
What are the different ways to increase ejection fraction?
Your care plan will depend on if your low ejection fraction is linked to another heart condition. We may recommend: Lifestyle changes, such as getting exercise, losing weight, quitting smoking or reducing salt Medication, such as beta blockers or diuretics, to help improve your heart function or get rid of excess fluids
What are the causes of lowered ejection fraction?
12 rows · Mar 21, 2022 · Evidence-based treatment options are available only for congestive heart failure with a low ...
What is the lowest ejection fraction to sustain life?
Nov 09, 2021 · Some of the most common treatments include: Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), or beta-blockers. These... Diuretics. These drugs can help get rid of excess fluid that’s causing swelling and shortness of breath. Eplerenone or spironolactone. These ...
What is most likely to increase ejection fraction?
Dec 01, 2016 · The treatments for systolic heart failure, which is what you are dealing with are either medications. Some possibilities are things like beta blockers, diuretics, ARBs, ACE inhbitors. Another possibility is a bi-ventricular pacemaker or defibrillator. It sounds like you need to find out what is causing your systolic heart failure.

What is the best medication for low ejection fraction?
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers and beta-blockers are the cornerstone of the heart failure therapy; indicated in virtually every patient with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction.
What medications improve ejection fraction?
They work by widening blood vessels. Examples of these drugs include the ACE inhibitors lisinopril (Zestril, Qbrelis, Prinivil), enalapril (Epaned, Vasotec), or captopril; the ARNI sacubitril-valsartan (Entresto), or the single agent ARBs like candesartan (Atacand), losartan (Cozaar) or valsartan (Diovan).Dec 27, 2021
What is the lowest ejection fraction you can live with?
If you have an EF of less than 35%, you have a greater risk of life-threatening irregular heartbeats that can cause sudden cardiac arrest/death. If your EF is below 35%, your doctor may talk to you about treatment with an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) or cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT).Apr 29, 2019
Is it possible for ejection fraction to improve?
These findings suggest many patients with HF with reduced ejection fraction may improve their left ventricular ejection fraction over time with medical therapy. This study may also inform discussions on therapies for HF with reduced ejection fraction, such as ICDs, and future research on myocardial recovery.Jun 25, 2020
Does a pacemaker help low ejection fraction?
Biventricular pacemaker is a special pacemaker, which is used to synchronize the contractions of the left ventricle with the right ventricle, to improve the ejection fraction in patients with severe and moderately severe symptoms of heart failure.
How long does it take to improve ejection fraction?
If after 3 to 6 months of therapy the EF has increased (taking into account the variability in repeated readings), the therapy may be deemed successful. If the EF has risen to a normal level or to at least more than 40 or 45%, the patients may be classified as having “improved” or even “recovered” EF.Jun 20, 2017
Can you live a long life with a low ejection fraction?
The good news is that recent research shows that taking a combination of medications for heart failure helps extend life expectancy in people with reduced ejection fraction, Fonarow says. In one study, the medication combination boosted survival by an average of 6 years across all age groups.Jan 26, 2021
What is normal ejection fraction for a 70 year old?
An ejection fraction of 50 percent to 65 percent is considered normal.Nov 4, 2007
Does dapagliflozin improve ejection fraction?
The Dapagliflozin Evaluation to Improve the LIVEs of Patients With PReserved Ejection Fraction Heart Failure (DELIVER) trial is testing the hypothesis that the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin will reduce cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization in patients with heart failure with a LVEF >40% (HFpEF and ...May 29, 2021
How can I naturally increase my ejection fraction?
How to improve your ejection fractionPartner up with a doctor. Whether it's a cardiologist or your primary care physician, talk to a doctor about your symptoms. ... Be a heart detective. Put this on your doctor's to-do list, too. ... Get moving. ... Watch your weight. ... Go on a salt strike. ... Just say no. ... Say goodbye to stress.Aug 12, 2019
How long can you live taking Entresto?
The investigators calculated a consistent survival benefit of 1-2 years across a broad range of patient ages. According to their estimates, the life expectancy of a 55-year-old patient would be extended by 1.4 years (CI -0.1-2.8), from 11.6 years for enalapril to 12.9 years with sacubitril-valsartan.Dec 2, 2015
What causes ejection fraction to drop?
Some things that may cause a reduced ejection fraction are: Weakness of the heart muscle, such as cardiomyopathy. Heart attack that damaged the heart muscle. Heart valve problems.
What Is Ejection fraction?
