What causes elevated lead levels?
If a child does have high levels of lead in their blood, they may receive chelation therapy, which is a medical treatment used to remove lead from the body. For more information on caring for children with lead in their blood, refer to CDC’s Recommended Actions Based on Blood Lead Level. Blood Lead Reference Value
When to check lead levels?
If a worker’s blood lead level is consistently found to be above 50 µg/dL the employer must remove the worker from any tasks that could expose them to lead until their blood lead level drops below 40 µg/dL. The EPA has set a treatment technique action level of 15 parts per billion (ppb) for public water supplies.
What causes high lead levels in blood?
What Abnormal Results Mean. In adults, a blood lead level of 5 µg/dL or 0.24 µmol/L or above is considered elevated. Treatment may be recommended if: Your blood lead level is greater than 80 µg/dL or 3.86 µmol/L. You have symptoms of lead poisoning and your blood lead level is greater than 40 µg/dL or 1.93 µmol/L.
What are the normal levels of lead?
Jul 05, 2021 · Treatment consists of taking a drug that binds to the lead and helps the body to remove it. This process is called chelation therapy. Doctors decide whether to use chelation therapy on a case-by-case basis. Very high levels of lead (70 mcg/dL or greater) sometimes require hospitalization to begin therapy.
What is the best treatment for high lead levels?
For some individuals with high lead levels, however, more advanced treatment, such as chelation therapy , may be needed.
How is lead poisoning treated?
Lead poisoning is treated with chelation therapy using a chelating agent that binds to lead so that it can be excreted from the body in urine. There are different chelating agents, some of which are taken by mouth, such as Chemet (succimer), and others that are delivered by injection or intravenous infusion, such as EDTA (edetate calcium disodium) and dimercaprol. 14
How much lead is in chelation?
Chelation therapy is generally considered when lead levels in the blood are 45 micrograms per deciliter (µg/mL) or higher, especially in children. In adults, chelation therapy may be delayed if the person can be removed from the source of the lead exposure. 15
What is the recommended level of chelation therapy?
It's important to note that chelation therapy for those testing above 45 μg/dL is a guideline and not a concrete protocol. Not everyone above that level should receive the therapy, and there are cases where children, especially, might need to be chelated despite having lead levels below 45 μg/dL.
How long does it take to cure lead poisoning?
It depends on the severity of the lead poisoning and the type of chelating agent used. With oral drugs like Chemet, the standard course of treatment is 14 days, after which the blood is retested and an additional course is given if needed.
What nutrients help protect against lead?
Certain nutrients—like iron and calcium — have been shown to help protect the body against lead by binding with it and stopping it from being absorbed or stored. 6 These nutrients are already a part of a healthful, balanced diet, so for most individuals, sticking to standard nutritional guidelines 7 will go a long way in helping the body protect itself from high levels of lead.
What to do if you have lead paint in your home?
Generally speaking, however, there are a few things that families can begin to do right away 3 to prevent any further exposure to lead: Ensure there aren't any peels, chips, or chewable surfaces where lead paint has been used. Vacate any home built before 1978 that's undergoing renovation 4 until everything's been cleaned up.
What to do if a child has high lead levels?
If a child has very high levels of lead in their blood, health care providers may recommend other types of testing (such as an x-ray) or chelation therapy to remove some lead from the blood.
How to treat lead in children?
If a child has an elevated blood lead level, their doctor may recommend follow-up services. These include finding and removing lead from the child’s environment, feeding the child a diet high in iron and calcium, connecting the child to early educational services, and scheduling follow-up blood testing . Early identification of elevated blood lead levels is key to reducing the long-term effects of lead exposure. If a child has very high levels of lead in their blood, health care providers may recommend other types of testing (such as an x-ray) or chelation therapy to remove some lead from the blood.
What is the lead level in blood?
