be at higher risk of severe illness. This includes older adults (65 years and older) and people of any age with serious underlying medical conditions. By using strategies that help prevent the spread of COVID-19 in the workplace, you will help protect all employees, including those at higher risk.
How long do antibodies last in people who have mild Covid-19 cases?
A UCLA study shows that in people with mild cases of COVID-19, antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 — the virus that causes the disease — drop sharply over the first three months after infection, decreasing by roughly half every 36 days. If sustained at that rate, the antibodies would disappear within about a year.
How long does immunity last after the Pfizer Covid-19 vaccine?
Antibodies able to block the omicron coronavirus variant last four months after a third dose of Pfizer-BioNTech's vaccine, according to a study published Jan. 22 by bioRxiv.Jan 25, 2022
How long could protective immunity last after being vaccinated for Covid-19?
One recent study from the U.K. Health Security Agency showed that protection against infection from two doses of vaccine may last for up to six months.Feb 25, 2022
What are monoclonal antibodies?
Monoclonal antibodies to fight COVID-19 are artificially manufactured antibodies designed to mimic your body’s natural antibodies.
Who is eligible for monoclonal antibodies?
Monoclonal antibody treatments are only available to certain patients.
How monoclonal antibodies are administered
Monoclonal antibodies are only given intravenously (through an IV) or as a subcutaneous injection (as a shot). That means that in order to receive them, you need to be seen in a medical setting — which limits the overall availability of the treatment.
How monoclonal antibodies compare to vaccination
If you’re not yet fully vaccinated when you receive monoclonal antibodies, you’ll have to wait 90 days to get the vaccine. Otherwise, the antibodies may impact the vaccine’s effectiveness.
Why are antibodies made?
Antibodies are naturally made in our bodies to fight infection. Without antibodies, a virus can enter and infect a cell. With antibodies, however, when the virus tries to enter the cell, antibodies block the virus. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are antibodies developed in a laboratory to help our bodies fight infection.
What is a monoclonal antibody?
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are antibodies developed in a laboratory to help our bodies fight infection. Nearly 100 mAbs are FDA-approved to treat health conditions including cancers and autoimmune diseases. Monoclonal antibodies are also being studied for the treatment and prevention of COVID-19. They are given through intravenous infusion (i.e., ...
What is a monoclonal antibody?
Monoclonal antibodies are lab-made proteins, that can mimic the immune system's ability to fight off threats like the coronavirus.
Can they prevent Covid-19?
The antibody therapy made by Regneron is also authorized to be used as a preventative treatment, or what's known as a post-exposure prophylaxis.
Who can get monoclonal antibody treatments for Covid-19?
The treatments for people infected with Covid-19 are for non-hospitalized adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older who have a risk of getting severe Covid-19.
How does someone access the treatment?
The drugs don't come in a simple pill, so they wouldn't typically be available at the average doctor's office, but a doctor can prescribe them.
How effective are the treatments?
Studies show mAbs are highly effective at preventing high-risk patients from developing severe Covid-19 symptoms.
Are there side effects?
Allergic reactions are unlikely, but possible. Worsening symptoms after treatment can also happen, according to the FDA.
How much do the treatments cost?
The US has spent more than $2 billion on monoclonal antibody treatment doses. But as of now, the treatment is free to patients, although there may be an administration fee.