Explore
Treatment The main treatment for giant cell arteritis consists of high doses of a corticosteroid drug such as prednisone. Because immediate treatment is necessary to prevent vision loss, your doctor is likely to start medication even before confirming the diagnosis with a biopsy.
What is the treatment for giant cell arteritis?
Large Red Blood Cells (Macrocytosis) 1 Macrocytosis is a term used to describe abnormally large red blood cells... 2 Signs and Symptoms. People with enlarged red blood cells are normally unaware... 3 Causes of Macrocytosis. Proper development of red blood cells could be affected by a variety... 4 Diagnosis of Macrocytosis. Since there are no...
What does it mean to have large red blood cells?
The two most common causes of megaloblastic anemia are deficiencies of vitamin B-12 or folate. These two nutrients are necessary for producing healthy red blood cells. When you don’t get enough of them, it affects the makeup of your red blood cells. This leads to cells that don’t divide and reproduce the way they should.
What causes megaloblastic anemia and how is it treated?
If the underlying cause is resulting in severe anemia, you might need a blood transfusion. Kaferle J, et al. Evaluation of macrocytosis. American Family Physician. 2009;79:203.
When is a blood transfusion indicated in the treatment of macrocytosis?
Can enlarged red blood cells be cured?
Most cases of macrocytic anemia that are caused by vitamin B-12 and folate deficiencies can be treated and cured with diet and supplements. However, macrocytic anemias can cause long-term complications if left untreated. These complications can include permanent damage to your nervous system.
Why are my red blood cells large?
Macrocytic anemia is a blood disorder that happens when your bone marrow produces abnormally large red blood cells. These abnormal blood cells lack nutrients red blood cells need to function normally. Macrocytic anemia isn't a serious illness but it can cause serious medical issues if left untreated.
What diseases cause enlarged red blood cells?
AdvertisementVitamin B-12 deficiency.Folate deficiency.Liver disease.Alcoholism.Hypothyroidism.A side effect of certain medications, such as those used to treat cancer, seizures and autoimmune disorders.Increased red blood cell production by the bone marrow to correct anemia, for example, after blood loss.More items...
How long can you live with macrocytosis?
Mild macrocytosis is unlikely to lead to complications. If severe macrocytosis is left untreated for periods longer than six months, however, neurological complications due to low oxygen levels in the body can develop.
Should I be concerned about large red blood cells?
Macrocytosis is a condition in which your red blood cells are larger than they should be. While it isn't a condition of its own, macrocytosis is a sign that you have an underlying health condition and may lead to a severe form of anemia called macrocytic normochromic anemia.
Who is at risk for macrocytic anemia?
A folate deficiency, sometimes known as vitamin B-9 deficiency, can also cause macrocytic anemia. Pregnant and breast-feeding women use more folate and have a higher risk of becoming deficient. People who do not eat enough folate-rich foods can also become deficient.
How can I lower my red blood cell count naturally?
If you have a high RBC count:Exercise to improve your heart and lung function.Eat less red meat and iron-rich foods.Avoid iron supplements.Keep yourself well hydrated.Avoid diuretics, including coffee and caffeinated drinks, which can dehydrate you.Stop smoking, especially if you have COPD or pulmonary fibrosis.More items...•
What are two conditions that cause polycythemia?
The most common causes of secondary polycythemia include obstructive sleep apnea, obesity hypoventilation syndrome, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Other causes include testosterone replacement therapy and heavy cigarette smoking.
How serious is macrocytosis without anemia?
Macrocytosis without anemia is unlikely to result in specific signs or symptoms, and in many cases, may have minimal clinical significance. Patients should be screened for symptoms of anemia, including fatigue, generalized weakness, dyspnea, palpitations, lightheadedness, and syncopal or near-syncopal events.
What is a major cause of macrocytosis?
Macrocytosis can occur when there is increased RBC production secondary to peripheral blood cell destruction (i.e., hemolysis) or loss (i.e., hemorrhage), leading to a reticulocytosis. Reticulocytes are incompletely processed RBCs and, therefore, are slightly larger than the average RBC.
Which drugs cause macrocytosis?
Common drugs that cause macrocytosis are hydroxyurea, methotrexate, zidovudine, azathioprine, antiretroviral agents, valproic acid, and phenytoin (Table 1).
How long does it take for MCV to return to normal?