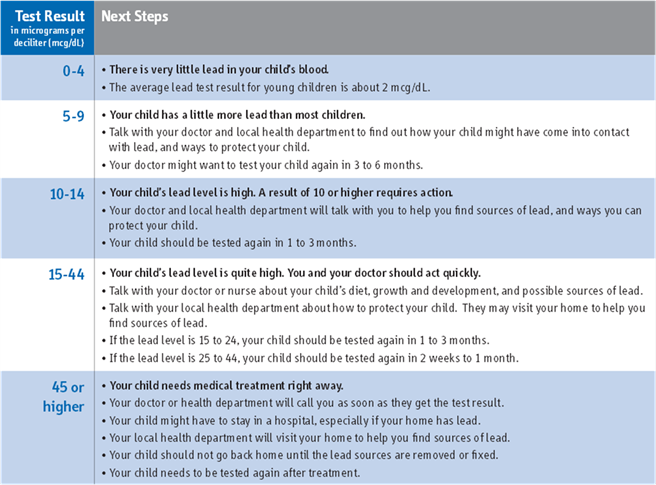
The amount of lead in blood is referred to as blood lead level, which is measured in micrograms of lead per deciliter of blood (μg/dL). CDC currently uses a blood lead reference value of 5 micrograms per deciliter to identify children with blood lead levels that are higher than most children’s levels.
How to test for lead in blood?
Testing Blood Lead Levels 1 A finger-prick, or capillary, test is usually the first step to determine if a child has elevated blood lead levels. While finger-prick tests can provide fast results, they also can produce higher results if lead on the skin is captured in the sample. For this reason, a finger-prick test that shows an elevated result is usually followed by a second test to confirm. 2 A venous blood draw takes blood from the child’s vein. This type of test can take a few days to receive results and is often used to confirm elevated blood lead levels seen in the first capillary test.
What is the first step in blood testing for lead?
Two types of blood tests may be used. A finger-prick, or capillary , test is usually the first step to determine if a child has elevated blood lead levels. While finger-prick tests can provide fast results, they also can produce higher results ...
What is the best way to assess a person's exposure to lead?
Presence of other underlying health conditions. Although lead in blood represents only a portion of the total amount of lead present in the body, a blood lead test is the best available way to assess a person’s exposure to lead.
How does lead get into a child's body?
Once a child’s exposure to lead stops, the amount of lead in the blood decreases gradually. The child’s body releases some of the lead through urine, sweat, and feces. Lead is also stored in bones.
How can lead be reduced?
Exposure to lead in the workplace can be lowered through the use of engineering controls that reduce air-lead levels . Exposure can also be reduced through the use of protective clothing and respirators. If a person could be exposed to lead at work, he or she should wash hands and face before eating or drinking, eat and drink in areas free of lead dust and fumes, change into different clothes and shoes before working with lead, shower after working with lead before going home, and wash clothes separately from other family members’ clothes.
What happens if you have high lead levels?
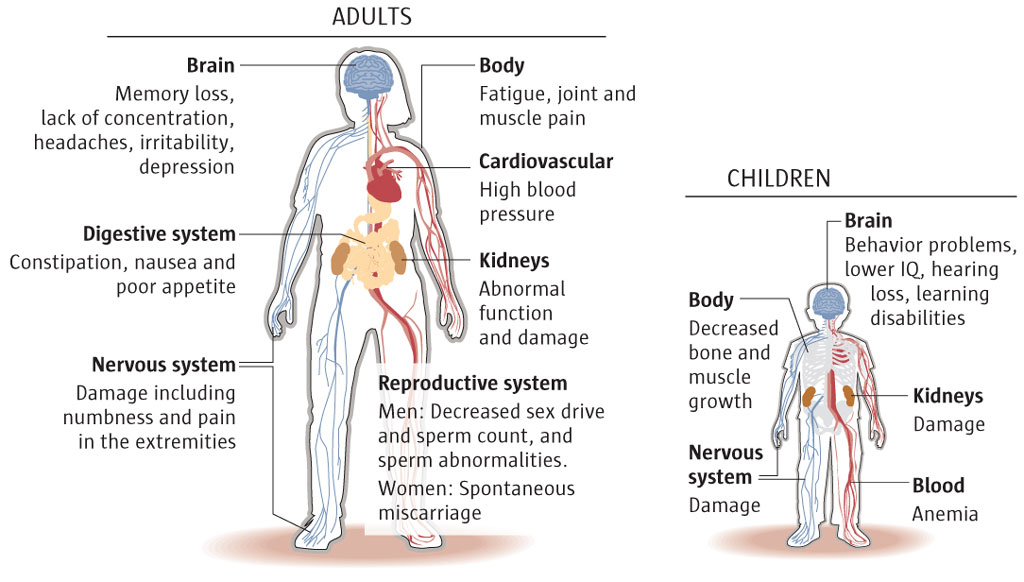
At very high blood lead levels, a person can develop nerve damage that causes numbness in the hands and feet and a condition called “foot drop” where it is hard to raise the toes when the foot is lifted off the ground. Anemia is also common. Extremely high blood lead levels can result in seizures and even death.