Ejection fraction, or EF, is a measurement that indicates how well your heart is functioning. This number tracks how much blood your heart is pumpi...
What Is Low Ejection fraction?
Low ejection fraction, sometimes called low EF, is the term we use to describe your ejection fraction if it falls below 55%. It means your heart is...
Low Ejection Fraction Causes
Many different heart and vascular diseases can lead to low ejection fraction, including: 1. Cardiomyopathy: This condition causes areas of heart ti...
What is the normal ejection fraction?
Generally, a normal range for ejection fraction is between 55% and 70%. Low ejection fraction, sometimes called low EF, is when your ejection fraction falls below 55%. It means your heart isn’t functioning as well as it should. Your doctor will want to thoroughly check you for a heart condition to find the cause. A low number can be serious.
How to measure ejection fraction?
With advanced technology in labs that are among the best-equipped in the country, we’ll use one or more imaging tests to precisely measure your ejection fraction. These tests may include: 1 Radiographic imaging, such as a CT scan or MRI 2 Echocardiogram, a heart ultrasound 3 Nuclear cardiology imaging , which uses a safe dose of radioactive material to evaluate blood flow through your heart 4 Cardiac catheterization, a minimally invasive procedure where we gently guide a thin tube, or catheter, with a tiny camera through a blood vessel to your heart
What does ejection fraction mean?
Ejection fraction measures how well your heart is functioning. It’s expressed as a percentage and indicates how much blood your heart is pumping out with each contraction. For example, an ejection fraction of 60% means your heart is pumping 60% of your blood out of your left ventricle (its main pumping chamber) every time your heart beats.
What causes a heart muscle to become enlarged?
Cardiomyopathy, which causes your heart muscle to become enlarged, thick or stiff. Coronary artery disease, where plaque builds up in the two main arteries that supply blood to your heart and blocks blood flow. Heart attack, when blood flow to your heart muscle became blocked and damaged it.
What causes a heart valve to not open?
Heart attack, when blood flow to your heart muscle became blocked and damaged it. Heart valve disease, when one or more of your heart valves don’t open and close the way they should. Systolic heart failure, when your heart’s left ventricle can’t pump blood forcefully enough.
What is an ICD?
Implantable cardiac defibrillator (ICD), a device that sends small electrical pulses to your heart to restore a healthy rhythm, especially treating those arrythmias that can cause your heart to stop beating. Heart transplant when other treatments are unable to help dangerously low ejection fraction and severe heart problems.
How to reduce heart failure symptoms?
Although the correlations between heart failure and stress are unclear, being stressed can increase heart rate and blood pressure, two things that can worsen heart failure symptoms. Practice stress-reducing habits.
What to do if you have heart failure?
If your heart failure is stable, and you have your doctor’s okay, do what moves you. Here are some exercise tips to keep in mind. Consider a cardiac rehab program. It offers some unique benefits, and you may even be able to join a supervised home-based exercise program.
Why is tracking your weight important?
Your weight is important. Tracking your weight can give you important clues about how well your heart is managing its load. Track and respond to weight fluctuations. You may notice patterns that help you respond appropriately to situations before they get worse. Maintain a healthy body weight.
What are the risk factors for heart failure?
Several risk factors are associated with heart failure like high blood pressure, or hypertension, diabetes and metabolic syndrome. By managing those conditions, you may be able to help your heart failure and your ejection fraction improve. Know your plan and follow it carefully. If you have been prescribed medications for heart failure, diabetes, ...
How to get rid of lightheadedness and dizziness?
A brief warm up and cool down can help your body transition smoothly in and out of your exercise zone and reduce symptoms of dizziness and/or lightheadedness. 4. Pay attention to your weight. Your weight is important. Tracking your weight can give you important clues about how well your heart is managing its load.
How to improve your walking?
It’s easy to do, and it may help you learn to pace yourself. Your provider may do a 6-minute walk test to help measure your improvements over time. You simply start by seeing how far you can walk in one six minute session.
Does alcohol cause heart failure?
Alcohol can increase the risk of heart failure and worsen symptoms. By eliminating alcohol, the signs and symptoms of heart failure often improve. Quit smoking. Smoking cigarettes is especially hazardous to people with heart failure. Discover the resources that can help you quit for good.
What is evidence based treatment?
Evidence-based treatments. Evidence-based treatments are available only for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). The basic principle here—besides treating the underlying cause (for example, by means of revascularization or heart valve surgery)—is neurohumoral inhibition by means of ACE inhibitors, ...