Because the MCV usually returns to normal within 2 to 4 months of abstinence, the increase in RBC size apparently is a direct effect of alcohol on RBC production.
Why is it important to have a blood test for macrocytosis?
Additional blood tests can also help find the cause of your macrocytosis and anemia. This is important because treatment depends on the underlying cause. While nutrient deficiencies cause most macrocytic anemias, other underlying conditions may cause the deficiencies.
What is megaloblastic anemia?
Megaloblastic macrocytic anemia. Most macrocytic anemias are also megaloblastic. Megaloblastic anemia is a result of errors in your red blood cell DNA production. This causes your body to make red blood cells incorrectly. Possible causes include:
What test can you do to check for anemia?
Blood tests. Your doctor will order blood tests to check for anemia and enlarged red blood cells. If your complete blood count indicates anemia, your doctor will do another test known as a peripheral blood smear. This test can help spot early macrocytic or microcytic changes to your red blood cells.
What is the difference between macrocytosis and anemia?
Macrocytosis is a term used to describe red blood cells that are larger than normal. Anemia is when you have low numbers of properly functioning red blood cells in your body. Macrocytic anemia, then, is a condition in which your body has overly large red blood cells and not enough normal red blood cells.
What doctor can diagnose anemia?
They may also do blood tests to check for alcohol use disorder, liver disease, and hypothyroidism. Your primary care doctor may also refer you to a hematologist. Hematologists specialize in blood disorders. They can diagnose the cause and specific type of your anemia.
What to ask your doctor about anemia?
Your doctor will ask about your medical history and lifestyle. They may also ask about your eating habits if they think that you have a type of anemia. Learning about your diet can help them find out if you are deficient in iron, folate, or any of the other B vitamins.
Can macrocytic anemia be cured?
Most cases of macrocytic anemia that are caused by vitamin B-12 and folate deficiencies can be treated and cured with diet and supplements. However, macrocytic anemias can cause long-term complications if left untreated. These complications can include permanent damage to your nervous system.
What is the term for red blood cells that are larger than normal?
Macrocytosis is a term used to describe red blood cells that are larger than normal. Also known as megalocytosis or macrocythemia, this condition typically causes no signs or symptoms and is usually detected incidentally on routine blood tests.
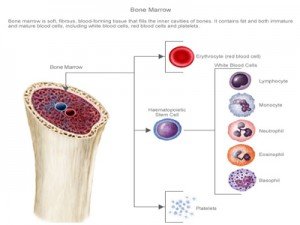
What causes increased red blood cell production in the bone marrow?
Increased red blood cell production by the bone marrow to correct anemia, for example, after blood loss. An underlying bone marrow cancer called myelodysplastic syndrome. If you have macrocytosis, blood tests can help determine its cause.
What causes macrocytosis?
Common causes of macrocytosis include: Vitamin B-12 deficiency. Folate deficiency. Liver disease. Alcoholism. Hypothyroidism. A side effect of certain medications, such as those used to treat cancer, seizures and autoimmune disorders. Increased red blood cell production by the bone marrow to correct anemia, for example, after blood loss.
What is the unit used to measure the size of blood cells?
A unit called femtoliters (fL) is used to measure the size of blood cells. Usually, red blood cells are between 80–100 fL. . Red blood cells larger than 100 fL are considered macrocytic. When the cells grow too large, there are fewer of them than there needs to be and they carry less hemoglobin.
What is the first line of treatment for macrocytic anemia?
They may also ask questions about a person’s diet, lifestyle, and other symptoms. In most cases, vitamin injections are the first line of treatment.
Why is macrocytic anemia rare?
In very rare cases, macrocytic anemia can be caused by a bone marrow disorder that prevents the body from producing enough healthy blood cells.
Why do animals have macrocytic anemia?
Macrocytic anemia is usually caused by a deficiency of folate or vitamin B-12, which is abundant in animal products. Macrocytic anemia is almost always due to a deficiency of folate or vitamin B-12.
Can macrocytic anemia cause heart failure?
The body may try to fix this by increasing the heart rate or blood pressure. Left untreated, anemia can cause heart failure, an enlarged heart, and circulatory problems. When macrocytic anemia is due to a problem with the bone marrow or an organ, this underlying cause can trigger further complications.
Is macrocytic anemia a single disease?
Low blood oxygen can cause a range of symptoms and health problems. Macrocytic anemia is not a single disease, but a symptom of several medical conditions and nutritional problems. One of the most common types of macrocytic anemia is megaloblastic macrocytic anemia.
