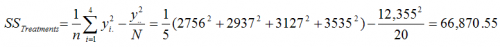
How do you find the treatment mean square in ANOVA?
Jun 22, 2021 · In the context of an ANOVA, a treatment refers to a level of the independent variable included in the model. Why do we calculate sum of squares? Besides simply telling you how much variation there is in a data set, the sum of squares is used to calculate other statistical measures, such as variance, standard error, and standard deviation.
What is the sum of squares in ANOVA?
In analysis of variance (ANOVA), the total sum of squares helps express the total variation that can be attributed to various factors. For example, you do an experiment to test the effectiveness of three laundry detergents. The total sum of squares = treatment sum of squares (SST) + sum of squares of the residual error (SSE)
What is the sum of squares for the treatment?
4 rows · This result is called the sums of squares decomposition formula. We use these results to build our ...
What is the goal of a 2-way ANOVA?
Feb 27, 2020 · What is sum of squares in Anova table? In the context of ANOVA, this quantity is called the total sum of squares (abbreviated SST) because it relates to the total variance of the observations. Thus: The denominator in the relationship of the sample variance is the number of degrees of freedom associated with the sample variance.

Why do we use sum of squares in ANOVA?
In analysis of variance (ANOVA), the total sum of squares helps express the total variation that can be attributed to various factors. For example, you do an experiment to test the effectiveness of three laundry detergents.
What is the purpose of the sum of squares?
What is sum of squares between in ANOVA?
Which sum of squares measure the treatment effect?
What is SS treatment?
Why do we square the residuals?
What is the difference between sum of squares and variance?
What is SS and MS in ANOVA?
What is sum of squares in statistics?
What is ANOVA treatment?
What is a treatment in an ANOVA process?
What does F stand for in ANOVA?
Is SS A positive or negative?
In contrast to our previous test statistics where positive and negative differences were possible, SS A is always positive with a value of 0 corresponding to no variation in the means. The larger the SS A, the more variation there was in the means.
Can total variation change?
In a permutation situation , the total variation (SS Total) cannot change - it is the same responses varying around the grand mean. However, the amount of variation attributed to variation among the means and in the residuals can change if we change which observations go with which group.
What does the sum of squares mean in ANOVA?
What does sum of squares mean in Anova? In the context of ANOVA, this quantity is called the total sum of squares (abbreviated SST) because it relates to the total variance of the observations. Thus: The denominator in the relationship of the sample variance is the number of degrees of freedom associated with the sample variance.
What is the sum of squares in regression?
Likewise, what is the model sum of squares? Sum of squares (SS) is a statistical tool that is used to identify the dispersion of data as well as how well the data can fit the model in regression analysis. The sum of squares got its name because they are calculated by finding the sum of the squared differences.
How to find the sum of squares?
To calculate the sum of squares, subtract each measurement from the mean, square the difference, and then add up (sum) all the resulting measurements . Likewise, what is the model sum of squares?
Why is the sum of squares called the sum of squares?
The sum of squares got its name because they are calculated by finding the sum of the squared differences. Moreover, what does mean square mean in Anova? In ANOVA, mean squares are used to determine whether factors (treatments) are significant.
What is the goal of a 2 way ANOVA?
The goal of a 2-way ANOVA is to split the to t al variation of a dependent variable (measured as Sums of Squares) into different sources of variation. This allows us to find out whether our independent variables have a significant effect on the dependent variable.
Do Type II sums of squares have an interaction effect?
Secondly, the Type II Sums of Squares do not take an interaction effect.
What is a type III sum of squares?
The Type III Sums of Squares are also called partial sums of squares again another way of computing Sums of Squares: Like Type II, the Type III Sums of Squares are not sequential, so the order of specification does not matter. Unlike Type II, the Type III Sums of Squares do specify an interaction effect.
