What do you use to treat hyperkalemia?
7 rows · Jan 26, 2012 · Hyperkalemia with potassium level more than 6.5 mEq/L or EKG changes is a medical emergency and ...
When to correct hyperkalemia?
This may include: Water pills (diuretics) help rid your body of extra potassium. They work by making your kidney create more urine. Potassium binders often come in the form of a powder. They are mixed with a small amount of water and taken with food.
What is the emergency treatment of hypokalemia?
When to treat hyperkalemia?

What is the emergency treatment for hyperkalemia?
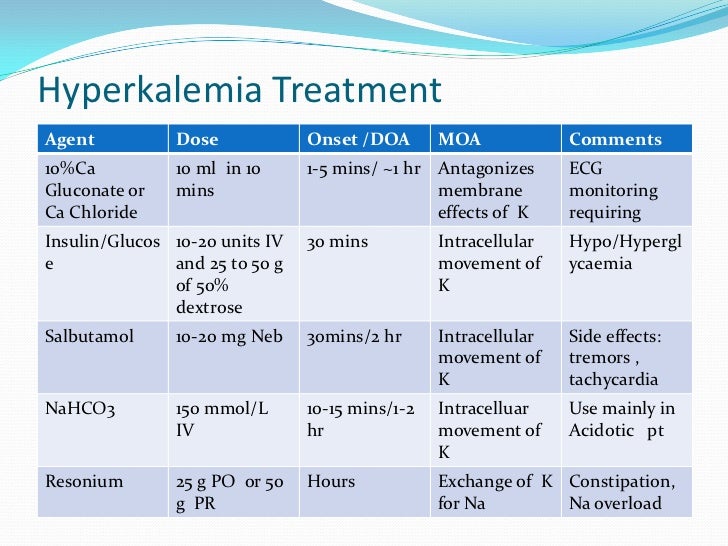
Membrane stabilization by calcium salts and potassium-shifting agents, such as insulin and salbutamol, is the cornerstone in the acute management of hyperkalemia. However, only dialysis, potassium-binding agents, and loop diuretics remove potassium from the body.
What is the first line treatment for hyperkalemia?
Calcium gluconate should be used as a first-line agent in patients with EKG changes or severe hyperkalemia to protect cardiomyocytes. Insulin and glucose combination is the fastest acting drug that shifts potassium into the cells. B-agonists can be used in addition to insulin to decrease plasma potassium levels.
What medication is given for high potassium?
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate), which removes potassium through your intestines before it's absorbed. Patiromer (Veltassa), which binds to potassium in the intestines. Sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (Lokelma), which binds to potassium in the intestines.
Why is insulin given for hyperkalemia?
Drugs used in the treatment of hyperkalemia include the following: Calcium (either gluconate or chloride): Reduces the risk of ventricular fibrillation caused by hyperkalemia. Insulin administered with glucose: Facilitates the uptake of glucose into the cell, which results in an intracellular shift of potassium.Jul 9, 2021
Do you give insulin or dextrose first for hyperkalemia?
Intravenous (IV) insulin is therefore often the first-line therapy for acute hyperkalemia in hospitalized ESRD patients. It is typically used in conjunction with dextrose to prevent hypoglycemia, and is often combined with other therapies such as nebulized albuterol.May 2, 2014
What is the quickest way to lower potassium levels?
To help keep your potassium levels within normal range, your doctor may recommend the following:Following a low-potassium diet, if needed. ... Try avoiding certain salt substitutes. ... Avoiding herbal remedies or supplements. ... Taking water pills or potassium binders, as directed by your healthcare provider.More items...•Feb 25, 2016
What medications lower potassium levels?
Some medications lower potassium slowly, including: 1 Water pills (diuretics), which rid the body of extra fluids and remove potassium through urine 2 Sodium bicarbonate, which temporarily shifts potassium into body cells 3 Albuterol, which raises blood insulin levels and shifts potassium into body cells 4 Sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate), which removes potassium through your intestines before it’s absorbed 5 Patiromer (Veltassa), which binds to potassium in the intestines 6 Sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (Lokelma), which binds to potassium in the intestines
What is the best way to remove potassium from the body?
Water pills (diuretics), which rid the body of extra fluids and remove potassium through urine. Sodium bicarbonate, which temporarily shifts potassium into body cells. Albuterol, which raises blood insulin levels and shifts potassium into body cells.
What is the best treatment for hyperkalemia?
Calcium gluconate should be used as a first-line agent in patients with EKG changes or severe hyperkalemia to protect cardiomyocytes. Insulin and glucose combination is the fastest acting drug that shifts potassium into the cells. B-agonists can be used in addition to insulin to decrease plasma potassium levels.
What is the mechanism of hyperkalemia?
The change in resting membrane potential caused by hyperkalemia is the principle pathophysiologic mechanism behind most of its symptoms. The decrease in the resting membrane potential decreases the number of sodium channels activated that in turn decrease the magnitude of inward sodium current.
What is pseudohyperkalemia?