Can macrocytic anemia be diagnosed?
Macrocytic anemia often goes undiagnosed until it becomes severe. People who have symptoms of anemia, a family history of anemia, or who have or are at risk of a condition linked to macrocytic anemia should see a doctor for a blood test.
How big is a red blood cell?
It is about 6 to 8 micrometers in diameter and about 2 micrometers thick on average .
What is macrocytosis in blood?
What is macrocytosis? Macrocytosis is the term for enlarged red blood cells. These blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, may be larger than normal for various reasons that affect its development. Therefore further investigations are necessary to identify the cause, as some of these causative factors can be very serious in nature.
What causes macrocytosis?
Macrocytosis Causes. Dietary deficiency of vitamin B12 and folic acid. Surgical removal of part of the stomach or the entire stomach – gastrectomy. Malabsorption syndrome due to inflammation of the bowels, infections, drugs or other causes. Alcoholism – long term alcohol misuse. Pregnancy – increased demands.
What is it called when the hemoglobin is low and the MCV is high?
This is known as macrocytic anemia.
How to calculate hematocrit?
The hematocrit is then divided by the total number of red blood cells and then multiplied by 10. The result is an indication of the size of the red blood cells or the number of red blood cells. It is expressed as femtoliters or fL.The normal range is between 80 to 99fL and the value is greater than 100fL in macrocytosis.
What is the first test to determine if you have macrocytosis?
Therefore the first conclusive indication of the possibility of macrocytosis is upon blood tests like a complete blood count (CBC). The mean cell volume (MCV) is higher than normal. Other tests that may be conducted includes : Peripheral blood smear where the blood cells are examined under a microscope.
What is the meaning of MCV in blood work?
Macrocystosis and MCV. Macroytosis is often reported in terms of mean cell volume (MCV) also known as mean corpuscular volume. It is a test that is done as part of a complete blood count (CBC). Blood is placed in a centrifuge which is device that spins it around at high speed. The red blood cells become packed together and this is known as ...
What is the name of the disorder in which the number of red blood cells is lower than usual?
Megaloblastic Anemia . Anemia is a blood disorder in which the number of red blood cells (RBCs) is lower than usual. RBCs transport oxygen through the body. When your body doesn’t have enough RBCs, your tissues and organs don’t get enough oxygen. There are many types of anemia with different causes and characteristics.
What are the causes of megaloblastic anemia?
Causes of megaloblastic anemia. The two most common causes of megaloblastic anemia are deficiencies of vitamin B12 and folate. These two nutrients are necessary for producing healthy RBCs. When you don’t get enough of them, it affects the makeup of your RBCs.
What is anemia in blood?
Anemia is a blood disorder in which the number of red blood cells (RBCs) is lower than usual. RBCs transport oxygen through the body. When your body doesn’t have enough RBCs, your tissues and organs don’t get enough oxygen. There are many types of anemia with different causes and characteristics. Megaloblastic anemia is characterized by RBCs ...
Why aren't RBCs produced?
When RBCs aren’t produced properly, it results in megaloblastic anemia. Because the blood cells are too large, they may not be able to exit the bone marrow to enter the bloodstream and deliver oxygen.
Can RBCs be underdeveloped?
As part of the CBC, a healthcare professional can check the number and appearance of your RBCs. They’ll appear larger and underdeveloped if you have megaloblastic anemia. Your doctor will also gather your medical history and perform a physical exam to rule out other causes of your symptoms.
Can you treat megaloblastic anemia with folate?
Outlook for people living with megaloblastic anemia. In the past, megaloblastic anemia was difficult to treat. Today, people with megaloblastic anemia due to either vitamin B12 or folate deficien cy can manage their symptoms and feel better with ongoing treatment and dietary supplements.
What is the treatment for macrocytosis?
In the case of vitamin B-12 or folate deficiency, treatment may include diet modification and dietary supplements or injections. If the underlying cause is resulting in severe anemia, you might need a blood transfusion.
What to do if you have anemia?
If the underlying cause is resulting in severe anemia, you might need a blood transfusion. Addressing a vitamin B12 deficiency. If you’re not getting enough vitamin B12 or folate in your diet, eat foods rich in these nutrients. If you’re still not getting enough, you may need to take supplements.
What is macrocytosis in blood?