What is less is more?
Less is more: heart rate monitoring. As a result of the reduced cardiac output due to the reduced ejection fraction, the heart rate increases as a reflex. In heart failure patients, an elevated heart rate leads to less economical ventricular function and has been repeatedly associated with a poorer prognosis (e9).
What is pharmacotherapy based on?
Pharmacotherapy is based on neurohumoral inhibition of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and the adrenergic system. The prognosis of patients with this condition has been further improved recently through the introduction of combined angiotensin receptor antagonists and neprilysin inhibitors.
Does digitalis help with heart failure?
A meta-analysis on the studies available to date on digitalis in heart failure revealed that treatment with digitalis reduces hospitalizations and improves the symptoms of heart failure (16). In older, multimorbid patients with reduced renal function, digoxin poses the risk of accumulation and possible toxicity.
What does ejection fraction mean?
A heart at rest holds a certain amount of blood. Ejection fraction refers to the percentage of that blood your heart pumps out with each beat. “Assuming a normal heart size and rate, when ejection fraction is normal, the heart is pumping a normal amount of blood,” Dr. Finet explains. “We can assume the blood is moving at a normal speed around ...
How to take care of ticker?
Here are some ways to do that: Advertising Policy. 1. Partner up with a doctor. Whether it’s a cardiologist or your primary care physician, talk to a doctor about your symptoms.
What are the two main chambers of the heart?
The heart has two main muscular chambers: the left and the right ventricle. Each chamber has MVP status in the body, working together to perform jobs you literally couldn’t live without: 1 Right ventricle: Pumps blood to the lungs to get oxygenated. 2 Left ventricle: Pumps oxygenated blood throughout your body.
What happens if you consume too much salt?
Consuming too much sodium, or salt, can have a domino effect: Diseased heart muscle, or cardiomyopathy, provides less blood to the kidneys. The kidneys retain sodium and fluid to compensate for the low blood flow. Sodium traps water, which abnormally accumulates on the heart and blood vessels.
Does losing weight improve ejection fraction?
“Losing weight won’t necessarily improve ejection fraction, but it can make you feel better,” Dr. Finet says. Tracking your weight will also help you and your doctor determine whether fluid is being built up due to the abnormal heart function.
What is the ejection fraction of the heart?
It takes more than a single contraction to pump all of the blood out of your heart. Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement doctors use to calculate the percentage of blood flowing out ...
Why is my EF low?
Causes of low EF. As we age, our hearts do too. Heart walls thicken and lose some of their capacity to contract and relax as the years go on. But, a low EF reading can also indicate some form of heart damage, including: Cardiomyopathy. This condition thickens your heart tissues. Heart attack.
What does it mean when your heart is not contracting?
This occurs when one of your heart’s four chambers can’t contract properly. Symptoms might include shortness of breath, exhaustion, or heart palpitations. HFpEF (diastolic dysfunction). This is heart failure with a preserved, or normal, ejection fraction. This occurs when your ventricles don’t relax.
How to manage a symtom?
Remember to pay attention to your body. Try to eat a balanced, low-fat diet with plenty of leafy green vegetables. Get daily exercise and maintain a regular sleep schedule.
What does a high EF mean?
A high EF reading can indicate a heart condition known as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HC). This condition abnormally thickens parts of your heart muscle without an obvious cause. HC is often genetic. It’s tough to diagnose because many people can live a symptom-free life.
What is the best medicine for heart disease?
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), or beta-blockers. These medications can reduce the amount of hormones that weaken your heart muscle. They can also slow the progression of heart disease.
What is the best medicine to lower blood pressure?
This device can be directly implanted into your chest. It sends small electrical triggers to your heart to keep it beating regularly. Hydralazine-nitrate. These two drugs have been successful in lowering blood pressure in people who still have symptoms when taking ACE, ARBs, and beta-blockers.
What is Normal Ejection Fraction for the Heart?
Heart ejection fraction is measured at the point where your left ventricle pumps blood out to your aorta. It can be calculated non-invasively with an echocardiogram or more directly during an angiogram of the heart. A noninvasive MUGA scan of the heart will also estimate the heart ejection fraction.
Symptoms of Low Ejection Fraction
While ejection fraction can have no symptoms at all, especially if it’s only slightly low, symptoms of low ejection fraction can include:
What Are the Causes of Low Ejection Fraction?