Pseudohyperkalemia (fictitious hyperkalemia) Pseudohyperkalemia commonly arises from shifts of potassium from blood cells to blood plasma by mechanical trauma during venipuncture or during the clotting process in vitro. These effects are further enhanced when there is marked leukocytosis or thrombocytosis.
How to remove potassium from the body?
Treatment should be started with calcium gluconate to stabilize cardiomyocyte membranes, followed by insulin injection, and b-agonists administration. Hemodialysis remains the most reliable method to remove potassium from the body and should be used in cases refractory to medical treatment.
Is sodium bicarbonate effective for hyperkalemia?
Exchange resin has very slow action and is therefore indicated for treatment of chronic hyperkalemia. Hemodialysis is the most effective and reliable method to remove potassium from the body.
What are the side effects of beta agonists?
The most common side effects of beta-agonists are tachycardia and tremors.
Does insulin increase potassium?
Insulin also maintains potassium balance between extracellular and intracellular compartments, and decrease in insulin causes a rise in extracellular potassium (commonly seen in diabetic patients). Furthermore, serum hypertonicity from hyperglycemia enhances hyperkalemia.
What causes hyperkalemia in kidneys?
Advanced kidney disease is a common cause of hyperkalemia. A diet high in potassium. Eating too much food that is high in potassium can also cause hyperkalemia, especially in people with advanced kidney disease. Foods such as cantaloupe, honeydew melon, orange juice, and bananas are high in potassium. Drugs that prevent the kidneys ...
How to get potassium out of your body?
Some people may also need special medicine to help remove extra potassium from the body and keep it from coming back. This may include: Water pills (diuretics) help rid your body of extra potassium. They work by making your kidney create more urine. Potassium is normally removed through urine.
What causes a swollen thigh?
Other (less common) causes include: 1 Taking extra potassium, such as salt substitutes or supplements. 2 A disorder called “Addisons disease”, which can occur if your body does not make enough of certain hormones. Hormones are chemicals produced by different glands and organs, including the kidneys, to trigger certain responses in your body. 3 Burns or other severe injuries. This occurs because your body, in response to severe burns or injuries releases extra potassium in your blood. 4 Poorly controlled diabetes. 5 When diabetes is not controlled, it has a direct effect on your kidneys which are responsible for balancing potassium in your body.
What happens if your kidneys don't work?
Kidney Disease. Hyperkalemia can happen if your kidneys do not work well. It is the job of the kidneys to balance the amount of potassium taken in with the amount lost in urine. Potassium is taken in through the foods you eat and the liquids you drink. It is filtered by the kidneys and lost through the urine.
Why does potassium rise?
This can cause your potassium levels to rise. Other (less common) causes include: Taking extra potassium , such as salt substitutes or supplements. A disorder called “Addisons disease”, which can occur if your body does not make enough of certain hormones.
What happens if you have high potassium levels?
If hyperkalemia comes on suddenly and you have very high levels of potassium, you may feel heart palpitations, shortness of breath, chest pain, nausea, or vomiting. Sudden or severe hyperkalemia is a life-threatening condition. It requires immediate medical care.
How long does it take for a symtom to show up?
You may feel some muscle weakness, numbness, tingling, nausea, or other unusual feelings. It usually develops slowly over many weeks or months and is often mild. It can recur.
What is the FDA approved treatment for hyperkalemia?
Sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (Lokelma) was approved by the FDA in May 2018 to treat hyperkalemia in adults. It preferentially captures potassium in exchange for hydrogen and sodium, which reduces the free potassium concentration in the lumen of the GI tract, and thereby lowers the serum potassium level.
Can IV insulin cause hypoglycemia?
IV insulin (even when administered with dextrose) can cause hypoglycemia. Patients with acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease are especially susceptible. Measure glucose and potassium levels every 2 hours. Continue monitoring glucose levels for at least 6 hours after administering insulin-glucose.
Can potassium supplements cause hyperkalemia?
In most cases, all 3 of those etiologic factors contribute to hyperkalemia. It is particularly important to reevaluate the use of potassium supplements (including salt substitutes) in patients with renal insufficiency or in patients taking medications that impair renal excretion of potassium.
Can SPS be used for hyperkalemia?
SPS is not useful for acute control of hyperkalemia, because its effect on potassium is delayed for at least 2 hours, peaking at 4-6 hours. SPS can decrease serum potassium by 2 mEq/L. Oral SPS is useful in patients with advanced renal failure who are not yet on dialysis or transplant candidates.
Can potassium be monitored?
Once the potassium level is restored to normal, the potassium-lowering therapies can be discontinued, and the serum potassium level can be monitored. Continuous cardiac monitoring should be maintained. Further workup should be initiated to determine the inciting cause and to prevent future episodes.
Is hyperkalemia aggressive therapy?
The aggressiveness of therapy for hyperkalemia is directly related to the rapidity with which the condition has developed, the absolute level of serum potassium, and the evidence of toxicity. The faster the rise in the potassium level, the higher it has reached, and the greater the evidence of cardiotoxicity, the more aggressive therapy should be.