Understanding Macrocytosis. Macrocytosis is also called megalocytosis or macrocythemia. When you complete blood tests, the size of red blood cells is reported in your complete blood count. Because macrocytosis often develops into severe anemia, called macrocytic anemia, it is important to pay attention to these blood test results..
What is the diagnosis of macrocytosis?
Diagnosing Macrocytosis. Treating Macrocytosis. Macrocytosis is a condition in which your red blood cells are larger than they should be. While it isn’t a condition of its own, macrocytosis is a sign that you have an underlying health condition and may lead to a severe form of anemia called macrocytic normochromic anemia.
How many fluid liters per cell for macrocytosis?
When macrocytosis is fully developed, your MCV levels are 100 fluid liters per cell if you don’t also have an iron deficiency, thalassemia trait, or kidney disease. Other indicators include: Keep in mind that if you do have an iron deficiency, macrocytosis may be overlooked.
What causes a lot of blood to be lost?
Hypothyroidism. Macrocytosis may also be the side effect of some medications prescribed to treat cancer, seizures, or autoimmune disorders. If you lose a lot of blood because of an accident or injury, your bone marrow may produce more red blood cells to address the problem.
Can bone marrow cancer cause macrocytosis?
Bone marrow cancer, also called myelodysplastic syndrome, may also lead to macrocytosis. Following a blood test, your doctor may want to assess the severity of your anemia. Your doctor will assess your health history to determine the likelihood of macrocytic anemia.
What causes enlarged red blood cells?
Among the most common are vitamin B12 deficiency, folate deficiency, alcoholism, hypothyroidism (under-active thyroid) and liver disease. Other causes include increased red blood cell production ...
Why do red blood cells turn red?
Other causes include increased red blood cell production secondary to acute blood loss or the side-effects of medications such as those used to treat cancer. According to the American Society of Hematology, red blood cells are the largest component of human blood, making up 40 to 45 percent of its volume. They get their bright red color ...
What causes macrocytosis?
The most common cause of macrocytosis is vitamin B12 deficiency or pernicious anemia, a disorder in which the cells of the intestine do not properly absorb Vitamin B12. In some cases, particularly in people with alcoholic liver disease, ...
How do red blood cells get their color?
They get their bright red color from the protein hemoglobin, which is responsible for transporting oxygen to the body’s cells. Under normal circumstances, red blood cells are a uniform shape and size, the latter of which is defined as the mean corpuscular volume or MCV.
Which reverse transcriptase inhibitors are used for HIV?
In recent years, a large increase in the number of patients diagnosed with this condition has been attributed to the reverse transcriptase inhibitors such as stavudine , lamivudine and zidovudine that are used in the treatment of HIV.
What tests are used to diagnose giant cell arteritis?
Imaging tests. These might be used to diagnose giant cell arteritis and to monitor your response to treatment. Tests might include: Doppler ultrasound. This test uses sound waves to produce images of blood flowing through your blood vessels. Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA).
How to diagnose giant cell arteritis?
Biopsy. The best way to confirm a diagnosis of giant cell arteritis is by taking a small sample (biopsy) of the temporal artery. This artery is situated close to the skin just in front of your ears and continues up to your scalp. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis using local anesthesia, usually with little discomfort or scarring.
Why is giant cell arteritis so difficult to diagnose?
Giant cell arteritis can be difficult to diagnose because its early symptoms resemble those of other common conditions. For this reason, your doctor will try to rule out other possible causes of your problem.
How to prevent thinning bones?
Eating well can help prevent potential problems, such as thinning bones, high blood pressure and diabetes. Emphasize fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean meats and fish, while limiting salt, sugar and alcohol.
Can you have a negative biopsy of giant cell arteritis?
It's possible to have giant cell arteritis and have a negative biopsy result. If the results aren't clear, your doctor might advise another temporal artery biopsy on the other side of your head.
Can you have a biopsy of a giant cell artery?
The sample is examined under a microscope in a laboratory. If you have giant cell arteritis, the artery will often show inflammation that includes abnormally large cells, called giant cells, which give the disease its name. It's possible to have giant cell arteritis and have a negative biopsy result. If the results aren't clear, your doctor might ...
Can giant cell arteritis be treated early?
When giant cell arteritis is diagnosed and treated early, the prognosis is usually excellent. Your symptoms will likely improve quickly after beginning corticosteroid treatment, and your vision isn't likely to be affected.