What is the PEL for lead?
OSHA has set a permissible exposure limit (PEL) for lead in air of 50 micrograms per cubic meter (µg/m3) over an eight hour time-weighted average. Workplaces are required to monitor the blood lead levels of workers who are exposed to lead above a certain action level and provide appropriate personal protective equipment to their workers. If a worker’s blood lead level is consistently found to be above 50 µg/dL the employer must remove the worker from any tasks that could expose them to lead until their blood lead level drops below 40 µg/dL.
What is the lead level in a blood test?
Elevated blood lead levels that are greater than or equal to 5 μg/dL in adults (16 years or older) are reportable by regulation to the Virginia Department of Health.
What does it mean when your lead level is high?
Having an elevated blood lead level over a long period of time is associated with high blood pressure and kidney damage in adults. A high blood lead level in both men and women is associated with infertility.
What are the most dangerous jobs for lead?
Occupations that have the greatest risk include battery manufacturing, lead smelters, sandblasters, soldering, automobile repair, and construction workers.
How does lead affect your health?
How can lead affect my health? At low blood lead levels a person may have no symptoms. At higher blood lead levels a person may develop general symptoms of illness like abdominal pain, headache, fatigue, irritability, and joint or muscle aches. At very high blood lead levels, a person can develop nerve damage that causes numbness in ...
Why do we need a lead test?
The test is also used to diagnose lead poisoning when a person has symptoms of the condition. It is also used to measure how well treatment for lead poisoning is working. Lead is common in the environment, so it is often found in the body in low levels.
What is the normal lead level in adults?
In adults, a blood lead level of 5 µg/dL or 0.24 µmol/L or above is considered elevated. Treatment may be recommended if:
How much lead is in blood?
Less than 10 micrograms per deciliter (µg/dL) or 0.48 micromoles per liter (µmol/L) of lead in the blood
What is the lead level in a child's blood?
A lead level greater than 45 µg/dL or 2.17 µmol/L in a child's blood most often indicates the need for treatment.
Can you use the information provided herein for medical emergencies?
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright ©2019 A.D.A.M., Inc., as modified by University of California San Francisco. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
Is lead poisoning harmful?
Small amounts of lead in adults are not thought to be harmful. However, even low levels of lead can be dangerous to infants and children. It can cause lead poisoning that leads to problems in mental development.
What is the treatment for high levels of lead in the blood?
Treatment consists of taking a drug that binds to the lead and helps the body to remove it. This process is called chelation therapy .
What can you do with lead?
Drinking water from pipes that are made of lead or use lead solder. Using ceramic dishes made with lead. Using products made with lead-containing paint (often imported from other countries) Playing in lead-contaminated soil. Using lead in hobbies or crafts such as making stained glass.
What to do if your child is exposed to lead?
See the child's doctor immediately if you notice symptoms of lead poisoning or suspect that the child has been exposed to lead.
What does a doctor do if he thinks someone has lead poisoning?
A doctor who thinks someone has lead poisoning will do a physical examination. He or she will ask about:
How to diagnose lead poisoning?
Lead poisoning is diagnosed with a simple blood test.
What happens after you remove lead from your body?
