
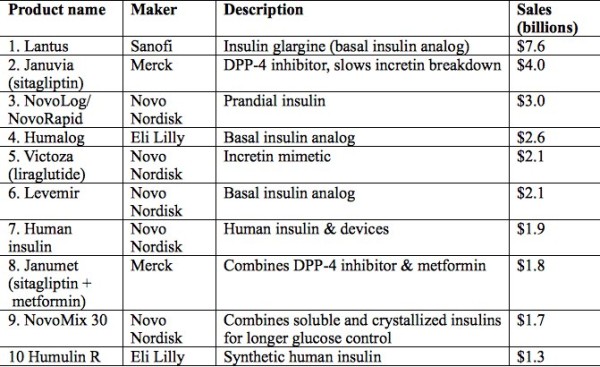
Medication
Treatment of type 1 diabetes usually involves a combination of insulin therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. Insulin If your body is no longer producing enough insulin, you’ll need to take insulin every day to help regulate your blood sugar.
Nutrition
This section focuses on the medical management of type 1 diabetes. And as the term “medical management” implies, this management is done with the guidance of your medical provider and medical team. The key principles of medical management are: Regular blood sugar (and ketone) self monitoring as a part of daily living Taking insulin
See more
Nov 20, 2017 · Insulin therapy itself is the basis in treatment of type 1 diabetes. Recent years have brought multiple solutions in the implementation of the treatment. New types of insulin, modern glycaemia monitoring, and insulin administration techniques revolutionized the capabilities of contemporary insulin therapy.
What are various treatment options for Type 1 diabetes?
Dec 09, 2021 · What medicines do I need to treat my type 1 diabetes? If you have type 1 diabetes, you must take insulin because your body no longer makes this hormone. Different types of insulin start to work at different speeds, and the effects of each last a different length of time. You may need to use more than one type. You can take insulin a number of ways.
Is it possible to cure type 1 diabetes?
Mar 11, 2022 · If you have type 1 diabetes, you’ll need to take insulin shots (or wear an insulin pump) every day. Insulin is needed to manage your blood sugar levels and give your body energy. You can’t take insulin as a pill. That’s because the acid in your stomach would destroy it before it could get into your bloodstream.
How to overcome type 1 diabetes?
Jan 15, 2019 · Treatment for Type 1 Diabetes. Central to the treatment of type 1 diabetes is to keep a balance of the right amount of insulin to keep blood glucose levels from being either too high or too low. In type 1 diabetes the body’s immune system kills of the insulin producing cells leaving the pancreas unable to produce enough insulin to keep blood glucose levels at healthy …
How bad is type 1 diabetes?
What Is Type 1 Diabetes? Overview of causes, symptoms, and daily management. Just Diagnosed. The basics of everyday diabetes care for newly diagnosed people. Types of Insulin. Your guide to insulin types and how they work. 4 Ways To Take Insulin. Insulin pens, pumps, and 2 other methods for taking insulin.
See more
Pancreatic islet transplantation is an experimental treatment for poorly controlled type 1 diabetes. Pancreatic islets are clusters of cells in the pancreas that make the hormone insulin. In type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system attacks these cells.
What is the main treatment for type 1 diabetes?
If you have type 1 diabetes, you'll need to use insulin to treat your diabetes. You take the insulin by injection or by using a pump. If you have Type 2 diabetes, you may have to use insulin or tablets, though you might initially be able to treat your diabetes by eating well and moving more.
How is type 1 diabetes permanently treated?
Currently, there is no cure for type 1 diabetes. Insulin injection is the only medication; however, it accompanies serious medical complications. Current strategies to cure type 1 diabetes include immunotherapy, replacement therapy, and combination therapy.
Which is worse type 1 or 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is often milder than type 1. But it can still cause major health complications, especially in the tiny blood vessels in your kidneys, nerves, and eyes. Type 2 also raises your risk of heart disease and stroke.Dec 8, 2021
Can type 1 diabetes be treated without insulin?
The kids obviously don't know the symptoms of type 1, and their parents might not either, so the child's blood glucose levels go up and up, unidentified as type 1 diabetes until things get serious. So that's why people with type 1 diabetes cannot go “insulin free” no matter how carefully controlled their diet.Nov 10, 2015
Overview
With type 1 diabetes, your pancreas loses the ability to make enough insulin, a hormone that helps the body absorb blood sugar, or glucose, and convert it to energy. When this happens, the sugar builds up in your blood.
Insulin
If your body is no longer producing enough insulin, you’ll need to take insulin every day to help regulate your blood sugar. Because glucose levels can fluctuate, people with type 1 diabetes usually need to check their blood sugar throughout the day to determine how much insulin they need to take.
Metformin
Metformin is an oral medication that is often prescribed to people with type 2 diabetes to help them control their glucose levels. This medication does not increase insulin in the body. Instead, it lowers glucose production, and also helps insulin work more effectively.