There are numerous conditions that can lead to low ejection fraction, including:
Treating Low Ejection Fraction
Treatments for low ejection fraction will depend on how low your ejection fraction is, the cause of your low ejection fraction, and your overall health. So, you want to work very closely with your doctor to treat it.
Don't Miss Out!
Advice from our doctors plus valuable savings, sent right to your inbox! Plus, 20% off and free shipping on your next order!
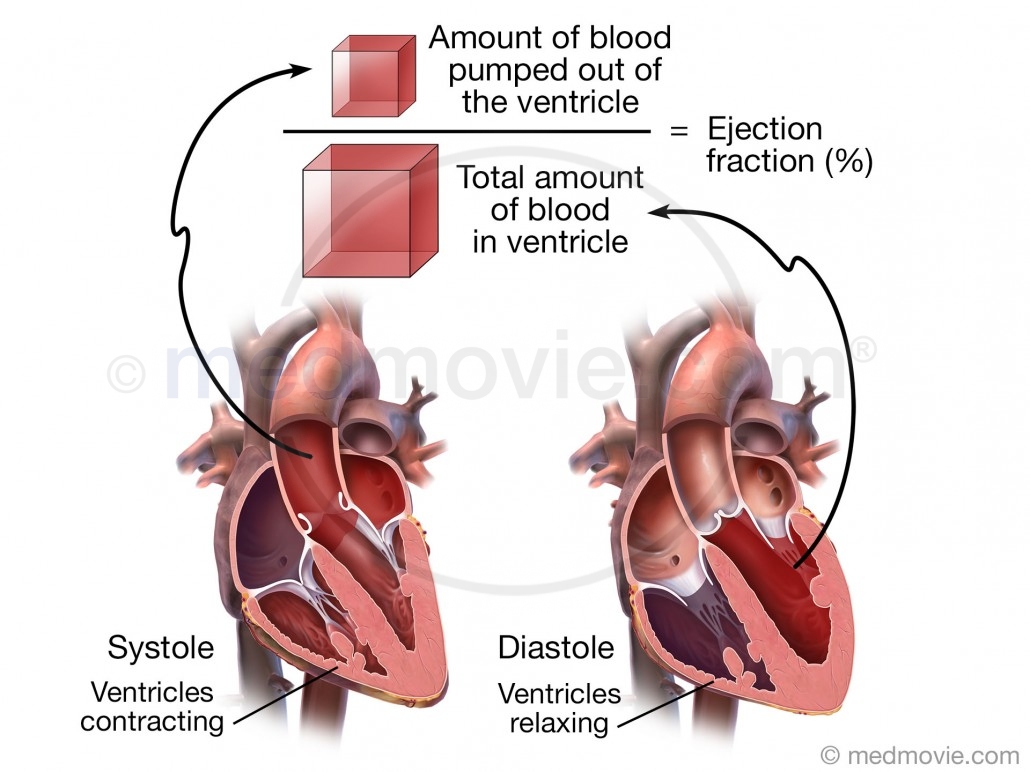
What Is Low Heart Ejection fraction?
- A low ejection fraction (or low EF) is typically 45 or less and can be evidence of heart failure or cardiomyopathy (a disease of the heart muscle). The heart’s ejection fraction (EF) refers to the amount – or percentage – of blood pumped (or ejected) out of the heart’s left ventricle with eac…
What Happens If Your Ejection Fraction Is Low?
- If your ejection fraction is low, below 50%, your heart is no longer efficiently pumping blood to meet your body's needs.
Signs and Symptoms
- More than one of the following low EF symptoms, particularly if a known heart condition is present, should prompt a physician’s visit: 1. Exercise intolerance 2. Fatigue and weakness 3. Feeling bloated or full 4. Heart palpitations 5. Loss of appetite 6. Mental confusion 7. Nausea 8. Rapid, forceful or irregular heartbeat 9. Shortness of breath 10. Swelling, especially in the feet an…
Diagnosis
- If you have a heart condition, measuring your ejection fraction can help you and your physician monitor its severity, determine your best course of treatment and check how well a treatment is working. Diagnostic tests for low EF include: 1. Echocardiogram: This ultrasound exam uses soundwaves to take moving pictures of the heart’s chambers and valves. 2. Magnetic resonanc…
Low Ejection Fraction Treatment
- If you have a low ejection fraction, your physician may recommend the following treatment options to help improve low EF:
Complications
- A low EF number is a serious issue, putting you at a significantly higher risk of sudden cardiac arrest.