After treatment and/or removal of the environmental lead source, the doctor normally will do more blood lead tests. Blood tests help track blood levels until they are no longer too high.
How long does it take for lead to leave the body?
It may take several weeks, months or years for lead to leave the body, even after there is no further exposure.
How to prevent lead poisoning?
Prevention. Simple measures can help protect you and your family from lead poisoning: Wash hands and toys. To help reduce hand-to-mouth transfer of contaminated dust or soil, wash your children's hands after outdoor play, before eating and at bedtime. Wash their toys regularly .
What are some remedies for lead poisoning?
Herbal or folk remedies. Lead poisoning has been linked to greta and azarcon, traditional Hispanic medicines, as well as some from India, China and other countries. Mexican candy. Tamarind, an ingredient used in some candies made in Mexico, might contain lead. Lead bullets.
What are the most common sources of lead poisoning in children?
Lead-based paint and lead-contaminated dust in older buildings are the most common sources of lead poisoning in children. Other sources include contaminated air, water and soil. Adults who work with batteries, do home renovations or work in auto repair shops also might be exposed to lead.
What can lead be found in?
Household dust can contain lead from lead paint chips or from contaminated soil brought in from outside. Pottery. Glazes found on some ceramics, china and porcelain can contain lead that can leach into food served or stored in the pottery. Toys. Lead is sometimes found in toys and other products produced abroad.
What bullets can lead to exposure?
Lead bullets. Time spent at firing ranges can lead to exposure.
How to get rid of lead in children?
Eat a healthy diet. Regular meals and good nutrition might help lower lead absorption. Children especially need enough calcium, vitamin C and iron in their diets to help keep lead from being absorbed.
How to keep lead based soil outside?
Remove shoes before entering the house. This will help keep lead-based soil outside.
Who can test for lead in blood?
A family doctor or pediatrician can perform a blood test for lead and provide information about the health effects of lead. State, city or county departments of health can also provide information about how you can have your child's blood tested for lead.
What factors affect the amount of lead in water?
A number of factors are involved in the extent to which lead enters the water, including: the chemistry of the water (acidity and alkalinity) and the types and amounts of minerals in the water, the amount of lead it comes into contact with, the temperature of the water, the amount of wear in the pipes, how long the water stays in pipes, and.
How does lead affect the fetus?
Lead can accumulate in our bodies over time, where it is stored in bones along with calcium. During pregnancy, lead is released from bones as maternal calcium and is used to help form the bones of the fetus. This is particularly true if a woman does not have enough dietary calcium. Lead can also cross the placental barrier exposing the fetus to lead. This can result in serious effects to the mother and her developing fetus, including:
What is the lead and copper rule?
To address corrosion of lead and copper into drinking water, EPA issued the Lead and Copper Rule (LCR) under the authority of the SDWA. One requirement of the LCR is corrosion control treatment to prevent lead and copper from contaminating drinking water.
How much lead is in water?
EPA estimates that drinking water can make up 20 percent or more of a person’s total exposure to lead. Infants who consume mostly mixed formula can receive 40 percent to 60 percent of their exposure to lead from drinking water.
Why are infants and children particularly vulnerable to lead?
Young children, infants, and fetuses are particularly vulnerable to lead because the physical and behavioral effects of lead occur at lower exposure levels in children than in adults. A dose of lead that would have little effect on an adult can have a significant effect on a child.
How much lead is in a child's blood?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that public health actions be initiated when the level of lead in a child’s blood is 5 micrograms per deciliter (µg/dL) or more. It is important to recognize all the ways a child can be exposed to lead.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle
Over-The-Counter (OTC) Therapies
Prescriptions
Chelation Therapy
Surgeries and Specialist-Driven Procedures
Summary
- The treatment of lead poisoning is initially focused on preventing further exposure to lead. This includes identifying and removing sources of lead from your home and environment. Diet and dietary supplements may aid in reducing lead absorption. If lead levels in the blood are excessive, a procedure known as chelation therapy can help remove lead f...
A Word from Verywell