Medications
Your doctor might prescribe other medications, such as blood pressure medication, cholesterol-lowering medications, or aspirin. These medications don’t treat the diabetes itself, but help reduce the risk of other health problems that can be related to diabetes, such as hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and kidney problems.
Artificial Pancreas
An artificial pancreas is a medical device that mimics the work of a real pancreas by monitoring your blood sugar levels and releasing insulin automatically. Instead of checking your glucose levels and injecting yourself throughout the day, you wear a sensor under your skin, a continuous glucose monitor, and an insulin pump.
Islet Cell Transplantation
Islet cell transplantation is a procedure that takes healthy insulin-producing cells from a donor pancreas, and transplants them into a person with type 1 diabetes.
Pancreas Transplant
In some cases, doctors can take a healthy transplant from a deceased donor, and transplant it into the body of someone with type 1 diabetes. While this procedure can restore the body’s natural insulin production, it’s also risky, because the medications you have to take to prevent your body from rejecting the pancreas can have serious side effects.
How to manage diabetes?
This section focuses on the medical management of type 1 diabetes. And as the term “medical management” implies, this management is done with the guidance of your medical provider and medical team. The key principles of medical management are: 1 Regular blood sugar (and ketone) self monitoring as a part of daily living 2 Taking insulin 3 Problem solving how and when to make adjustments in your food and insulin doses to prevent high or low blood sugars 4 Understanding complications and how to screen for, prevent and treat them
What is blood sugar monitoring?
Blood sugar & ketone monitoring: The tool that tells you whether your treatment is successful. Medications: Includes insulin, amylin analogs and use of the insulin pump. Self-management solutions: How to analyze what is causing you to have low blood sugars and/or high blood sugars. Complications:
Why do you need to monitor your blood sugar?
You need to problem solve if the self blood sugar monitoring shows your treatment is not successful. The self blood sugar monitoring will indicate if you need to adjust the dose of insulin.
What is medical management?
And as the term “medical management” implies, this management is done with the guidance of your medical provider and medical team. The key principles of medical management are: Regular blood sugar (and ketone) self monitoring as a part of daily living. Taking insulin. Problem solving how and when to make adjustments in your food ...
What are the health problems of type 1 diabetes?
foot problems. depression. sleep apnea. If you have type 1 diabetes, you can help prevent or delay the health problems of diabetes by managing your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol, and following your self-care plan.
Why is type 1 diabetes caused?
Experts think type 1 diabetes is caused by genes and factors in the environment, such as viruses, that might trigger the disease. Researchers are working to pinpoint the causes of type 1 diabetes through studies such as TrialNet. External link.
How do you know if you have diabetes?
What are the symptoms of type 1 diabetes? 1 breath that smells fruity 2 dry or flushed skin 3 nausea or vomiting 4 stomach pain 5 trouble breathing 6 trouble paying attention or feeling confused
What is the main source of energy for diabetes?
Diabetes occurs when your blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high. Blood glucose is your main source of energy and comes mainly from the food you eat. Insulin, a hormone made by the pancreas, helps the glucose in your blood get into your cells to be used for energy.
Why do you need insulin?
If you have type 1 diabetes, you must take insulin because your body no longer makes this hormone. Different types of insulin start to work at different speeds, and the effects of each last a different length of time. You may need to use more than one type. You can take insulin a number of ways.
What does A1C mean in blood work?
This blood test measures your blood glucose level at a single point in time. Sometimes health professionals also use the A1C blood test to find out how long someone has had high blood glucose. Even though these tests can confirm that you have diabetes, they can’t identify what type you have.
Does pramlintide help with diabetes?
Pramlintide, given by injection, helps keep blood glucose levels from going too high after eating. Few people with type 1 diabetes take pramlintide, however. The NIH has recently funded a large research study to test use of pramlintide along with insulin and glucagon in people with type 1 diabetes.
What is the cause of type 1 diabetes?
What Causes Type 1 Diabetes? Type 1 diabetes is thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction (the body attacks itself by mistake) that destroys the cells in the pancreas that make insulin, called beta cells. This process can go on for months or years before any symptoms appear.
How to prevent diabetes complications?
Keeping your blood sugar levels as close to target as possible will help you prevent or delay diabetes-related complications. Stress is a part of life, but it can make managing diabetes harder, including managing your blood sugar levels and dealing with daily diabetes care.
How to get diabetes educator?
Whether you just got diagnosed with type 1 diabetes or have had it for some time, meeting with a diabetes educator is a great way to get support and guidance, including how to: 1 Develop and stick to a healthy eating and activity plan 2 Test your blood sugar and keep a record of the results 3 Recognize the signs of high or low blood sugar and what to do about it 4 Give yourself insulin by syringe, pen, or pump 5 Monitor your feet, skin, and eyes to catch problems early 6 Buy diabetes supplies and store them properly 7 Manage stress and deal with daily diabetes care
Why do you need insulin every day?
If you have type 1 diabetes, you’ll need to take insulin shots (or wear an insulin pump) every day to manage your blood sugar levels and get the energy your body needs. Insulin can’t be taken as a pill because the acid in your stomach would destroy it before it could get into your bloodstream.
How long does it take for diabetes to show symptoms?
Type 1 diabetes symptoms can develop in just a few weeks or months. Once symptoms appear, they can be severe. Some type 1 diabetes symptoms are similar to symptoms of other health conditions.
Who manages diabetes?
Unlike many health conditions, diabetes is managed mostly by you, with support from your health care team (including your primary care doctor, foot doctor, dentist, eye doctor, registered dietitian nutritionist, diabetes educator, and pharmacist), family, teachers, and other important people in your life.
What is a DKA?
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening. DKA develops when your body doesn’t have enough insulin to allow blood sugar into your cells for use as energy. Very high blood sugar and low insulin levels lead to DKA. The two most common causes are illness and missing insulin shots.
How to treat type 1 diabetes?
Another form of treating type 1 diabetes is to have an injection of insulin producing cells. This procedure, known as islet cell transplantation, allows the transplanted insulin producing islet cells to produce insulin inside your body. Islet cell transplantation can help to reduce the amount of insulin you need to take ...
How does type 1 diabetes work?
By Editor. Central to the treatment of type 1 diabetes is to keep a balance of the right amount of insulin to keep blood glucose levels from being either too high or too low. In type 1 diabetes the body’s immune system kills of the insulin producing cells leaving the pancreas unable to produce enough insulin to keep blood glucose levels ...
Why is carbohydrate counting important?
Carbohydrate counting and insulin dose adjustment. Because the carbohydrate in food raises blood sugar levels, it is important that we balance the amount of insulin we take at meals in proportion with the amount of carbohydrate we eat. Carbohydrate counting and insulin dose adjustment are key skills to learn in order to best control type 1 diabetes.
What happens when you are diagnosed with type 1 diabetes?
The thought of injecting each day can be a big shock at first but once you get the hang of it, it becomes a manageable part of life.
What is the honeymoon phase of diabetes?
The time period when your body is producing a useful amount of insulin is known as the honeymoon phase of type 1 diabetes. After a number of months and sometimes up to a few years, your body will stop being able to produce as much insulin and you will find you need to take more insulin than you have been. When this happens you may also find that ...
Why do we need to test blood sugar?
Many of us don’t like testing blood sugar levels through the day but the benefits of testing is that it helps us to avoid unpleasant high and low sugar levels which can make us tired and uncomfortable as well as being potentially dangerous in the short and long term.
What is an alternative to insulin?
An alternative way of taking insulin is to use an insulin pump. An alternative name for insulin pump therapy is continuous insulin infusion therapy because insulin pumps work by continuously delivering small amounts of insulin into the body.
What is the treatment for poorly controlled type 1 diabetes?
Pancreatic islet transplantation is an experimental treatment for poorly controlled type 1 diabetes. Pancreatic islets are clusters of cells in the pancreas that make the hormone insulin. In type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system attacks these cells. A pancreatic islet transplant replaces destroyed islets with new ones that make and release insulin. This procedure takes islets from the pancreas of an organ donor and transfers them to a person with type 1 diabetes. Because researchers are still studying pancreatic islet transplantation, the procedure is only available to people enrolled in research studies. Learn more about islet transplantation studies#N#External link#N#.
What is the treatment for diabetes?
Other treatments include bariatric surgery for certain people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, and an "artificial pancreas" and pancreatic islet transplantation for some people with type 1 diabetes.
Why do you need insulin?
Type 1 diabetes. If you have type 1 diabetes, you must take insulin because your body no longer makes this hormone. You will need to take insulin several times during the day, including with meals. You also could use an insulin pump, which gives you small, steady doses throughout the day.
What is the best way to treat diabetes?
Taking insulin or other diabetes medicines is often part of treating diabetes. Along with healthy food choices and physical activity, medicine can help you manage the disease. Some other treatment options are also available.
How to take insulin?
Inhaler. Another way to take insulin is by breathing powdered insulin from an inhaler device into your mouth. The insulin goes into your lungs and moves quickly into your blood. Inhaled insulin is only for adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
Where to inject insulin?
Insulin works fastest when you inject it in your belly, but you should rotate spots where you inject insulin. Other injection spots include your thigh, buttocks, or upper arm. Some people with diabetes who take insulin need two to four shots a day to reach their blood glucose targets. Others can take a single shot.
What is premixed insulin?
Your doctor might also recommend premixed insulin, which is a mix of two types of insulin. Some types of insulin cost more than others, so talk with your doctor about your options if you're concerned about cost. Read about financial help for diabetes care .
Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment